13_15_Quiz_Show
advertisement
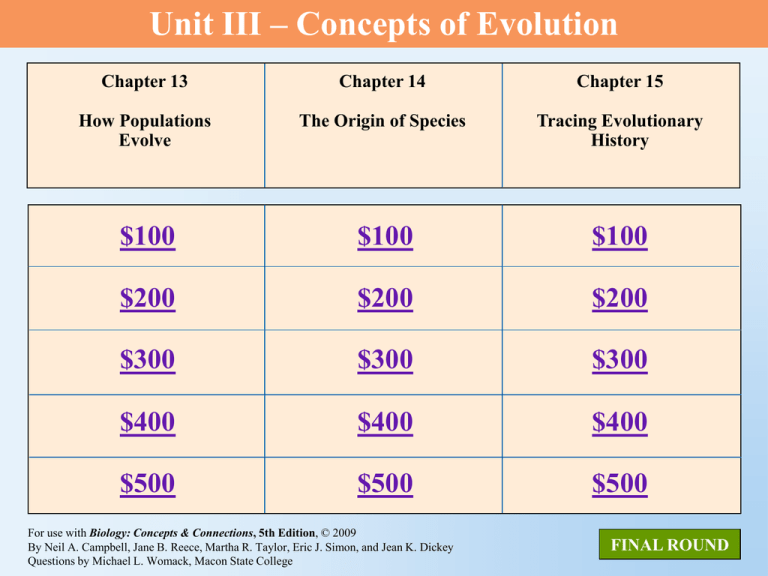
Unit III – Concepts of Evolution Chapter 13 Chapter 14 Chapter 15 How Populations Evolve The Origin of Species Tracing Evolutionary History $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 For use with Biology: Concepts & Connections, 5th Edition, © 2009 By Neil A. Campbell, Jane B. Reece, Martha R. Taylor, Eric J. Simon, and Jean K. Dickey Questions by Michael L. Womack, Macon State College FINAL ROUND Chapter 13 $100 Question Natural selection _________. a. results in evolutionary adaptation b. is the result of sampling error c. does not affect allelic frequencies d. prepares organisms for future changes in the environment ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $100 Answer Natural selection _________. a. results in evolutionary adaptation b. is the result of sampling error c. does not affect allelic frequencies d. prepares organisms for future changes in the environment BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $200 Question Biologically speaking, fitness increases when an organism _______________. a. survives many hardships b. lives for a long time c. passes on a greater proportion of its genes to the next generation d. is disease free ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $200 Answer Biologically speaking, fitness increases when an organism _______________. a. survives many hardships b. lives for a long time c. passes on a greater proportion of its genes to the next generation d. is disease free BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $300 Question Which of the following people developed a theory of evolution almost identical to Charles Darwin’s? a. Charles Lyell b. Alfred Wallace c. Louis Pasteur d. Gregor Mendel ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $300 Answer Which of the following people developed a theory of evolution almost identical to Charles Darwin’s? a. Charles Lyell b. Alfred Wallace c. Louis Pasteur d. Gregor Mendel BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $400 Question Genetic differences between populations tend to be reduced by ____________________. a. gene flow b. mutation c. genetic drift d. the founder effect ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $400 Answer Genetic differences between populations tend to be reduced by ____________________. a. gene flow b. mutation c. genetic drift d. the founder effect BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $500 Question Which type of selection shifts a phenotypic curve in favor of one extreme phenotype? a. diversifying selection b. directional selection c. optimal selection d. stabilizing selection ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 13 $500 Answer Which type of selection shifts a phenotypic curve in favor of one extreme phenotype? a. diversifying selection b. directional selection c. optimal selection d. stabilizing selection BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $100 Question What branch of biology is concerned with the naming and classifying of diverse life forms? a. ecology b. physiology c. histology d. taxonomy ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $100 Answer What branch of biology is concerned with the naming and classifying of diverse life forms? a. ecology b. physiology c. histology d. taxonomy BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $200 Question Which of the following reproductive barriers prevents individuals of different species from mating with each other? a. hybrid inviability b. hybrid sterility c. gametic isolation d. behavioral isolation ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $200 Answer Which of the following reproductive barriers prevents individuals of different species from mating with each other? a. hybrid inviability b. hybrid sterility c. gametic isolation d. behavioral isolation BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $300 Question Speciation requires _____________. a. periods of rapid evolutionary change b. genetic isolation c. long periods of time d. geographic isolation ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $300 Answer Speciation requires _____________. a. periods of rapid evolutionary change b. genetic isolation c. long periods of time d. geographic isolation BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $400 Question Sympatric speciation excludes ____________. a. mechanical isolation b. geographic isolation c. behavioral isolation d. temporal isolation ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $400 Answer Sympatric speciation excludes ____________. a. mechanical isolation b. geographic isolation c. behavioral isolation d. temporal isolation BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $500 Question A pattern of evolution in which most change in appearance occurs rapidly fits the ________ model of speciation. a. gradulism b. homeostatic c. isotonic d. punctuated equilibrium ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 14 $500 Answer A pattern of evolution in which most change in appearance occurs rapidly fits the ________ model of speciation. a. gradulism b. homeostatic c. isotonic d. punctuated equilibrium BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $100 Question Which kingdom(s) colonized land first? a. Monera b. Archaea c. Plantae and Fungi d. Protista and Fungi ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $100 Answer Which kingdom(s) colonized land first? a. Monera b. Archaea c. Plantae and Fungi d. Protista and Fungi BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $200 Question Which of the following eras is often called the “Age of Reptiles”? a. Permian b. Mesozoic c. Cenozoic d. Cambrian ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $200 Answer Which of the following eras is often called the “Age of Reptiles”? a. Permian b. Mesozoic c. Cenozoic d. Cambrian BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $300 Question It is estimated that our modern continents were beginning to take shape how many years ago? a. 65 million years ago b. 375 million years ago c. 500 million years ago d. 1.4 billion years ago ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $300 Answer It is estimated that our modern continents were beginning to take shape how many years ago? a. 65 million years ago b. 375 million years ago c. 500 million years ago d. 1.4 billion years ago BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $400 Question The abiotic origin of life is referred to as _________. a. spontaneous generation b. diversification c. endosymbiosis d. biogenesis ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $400 Answer The abiotic origin of life is referred to as _________. a. spontaneous generation b. diversification c. endosymbiosis d. biogenesis BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $500 Question The evolutionary history of a group of organisms is called __________________. a. phylogeny b. cladistics c. parsimony d. taxonomy ANSWER BACK TO GAME Chapter 15 $500 Answer The evolutionary history of a group of organisms is called __________________. a. phylogeny b. cladistics c. parsimony d. taxonomy BACK TO GAME FINAL ROUND Question Speciation without geographic isolation is called _____________. a. spontaneous generation b. adaptive radiation c. sympatric speciation d. allopatric speciation ANSWER BACK TO GAME FINAL ROUND Answer Speciation without geographic isolation is called _____________. a. spontaneous generation b. adaptive radiation c. sympatric speciation d. allopatric speciation BACK TO GAME