IB BIO- aquaporin ppt
advertisement
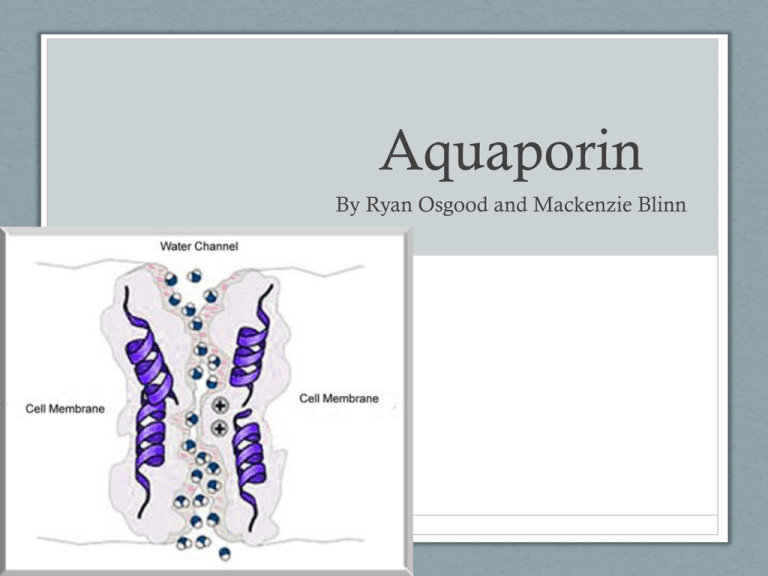
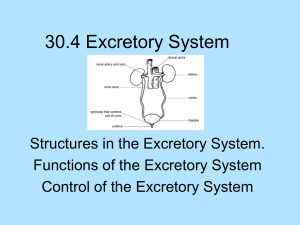
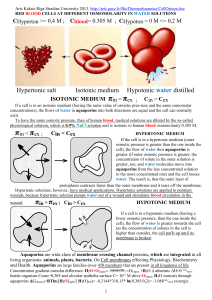
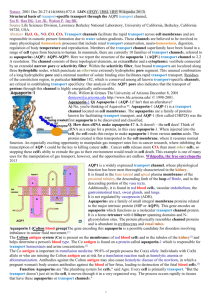
Aquaporin By Ryan Osgood and Mackenzie Blinn What they are • Aquaporin is a protein embedded in the cell membrane in order to regulate the flow of water • Water needs to move in and out of a cell, and this is facilitated by aquaporins (water channels) • The presence of these water channels increases the permeability to water of the cell membrane • These channels are allocated in all kingdoms of life including bacteria, plants, and mammals • 13 in mammals, 6 in kidney • In plants- 4 families Used for • Industrial water treatment • Regulates flow of water in organisms, particularly in the kidney. Who discovered them • In 1992 Peter Agre at John Hopkins University reported his unintentional discovery of aquaporin, he earned a Nobel Prize for his discovery in 2003 . • In 2000 Stroud’s lab at UCSF succeeded in solving the first high resolution structure of an aquaporin by using x-ray crystallography Primary Structure • Used for water reabsorption • Found in kidney • We can see its primary structure because of the amino acid linear sequence • Simple proteins- AQP monomer has 6x helical domains Secondary Structure • 6 trans membrane helices in a RH Bundle- it forms a tetrameter • Early evolutionary event • Used for water reabsorption in response to ADH (a hormone) • We can see its secondary structure because of the alphahelices Tertiary Structure • Found in kidney and medullary collecting duct • Used for water reabsorption and glycerol permeability • We can see its tertiary because of the tightness of the helixes folded in one compact globule. Quaternary Structure • Used for water reabsorption • Found in kidney More on that… • Some membranes are more permeable than others. RBC’s, kidney tubules • AQP 1 was reported in 1992. Diseases • Several diseases such as congenital cataracts and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus are relate to mutations in aquaporins, also fluid transport, brain swelling, strokes, meningities, multiple sclerosis. • A small number of people are found with a deficiency of aquaporins and they generally seem healthy, but they have a defect in the ability to concentrate solutes in urine and to conserve water when deprived of drinking water Bibliography • http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/aquaporins/ • http://www.bionaid.us/research.htm • http://www.aquaporins.org/disease.htm • http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/press/2003/octo ber/031008a.htm • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aquaporin