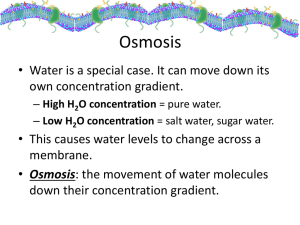
When the concentrations of solutions are the same on both sides of
advertisement

CELL TRANSPORT REVIEW Read each of the following questions and record your answer on your whiteboard. When I coundown “3, 2, 1” hold up your whiteboard with the answer facing forward. Any team that has all correct answers will earn a point. The team with the most points at the end wins! Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane? A. breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods B. stores water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates C. keeps the cell wall in place D. regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane? A. breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods B. stores water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates C. keeps the cell wall in place D. regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell Cell membranes consist mainly of A. protein pumps and some carbohydrates B. lipid bilayers with some carbohydrates C. lipid bilayers with some proteins D. proteins and some nucleic acids Cell membranes consist mainly of A. protein pumps and some carbohydrates B. lipid bilayers with some carbohydrates C. lipid bilayers with some proteins D. proteins and some nucleic acids The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one side to the other. What are these channels and pumps made of? A. carbohydrates B. lipids C. phospholipids D. proteins The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one side to the other. What are these channels and pumps made of? A. carbohydrates B. lipids C. phospholipids D. proteins Diffusion occurs because. A. molecules are attracted to one another. B. molecules constantly move and collide with each other. C. cellular energy forces molecules to collide with each other. D. cellular energy pumps molecules across the cell membrane. Diffusion occurs because. A. Molecules are attracted to one another. B. Molecules constantly move and collide with each other. C. cellular energy forces molecules to collide with each other. D. cellular energy pumps molecules across the cell membrane. A substance that moves by passive transport tends to move A. away from the area where it is less concentrated B. away from the area where it is more concentrated C. toward the area where it is more concentrated D. away from the area of equilibrium A substance that moves by passive transport tends to move A. away from the area where it is less concentrated B. away from the area where it is more concentrated C. toward the area where it is more concentrated D. away from the area of equilibrium When the concentrations of solutions are the same on both sides of the membrane, the two solutions are A. hypotonic B. dilute. C. isotonic D. hypertonic When the concentrations of solutions are the same on both sides of the membrane, the two solutions are A. hypotonic B. dilute. C. isotonic D. hypertonic The movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane is known as A. phagocytosis B. pinocytosis C. endocytosis D. osmosis The movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane is known as A. phagocytosis B. pinocytosis C. osmosis D. endocytosis Osmosis is a form of: A. Facilitated diffusion B. Molecular Transport C. Bulk Transport D. Active Transport Osmosis is a form of: A. Facilitated diffusion B. Molecular Transport C. Bulk Transport D. Active Transport Endocytosis and Exocytosis are examples of: A. Facilitated diffusion B. Passive Transport C. Active Transport D. Osmosis Endocytosis and Exocytosis are examples of: A. Facilitated diffusion B. Passive Transport C. Active Transport D. Osmosis If a more-concentrated salt solution is on one side of a membrane and a less-concentrated solution is on the other side, water molecules tend to pass through the membrane A. from the more-concentrated to the less-concentrated solution. B. until the cell membrane is broken down. C. from the less-concentrated to the more-concentrated solution. D. equally in both directions. If a more-concentrated salt solution is on one side of a membrane and a less-concentrated solution is on the other side, water molecules tend to pass through the membrane A. from the more-concentrated to the less-concentrated solution. B. until the cell membrane is broken down. C. from the less-concentrated to the more-concentrated solution. D. equally in both directions. The pressure exerted by water moving during osmosis is called __________________ pressure. A. Tonic B. Diffusion C. Selectively permeable D. Osmotic The pressure exerted by water moving during osmosis is called __________________ pressure. A. Tonic B. Diffusion C. Selectively permeable D. Osmotic Two examples of active transport are A. molecular transport and osmosis B. osmosis and facilitated diffusion C. facilitated diffusion and bulk transport D. molecular transport and bulk transport Two examples of active transport are A. molecular transport and osmosis B. osmosis and facilitated diffusion C. facilitated diffusion and bulk transport D. molecular transport and bulk transport The substance that dissolves to make a solution is called the ___________________ A. diffuser B. solvent C. solute D. concentrate The substance that dissolves to make a solution is called the ___________________ A. diffuser B. solvent C. solute D. concentrate White blood cells engulf, digest, and destroy invading bacteria using __________________. A. Facilitated diffusion B. phagocytosis C. pinocytosis D. exocytosis White blood cells engulf, digest, and destroy invading bacteria using __________________. A. Facilitated diffusion B. phagocytosis C. pinocytosis D. exocytosis