File
advertisement

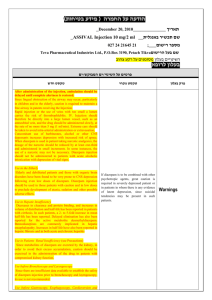
Mechanism of action It interacts with specific receptors in the CNS, particularly in the cerebral cortex. Benzodiazepine-receptor binding enhances the inhibitory effects of various neurotransmitters. ( GABA Facilitatory) Flumazenil (an imidazolebenzodiazepine) is a specific benzodiazepine-receptor antagonist that reverses most of the CNS effects of benzodiazepines. (Dose: 0.20.5mg IV to a maximum of 3mg) DIAZEPAM MIDAZOLAM LORAZEPAM Routes Oral, IM, IV IM, IV Oral, IM, IV Onset of action IV: 30-60 sec Oral: 1-2 hrs IM: 30 min IV: 30-60 sec IM: 30 min IV: 1-2 min Oral: 1-2 hrs IM: 30 min Preparation (IV) Oil based so injection is painful Water based so injection is not painful --------------- Elimination Half Life 30-60 hrs 2-3 hrs 15 hrs Dose of Sedation 0.05-0.2mg/kg 0.01-0.1mg/kg 0.03-0.04mg/kg Diazepam It is a colorless crystalline compound, insoluble in water and has a molecular weight of 284.74. Each mL contains 5 mg diazepam compounded with 40% propylene glycol, 10% ethyl alcohol, 5% sodium benzoate and benzoic acid as buffers, and 1.5% benzyl alcohol as preservative. Indications Diazepam is indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety. In acute alcohol withdrawal. Diazepam Injection is a useful adjunct in status epilepticus and severe recurrent convulsive seizures. Diazepam is a useful premedication (the IM route is preferred) for relief of anxiety and tension in patients who are to undergo surgical procedures. To prevent hallucination caused by Ketmaine. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Dosage should be individualized for maximum beneficial effect. The usual recommended dose in adults ranges from 2 mg to 20 mg IM or IV, depending on the indication and its severity. Anxiety Disorders and Symptoms of Anxiety: 2 mg to 5 mg, IM or IV Acute Alcohol Withdrawal The usual dose is 10 mg---- 3 or 4 times during the first 24 hours, then 5 mg---- 3 or 4 times daily as needed. Relief of Muscle Spasm The usual dose is 2mg to 10 mg----- 3 or 4 times daily. Convulsive Disorders The usual dose is 2 mg to 10 mg------- 2 to 4 times daily Systemic Effects CNS: Mainly acts on RAS and amygdala ( limbic system) producing sedation, anxiolysis and amnesia. Also acts on medulla producing muscle relaxation and on cerebellum producing ataxia. No any analgesic effects. Produce Muscle relaxation by acting on medullary and spinal cord (central action) and not at neuromuscular junction. Reduces cerebral metabolic rate, brain oxygen consumption and Intracranial pressure. Respiratory system: At higher dose cause respiratory depression and may lead to death. It is maximum seen with midazolam. Cardiovascular System Minimal reduction in blood pressure , heart rate and cardiac output. Hypotension is maximum with midazolam. Metabolism Metabolized in Liver. The major active metabolite of diazepam is des-methyl diazepam. Metabolites are excreted in Gut and Urine. Side effects Fatigue and ataxia; venous thrombosis and phlebitis at the site of injection CNS: confusion, depression, dysarthria, headache, slurred speech, syncope, tremor, vertigo. GI: constipation, nausea. GU: incontinence ,libido, urinary retention. Cardiovascular: bradycardia, cardiovascular collapse, hypotension. OTHERS : blurred vision, diplopia, nystagmus,urticaria, skin rash, jaundice. Contraindications and Precautions Valium Injection is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to this drug. Valium Injection should not be administered to patients in shock, coma. Should be used with precautions in patients with pulmonary and cardiovascular diseases. Usage in Pregnancy: An increased risk of congenital malformations associated with the use of diazepam during the first trimester of pregnancy has been suggested in several studies.