File

Misconceptions about
Conception
Menstrual cycle is not always 28 days.
Ovulation does not always occur on day 14.
It is true that there is a fixed amount of time between ovulation and menstruation, usually
12-16 days.
Conception can only within 24 hours after ovulation; however, women are considered
“fertile” for 2-3 days before ovulation.Maximum fertile day is day of ovulation.
Necessary ingredients to conception
An ovum, or egg that has been released
Sperm (average ejaculate contains 300-
350 million sperm)
Fertile-quality, “eggwhite” cervical fluid for the sperm to swim in
Fertile quality cervical fluid
Where conception occurs
Once the egg has been released, it is pulled from the ovary into the fallopian tube.
Most conceptions occur in the outer third of the fallopian tube.
The fertilized egg is called a zygote.
Corpus luteum
When the egg is released, a yellow spot is left behind on the ovary where the egg was. This is the corpus luteum.
Function of the corpus luteum: to secrete hormones to prepare the uterine lining to receive a fertilized egg.
If fertilization does not occur
The corpus luteum shrinks
Progesterone levels fall dramatically
Uterine lining is discarded through the menstrual cycle approximately 14 days past ovulation.
Zygote’s journey to the uterus
It takes 7-9 days for zygote to go from the fallopian tube to the uterus
Pulled along by the cilia of the fallopian tube
Then it implants in the uterine wall.
If you experience spotting (light bleeding) about 7-9 days after you ovulate, then there’s a good chance you’re pregnant. Called implantation bleeding.
hCG
After the zygote has burrowed into the uterus, it starts releasing human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG)…the pregnancy hormone.
It is the presence of this hormone that pregnancy tests detect.
Function of hCG is to send a message back to the corpus luteum to stay alive and start producing progesterone.
Role of Progesterone
Progesterone keeps the uterine lining from shedding.
Many very early miscarriages result from lack of progesterone.
Taking progesterone supplements in early pregnancy can prevent a miscarriage.
Placenta eventually takes over progesterone production from the corpus luteum.
Fertility rates by age
Age
15
Rate per cycle
40-50%
25 30-35%
35 15-20%
45 3-5%
General facts about pregnancy
Pregnancy lasts for 266 days on average.
Doctors count first day last menstrual period
(LMP)—not the day you conceive--as the first day of pregnancy
According to the medical model, pregnancy lasts 40 weeks; it’s actually 38 weeks from the time of conception until birth (on average).
Three distinct periods of development
Period of the zygote (weeks 1-2)-also called the germinal period
Period of the embryo (weeks 3-8)
Period of the fetus (weeks 9-38)
**These are not the same as first, second, and third trimester
Period of the zygote (germinal period)
First two weeks after conception
Period of rapid development
Zygote becomes the blastocyst--hollow inner layer of cells, which implants into the uterine lining on days 7-9
Trophoblast—outer layer of cells; becomes the placenta
Differentiation of cells begin
30-50% of conceptions don’t make it through this period
Placenta is formed at the end of this stage
Life support systems of the embryo
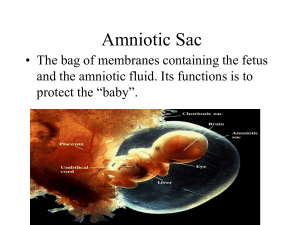
Amnion—sac filled with clear fluid in which embryo floats
Placenta—disk-shaped group of tissues that allows food and oxygen to reach the embryo; carries waste products away
Umbilical cord—contains two arteries and one vein that connect the baby to the placenta.
Embryo’s and mom’s blood supplies come in close contact but never mix directly
Placenta at around 8 weeks
Developmental trends
Cephalocaudal—from head to tail; development occurs head-down
Head region accounts for 50% of total length during the first month
Proximodistal—development occurs
“from the inside out”—midline outward
Same pattern of development throughout childhood
Period of the embryo
Dramatic and rapid growth takes place
Groundwork for all body structures and internal organs is laid
By the end of this period, all of the structures and internal organs a baby is born with are already formed
By the end of this period, embryo loses its gills and tail and looks more human.
The embryo at 6 weeks
Embryonic development at 8 weeks
Embryo is 1 ½ inches long and 1 oz. In weight
Arm and leg differentiate further
Elaborate peripheral nervous system in place
Glandular system operating
Internal sex organs developed (NOTE: Sex is determined at conception.)
Embryo can move, but movements can’t be felt by mom yet.
8-week-old embryo
Early Period of the fetus
(weeks 9-12)
Embryo becomes a fetus when bone replaces cartilage
Facial features become distinct, human-like
Vocal cords, nails, lungs have formed
External genitalia are identifiable
Heartbeat can be heard
Baby can urinate
Baby can smile, frown, suck, and swallow
About 3 inches long; weighs about 1 ounce
Middle months of period of the fetus (5
th
-6
th
month)
12-15 inches long, 12-32 ounces
Grasping reflex
Lung breathing is possible
Sleep/wake cycles similar to newborn’s
Eyes and ears are sensitive to light and sound
Grasping reflux; baby sucks thumb
All neurons present by 24 weeks’ gestation
Vernix and lanugo
Appear in 5 th -6 th month
Vernix—cheeselike covering to protect skin from chapping
Lanugo—white, downy hair on body to protect skin from chapping
Fetus with vernix and lanugo
Vernix and lanugo are often still present at birth, especially if the baby is preterm.
Age of viability
This is the age by which the fetus can survive outside the womb
Usually this is between 22-26 weeks’ gestation
By the 24 th week, the fetus has a 50% chance of survival.
Last months (7-9) of pregnancy
Lungs gradually mature
Rapid brain development causes sensory & behavioral capacities to expand
Antibodies are transferred from mom to baby
Baby becomes better able to regulate temperature
Gains 3.5 pounds in fat
Engagement (baby’s head in birth canal) by
36 weeks
Baby weighs on average 7 ½ pounds at birth
Sex Differences in Utero
Males are more physically active—they remain more active through childhood
Females are more sensitive to external stimulation
Females advance more rapidly in skeletal development and are 1-2 weeks ahead of males in bone development at birth. Trait remains through early adolescence.
More boys are conceived than girls, but the birth rate is roughly equal (105 males to 100 females)
Mozart effect
The finding that exposing fetuses and babies to classical music (specifically
Mozart) is associated with greater math and spatial ability test scores.
The finding has been disputed recently.
Seems to increase math skills in adults for about 30 minutes after listening to it.
Sounds and tastes infants prefer
They prefer their mother’s voice over all others
No preference in father’s voice over other men’s
Fetuses develop taste preferences and aversions; strong tastes such as garlic are present in the amniotic fluid (also in breast milk)
Fetal tastes may influence later taste preferences.
Habituation
Getting accustomed to a certain stimulus in the womb
Fetuses at 26 weeks of age show habituation to repeated stimuli
Some psychologists think that how quickly a fetus habituates to a routine stimulus predicts future intelligence.
This is debatable.
Teratogens
Any environmental agent that can interfere with the process of normal growth (even vitamins can be teratogens)
Especially harmful in the embryonic stage because this is when organs are being formed.
Effects of a teratogenic substance are worse on the body part or organ systems that are being formed at the time of exposure
Does a teratogen always cause damage?
No—a specific teratogen usually does NOT cause a specific birth defect.
Three factors influence the effects of a teratogen:
Dose—the greater the dose, the greater the effect.
Genetic susceptibility—both the mother’s and baby’s genotypes influence vulnerability.
Timing—Teratogens do more damage at specific times of development.
Why are teratogens harmful to baby but not to Mom?
Mother weighs a lot more
Mother’s organs aren’t developing like the baby’s are
The placenta and immature fetal liver may be unable to convert a harmful substance to a harmless one
Examples of teratogens
Over-the-counter, prescription, and illegal drugs
Caffeine—medical opinions differ as to whether it’s harmful or not (4 cups or more of coffee a day is considered harmful)
Tobacco—associated with low birth weight, miscarriage, SIDS, asthma, and childhood cancer
Alcohol—can result in fetal alcohol syndrome
Maternal malnutrition—smaller brain size
Maternal stress—associated with miscarriage, preterm labor, low birth weight
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Involves mental retardation, impaired motor coordination, poor attention and memory, and certain physical characteristics.
Prematurity
Babies born 3 weeks or more before the end of pregnancy OR who weigh less than 5.5 pounds
Birth weight is best predictor of infant survival and healthy development
Best scenario is to be at least 2 pounds at birth and 32 weeks’ gestation
Preterm babies are more difficult infants than other babies are and have a greater risk for abuse.
Three stages of birth
Stage 1: cervix dilates and effaces (thins out)…goes from totally closed to 10 cm
(completely open). Lasts 12-14 hours on avg. in a first birth, 4-6 hours in subsequent births
Stage 2: the stage where the baby is pushed out. Lasts around an hour in a 1 st birth, 15-20 minutes in later births.
Stage 3: placenta (“afterbirth”) is delivered.
Usually occurs 5-10 minutes after baby is born; this is usually not felt by the mother.
C-sections
C-section rates are currently 20-25% in US; varies by hospital
Main reason for C-section: having had a prior
C-section.
Fetal distress, prematurity, certain maternal illnesses (such as HIV), birth canal being too narrow, and labor that doesn’t progress are reasons for C-sections.
Push by some OB/GYNs to give women the right to elective C-sections.