Manegment in family practice
advertisement

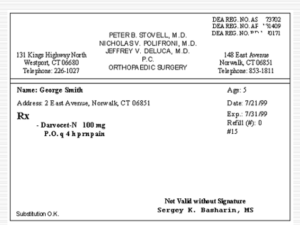
Management in Family practice Dr. JAWAHER AL-AHMADI MB. ABFM. SBFM. MD Programme Management option Problem solving Compliance 40 MIN 60 MIN 10 MIN Some early truths to remember The patient is as frightened as you are The patient think is more serious than you Illness is frightening but understanding what is going on helps Diagnostic process Cues Clinical,behvioral Hypothesis Unexpected cues revise Hypothesis testing Diagnosis managment Outcome evaluation Management option (CRAPRIOP) Clarifications Reassurance Advice Prescribing Referral Investigation Observations Prevention Involve pt. in management Choosing options Self–help & compliance Clarifications (CRAPRIOP) Good listing Feedback Flexible Respect Right way Personal experience Using patient cues Reassurance (CRAPRIOP) Active listening Objective discussion Physical examination The diagnosis most probably is ---It is common disease (prevalence is ----% The treatment is (----------) safety & effectivnss The prognosis is ------ Advice (CRAPRIOP) Explanation about the disease and the important of the management Short accurate information Organization Use the right way & practical method Response to patient cues Feed back & encouragement How to help himself Prescribing (CRAPRIOP) prescription A prescription is a physician's written instruction to a pharmacist to dispense medication for a patient. It includes directions to the pharmacist regarding the preparation and to the patient regarding use of the medication. However, a prescription represents much more than these directions. A prescription focuses on one slip of paper the diagnostic and therapeutic proficiency of the physician. Drug information must be provided to the patient in an understandable manner Communication can be both verbal and written. Comprehensive written patient information should be a supplement to face-to-face discussion between the physician and the patient. Pharmacist colleagues also contribute to patient education efforts Adverse drug reactions Adverse drug reactions have been said to be the inevitable price paid for the benefits of modern drug therapy. The reported incidence of adverse drug reactions ranges from 1 to 28 percent. Drug-induced hospitalizations account for approximately 5 percent of all admissions. Between 5 and 30 percent of hospitalized patients experience adverse drug reactions Referral (CRAPRIOP) To whom ? What for ? diagnosis treatment shared care When ? How ? patient opinion explanation referral letter Investigation (CRAPRIOP) Why ? How ? Misuse Why For For For For Diagnosis follow up reassurance screeneening How ? Explanation Be gradual Non invasive misuse As routine Unable to deal with it Observation (CRAPRIOP) Follow up appointment To do what Prevention (CRAPRIOP) Anticipatory care Opportunistic health promotion Modification of help sickening behavior Case 1 Salwa is 40 yrs house wife presented with headache. She had headache for years. She was seen by several doctors ( ENT,allergist, neurologist) CT scan normal Her pain improved by paracetamol temporally. By history she has (tension + migraine ) Family history of DM O/E: normal Case 2 Huda 32 yrs mother of two boys, complain from diarrhea 2 days mild pain and nausea. No fever or bloody stools. She has 6-8 stools motion per day. O/E: normal Case 3 Sara 33 yrs with 6 day nasal congestion and rhinorrhea. For 2 days her nasal discharge became greenish. She has headache and pain on bending. No history of asthma on the family O/E: nose: swollen erythematous turbinates sinuses: tender maxillary Case 4 Sami 5 yrs boy is smaller than other boys His past medical Hx is fine O/E : Ht below 3rd centile other is normal Case 5 Sameera, a 40-year old house wife,is diabetic. She was diagnosed 5 year ago and always had blood sugars of 12-15 mmole/liter. She tells you that she has stopped taking her 5 mg glibenclamide and start taking herbal medicine poor compliance Disease Psychiatric disorders Chronic illness (especially if asymptomatic) Minimal disability Asymptomatic or decreased symptoms Therapeutic regimen Multiple drug therapy Higher frequency of administration Longer duration of therapy Adverse effects Higher cost of medication Administration of medication Poor taste of medication Slow onset of therapeutic effect Physician-patient interaction Poor physician-patient relationship Inadequate follow-up or contact with physician Poor understanding of instructions Importance that physician places on adherence