Patient Safety and Risk Management
advertisement

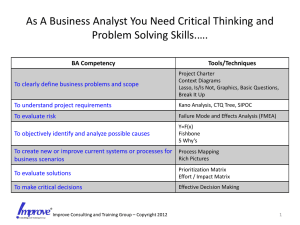
System Evaluation of Reported Adverse Events (SERAE) Risk Mitigation and Quality Improvement Patient Safety and Risk Management 2 Patient Safety and Risk Management “To Err is Human” – IOM Report - 1999 Injuries caused by medical management: 974,400 to 1,243,200 annually - 53% to 58% preventable 44,000 (8th leading cause of death) to 98,000 (4th leading cause of death) Americans die from preventable adverse events Cost: $17 to $29 billion US dollars Vehicle accidents 43,458; breast cancer 42,297; AIDS 16,516 3 Preventing Adverse Events After the occurrence – Root Cause Analysis Sentinel events (SE) 4 Patient Safety and Risk Management Before the Occurrence – Failure Modes & Effects Analysis (FMEA) “FMEA is a team-based, systematic, proactive technique that is used to prevent process and product problems before they occur.” Joint Commission Can assess severity but not probability of occurrence 5 Patient Safety and Risk Management Similarities of FMEA and RCA • Aim to reduce harm to patients • Detail and labor intensive Difference between FMEA and RCA 6 Characteristics Analysis FMEA Proactive RCA Reactive Questions Hypothetical Actual Approach Prospective retrospective Patient Safety and Risk Management An innovative approach Between RCA and FMEA System Evaluation of Reported Adverse Events (SERAE) 7 Patient Safety and Risk Management System Evaluation Reported Adverse Events (SERAE) SERAE is analysis of adverse events occurred and reported in other hospitals. a systematic, proactive technique that is used to prevent process and system problems before they occur in OUR hospital 8 Patient Safety and Risk Management Why SERAE? •Actual occurrence has transpired. •Actual data on interaction of failures can be obtained •Actual reference point and not just purely theoretical exercise •As in RCA, a “learn and prevent” mindset can prevail The boss (CCE) likes to know anyway….. 9 Patient Safety and Risk Management Advantages of conducting SERAE • Proactive • Timely • Less labor intensive • Meet standard • Less threatening to staff 10 Patient Safety and Risk Management Adverse event reported in other hospital/institution Flowchart of the SERAE NO Possible risk Report no risk YES Contact Department Manager//Unit-incharge Review existing system / policy /compliance ID problem/ risk for improvement recommendation for improvement Refer CQI Report to Cluster Director (Q&RM) Report to CCE 11 Patient Safety and Risk Management System Evaluation of Reported Adverse Events (SERAE) Would similar AE be happening in our hospital? Why did it happen? Underlying causes 12 proximate causes Why did that happen? processes Why did that happen? systems Patient Safety and Risk Management 8 Key Questions to Ask in SERAE 1. Would similar adverse event (AE) be happening in our hospital? 2. Is there any SOP in your department? 3. How are the processes done? Written document Direct review on-site 4. Are there non-compliance and failure modes? Evidence of similar AE Other failure modes Review past record AIRS 5. What are the severity ratings of possible AE? 6. Which are the failure modes to address? 7. What are the corrective actions? 8. What improvement is planned for corrective actions? 13 Patient Safety and Risk Management Stratification of RAE for different approaches • Inappropriate / inadequate resources • Suboptimal system problem 14 SSPI single party SSPII multiple parties Patient Safety and Risk Management Stratification of RAE • Inappropriate / inadequate resources Usually need simple corrective action Example Retention of laryngoscope light bulb in patient’s airway : Cause – detachable light bulb on blade Remedy – change to fiber-optic laryngoscope 15 Patient Safety and Risk Management Stratification of RAE •Suboptimal system problem SSPI - single party Example : Sharing of mortuary compartment leading to mixing up of dead body – involve mortuary 16 Patient Safety and Risk Management Suboptimal system problem SSPII - multiple parties Look Alike Drugs Dormicum Vs Magnesium Sulphate (MgSO4 ) Pitfalls: Look alike drugs Focus on clinical areas: A&E AICU CCU COD DR OTS PAM Involve doctors, pharmacy, nurses Remove all ward stock of MgSO4 Reinforce constant vigilance 17 Patient Safety and Risk Management 13 SERAE done in 2007 Over Utilization of Mortuary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Mixing of Intrathecal/Intravenous Administration of Cytotoxic Drug Wrong site and dosing of Teletherapy Look alike and sound alike medication error - Dormicum and Magnesium Sulphate Retained tip of Close-Suction Tubing Overdose of Protamine (Verbal Order) Retention of swab in a patient’s cavity Mixing up of disinfectants - OPA/Cidex and rinse water Resuscitation in private ward Fatal Fall Incident Double BCG Vaccination Wrong Labeling of Blood Specimens 18 Patient Safety and Risk Management 11 SERAE done in 2008 Adverse Transfusion Reaction Flying object in MRI Missed radioactive material (C-137) in lab Wrong corpse to families Mix-up of Biopsy Specimen Retained Detachable Light Bulb of Laryngoscope in patient Lost of USP with patient data - Data Security Post-PCI Death Wrong Site Surgery Wrong Radioactive Dye Delayed resuscitation for a Collapsed Victim outside hospital 19 Patient Safety and Risk Management 8 SERAE done in 2009 Missing baby corpse in mortuary An Eye nurse performed outside work without seeking approval Wrong identification of 2 newborns Expired BCG Vaccine was administered to 5 newborns Oral syrup Morphine was injected to a patient Penicillin was administered to a wrong neonates Shortage of specimen bottle in GOPCs Double doses of Influenza vaccine was administered to an elderly 20 Patient Safety and Risk Management 10 System Improvement through SERAE Increased 22 numbers of cold chambers and share usage of mortuaries in HKWC Removed all chemotherapy drugs ward stock Reinforced ‘time-out’ for all operations and procedures Removed all laryngoscope sets with detachable light bulbs Provide individual insulated containers for transportation of blood/blood components to prevent condensation and mix-up 21 Patient Safety and Risk Management Ten key Changes - continued Reinforced proper record and handling of abortus / fetus / stillbirth Revised the form on “Request for Human Tissue Disposal” Installed 16 small cold chambers for babies / fetus Reinforced newborn identification by encouraging rooming-in Minimize “ward dispensing practice” - limit ward stock 22 Patient Safety and Risk Management To get things done … we must be innovative 23 Patient Safety and Risk Management but…we must also be safe Thank You 24 Patient Safety and Risk Management