Soy and Heart Disease - Iowa Dietetic Association
advertisement

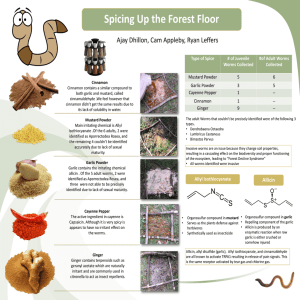
Herbal Supplements, which ones work? Jim Painter PhD, RD Professor, Eastern Illinois University Top 10 Herbal Supplements By Sales Supplement Sales 1 Soy $25,600,000 2 Cranberry $24,000,000 3 Garlic $20,500,000 4 Ginkgo $18,000,000 5 Saw Palmetto $17,000,000 6 Echinacea $14,400,00 7 Black Cohosh $8,600,000 8 Milk Thistle $8,600,000 9 Ginseng $8,400,000 19 St. John’s Wort $8,000,000 Cavaliere, C., et al.(2008).Herbal Supplement Sales in United States Basic Four Food Groups Everything that is bad for you tastes good Was good for you but not any more Everything that is good for you tastes bad If you eat that it you will kill you Popular Herbal Supplements 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Garlic Rosemary Ginger Soy, isoflavones Grapes, Resveratrol Black Cohosh Saw Palmetto Kava 9. St Johns Wort 10. Valerian 11. Cinnamon 12. Turmeric 13. Ginseng 14. Cranberry 15. Ginkgo 16. Glucosamine & Condroitin I. Ginger Zingiber officinale Ginger • Contains powerful antioxidants – Gingerols, Shogaols, zingerones • Use - prevent or ease nausea - Reduce motion sickness - Reduce morning sickness - Reduce post surgery nausea Nausea Score N/V in Motion Sickness N/V in Pregnancy Nausea Intensity Study by Ozgoli, Goli & Simbar, 2009 N/V Post-surgery 80 70 60 Percentage reporting POV symptoms 50 40 30 20 10 0 Ginger Placebo Study by Bone, et al., 1990. II. Soy/ legumes • Low in saturated fat • Contains protein and other compounds that help lower blood cholesterol Effect = reduced risk of heart disease Effects: Meta-analysis of Soy protein on Serum Lipids • 38 clinical studies; 730 people over 2 decades: - 20 studies used soy protein isolate - 15 used textured vegetable protein • Lowering of serum cholesterol in 34/38 studies • No effect in 4 studies •In all studies, cholesterol averaged <185 mg./dl. James W. Anderson, M.D., Bryan M. Johnstone, Ph.D., and Margaret E. Cook-Newell, M.S., R.D. N Engl J Med 1995; 333:276-282 Reduction of Total Cholesterol by Soy Initial Cholesterol (mg/dl) >335 259-332 201-255 127-198 0 20 40 60 Average Total Cholesterol Reduction (mg/dl) Reduction in Blood Cholesterol mg. Reduction of Blood Cholesterol with Soy Consumption 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 25 50 Soy Intake (grams) 75 Sources: Soy Protein Soy Food Amount Soy Protein Soy milk, plain 1 cup 8g Tofu ½ cup 10 g Soy flour, defatted ¼ cup 8g Soybeans, cooked ½ cup 13 g Roasted soynuts ¼ cup 12 g Tempeh ½ cup 16 g Source: United Soybean Board III. Garlic • Garlic has been used in traditional and folk medicine for over 4,000 years • Garlic contains sulfur compounds • Eating one clove of garlic per day may help decrease blood cholesterol levels Effects: Garlic • Prevents platelet “stickiness” • Inhibits constriction of arteries • Reduces LDL oxidation (leads to clotting) • Prevents high blood pressure • Reduces blood lipids Ackermann et al., 2001, Arch Intern Med, 161: 813-24. Butt et al., 2009, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 49(6): 538-51 Component Responsible for Lipid Lowering • Allicin, a sulfur compound • Volatile sulfur compounds are not present in intact cells • Release by: – chopping – steaming – crushing Garlic Compounds and the Effect on HMG-CoA Reductase Liu & Yeh, 2002, J Nutr 132: 1129-1134 Recommendations: Garlic • Experts still researching optimal dose • Conservative estimate = 1-3 cloves per day IV. Cinnamon Cinnamon • Source of Manganese, iron, calcium, and fiber – Cinnamaldehyde (Reduces stickiness of platelets) – Cinnamyl acetate (Antioxidant) – Cinnamyl alcohol (Antioxidant) Cinnamon – True Ceylon Cinnamon • Arthritis – Reduces uric acid production • Heart Health – reduce lipids/platelet adhesion • Type 2 Diabetes – lower blood glucose • Blood Pressure – Reduced blood pressure Meta-analysis: Cinnamon & A1C Allen, R. W., Schwartzman, E., Baker, W. L., Coleman, C. I., & Phung, O. J. (2013). Cinnamon Use in Type 2 Diabetes: An Updated Systematic Review and MetaAnalysis. Annals Of Family Medicine, 11(5), 452-459. doi:10.1370/afm.1517 V. Black Cohosh Actaea racemosa L. Fast Facts • Main use: ease menopausal symptoms like hot flashes or night sweats • Most popular brand is Remifemin- it is a standardized extract – Commonly given in 20 mg pills, twice a day Effect of Black Cohosh on Menopausal Symptoms 50 40 Average Kupperman Menopausal Index (KMI) Score 30 20 10 0 Week 0 Week 4 Week 8 KMI score is out of 51 points and scores the following symptoms: hot flushes, paraesthesia, insomnia, nervousness, melancholia, vertigo, weakness, arthralgia or myalgia, headache, palpitations, and formication. Week 12 Study by Vermes et al., 2005 Pilot Test of BC for hot flashes 100 90 80 Daily hot 70 flash scores (mean of all 60 participants) 50 40 30 20 10 0 Baseline Hot flash score is frequency of hot flashes X severity Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Study by Pockaj et al., 2004. Week 4 Summary: • Black cohosh is probably effective but may not work for everyone- try it for a few months to see if it works for you! VI. Turmeric: • Long used as a yellow food coloring and spice. • A principal ingredient in curry powder(28%). • Contains three major curcuminoids, which are responsible for the yellow color of the herb. • Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) is the most significant curcuminoid. Effect of Turmeric on lung cancer in Mice Percentage that developed cancer Curcumin & Taxol Curcumin Taxol Placebo 0 20 40 60 80 100 MD Anderson Study VII. Saw Palmetto Main use: relief from urinary symptoms associated with BPH BPH diagrams BPH Prevalence in Males Does it work?- Peak Urinary Flow Rate Peak Urinary Flow Rate (mL/min) 12.4 12.2 12 11.8 Saw Palmetto Placebo 11.6 11.4 11.2 11 Month 3 Month 6 Month 9 Month 12 Study by Bent et al., 2006. SP effect on DHT 6000 5000 4000 Pg/g Testosterone DHT (dihydrostes tosterone) 3000 2000 1000 0 Untreated Permixon Study by Di Silverio, et al., 1998. Maximal Urinary Flow Rate Maximal Urinary Flow Rate (mL/sec) VIII. Kava Kava Piper Methysticum Witte, D. Loew, D. & Gaus, W. (2005). Meta-analysis of the efficacy of the acetonic kava-kava extract WS 1490 in patients with anxiety disorders. Phytotherapy Research. 19, p. 183-188. non-psychotic Drug Interactions-Effective Uses • Sedative • Anxiolytic • Muscle Relaxant • Mood stabilization • Reduce mild nervous anxiety • Restlessness & Agitation • Tension & Stress • Mild anti-inflammatory actions Dosage • Oral Use • Supplied by: – Capsules: 100 500mg – Liquid: 1:1, 1:2 – Tea • Daily Dosage: – Capsules: Root extract: 150mg-300mg twice daily, with a daily dosage of Kava pyrones 50mg240mg. – Tincture: Taken as 30 drops with water 3 times daily – Infusion: Take ½ cup twice daily Study by Witte, D. Loew, D. & Gaus, W. (2005). Results Geier [3] Kinzler [4] Lehrl [5] Malsch [7] Volz [11] Warnecke [12] -15 -10 -5 0 5 HAMA Difference 10 15 20 25 30 Study by Witte, D. Loew, D. & Gaus, W. (2005). Results Younger Older Male Female All 0 -10 -5 0 5 10 HAMA Difference 15 20 25 30 IX. Valerian Root Valeriana Officinalis Dosage • Daily dosage: 100mg-1800mg • Total internal daily dose: 15g root powder, for restlessness 220mg three times daily, & for sleep aid 400mg-900mg of extract YEAR NUMBER OF PARTICIPANT DOSE DURATION SLEEP QUALITY INPROVEMENT LEATHWOOD 1997 128 400 mg qhs 1 Day YES BALDERER 1985 10 450 mg qhs 1 Day NO LEATHWOOD 1985 8 450 mg qhs 1 Day NO DIAPER 2004 16 300 mg qhs 1 Day NO FARAG 2003 25 320 mg 4 Days NR SCHULTZ 1994 14 405 mg tid 8 Days NO KAMM-KOHL 1984 80 90 mg tid 14 days YES KUHLMANN 1999 91 600 mg qhs 14 Days NO DONATH 2000 16 600 mg qhs 14 Days NO FRANCIS 2002 5 20 mg/kg 14 Days NO DELSIGNORE 1992 51 100 mg tid 21 Days NR COXETER 2003 21 225 mg qhs 21 Days NO JACOBS 2005 270 600 mg qhs 28 Days NO VORBACH 1996 121 600 mg qhs 28 Days YES CERNY 1999 98 360 mg qhs 30 Days YES JASEN 1977 150 100 mg tid 30 Day YES Dichotomous Outcomes for Sleep Quality (Sleep improved or not) Jansen Leathwood (1982) Vorbach Cerny Kamm-Kohl Jacobs 0.1 1.0 10.0 Relative Risk Study by Bent. S. et. Al. (2006). 100.0 X. St John’s Wort Hypericum Perforatum Quick Facts • Main Use: treatment for mild to moderate depression, • Extract is standardized to 0.3% hypericin; 300-600mg 3x/day • Treatment of depression requires 2-6 weeks of treatment, and for full therapeutic dose use up to 6months Total Score HAM-D (mean) SJW & Mild to Moderate Depression Kasper,S. et al, 2006 Total Score HAM-D (mean) SJW vs. Standardized Depression Medication Phillip,M. et al, 1999 XI. Ginkgo Biloba What is Ginkgo biloba? • Dietary Supplement • Composition – Extract, flavonoid glycosides (composition?), terpene lactones and ginkgolic acid – Main Uses: Improves cognitive function, antiinflammatory effects, and vascular effects Speed of Attention (total Msec) Time Kennedy, DO, Scholey, AB, Wesnes, KA. Psychopharmacology. 2000 Kennedy, DO, Scholey, AB, Wesnes, KA. Physiol Behav. 2002. Based on Bond-Lader Visual Analog Scales. Summary of effectiveness of Ginkgo and Ginkgo/Ginseng combination on cognition • Enhanced speed of attention at 240 and 360 mg but not at 120 mg • Quality of memory was enhanced at 120 mg and 240 mg of Ginkgo • Working memory was enhanced with Ginkgo/Ginseng combo vs. Ginkgo alone XII. Glucosamine & Chondroitin • Meta-analysis found that supplements used together narrowed joint space. • Improved pain and mobility • More than 500 studies were evaluated • 1,775 patients Richy, F., & Bruyere O., 2003 55 • Largest clinical trial: Glucosamine/chondroitin Arthritis Intervention Trial (GAIT) • GAIT has produced two sets of negative results. • Glucosamine and chondroitin, alone or together, did not reduce osteoarthritis knee pain more than a placebo. 56 • Glucosamine & chondroitin may reverse osteoarthritis and decrease inflammation • Both may relieve arthritis pain and stiffness with fewer side effects than conventional drugs. • Although positive reports outnumbered negative ones, the negative ones have been larger and better designed. 57 • Only for use with moderate-to-severe • Do not use with: – Warfarin arthritis – Asthma • Give supplement – Allergic reactions three months to – Constipation – Ulcers work – Liver disease • Buy from researched – Inflammatory bowl supplier disease 58 XIII. Chocolate • Cocoa processed with alkali is not beneficial • High fat chocolate is not beneficial • High sugar chocolate is not beneficial • Cocoa is beneficial Effects: Cocoa Comparison of Antioxidant Content • Black tea (2gm bag) 1000 C for 2 min. • Green tea (2gm bag) 1000 C for 2 min. • Wine 140 ml. California Merlot. • 2 tbs. commercial Cocoa pwd. 200 ml H20 Total Flavonoid and Phenolic Content of Tea, Wine and Cocoa (per serving) 700 600 500 400 mg 300 200 100 0 GAE ECE Black Tea Green Tea Wine cocoa Gallic acid equivalents (GAE), phenolic Epicatechin equivalents (ECE), flavonoid Lee et al. (2003). Cocoa Has More Phenolic Phytochemicals and Higher Antioxidant Capacity the Teas and Red Wine. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 51, 7292-7295. Cocoa Inhibits Blood flow and Vessel Dilation • Subjects 20 individuals at risk of CHD • Consumed a cocoa drink • 2 groups high and low flavanol • Brachial artery flow and dilation were measured Sies, et al. 2005. Cocoa Polyphenols and Inflammatory Mediators. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 81, 304s-12s. Vaso-dilation with Cocoa Flavanols 7 6 5 % FMD 4 Before 2 hr After 3 2 1 0 Low flavanol cocoa High flavanol cocoa FMD (Flow-mediated Dilation) Sies, et al. 2005. Cocoa Polyphenols and Inflammatory Mediators. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 81, 304s-12s. THANK YOU!! This Presentation Made Possible by: