A Team Approach
to Dysfunctional
Voiding and Elimination
Risk Factors for Urinary Tract
Infections & Dysfunctional Elimination
Poor Bladder Health
• HOLDING - NOT peeing at regular 2 hour
•
•
timed intervals throughout the day.
Poor Fluid Intake and excessive intake of
bladder irritants such as caffeinated and
high sugared drinks.
Poor peeing posture will negatively impact
the bladders ability to empty completely.
Poor Bowel Health
• CONSTIPATION – NOT establishing bowel
•
•
regularity.
HOLDING – ignoring the signal to poop
Poor wiping or soiling of underpants
Poor Genital Hygiene
• Must practice good
general body hygiene
• Always follow good hand
washing and fingernail
hygiene.
• Uncircumcised males
must provide optimal
care to the penis.
• Females need optimal
wiping habits and good
genital hygiene.
Poor Bladder Immunity
• Not Completely understood in the medical
•
community – but some children simply
have more problems with UTI’s
(infections) than others.
We can not cure children that are prone
to infections, your goal is to eliminate the
risk factors.
Gender
• GIRLS have more problems with UTI’s than
BOYS.
• Female anatomy predisposes girls to have
more problems
• The female urethra is shorter and the anus
and vagina are very close together
increasing the risk of cross-contamination
Structural defects of
urinary System
• VUR – Vesicle
Ureteral Reflux
• Bladder or Kidney
stones/calculi
• Ectopic Ureters
Diagnosis:
1. Must obtain a detailed
history and physical
including:
• Family history
• Birth History
• Medical and
Surgical history
• Developmental
milestones
• Bowel and
Bladder habits
• Current
medications
• Physical Exam
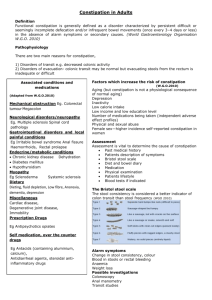
Problems with Constipation
1. Consequences of Constipation
• Pain and discomfort
• Chronic rectal distension
•
•
•
•
with loss of propulsion
Reduced perception of the
need to stool
A distended rectum
imparts pressure on the
bladder
Increased risk for UTI
Urine flow disturbances
Definition of Constipation
• No single definition exists
− Infrequent passage of stool
− Difficulty passing stool
− Straining to pass stool
− Small pebbly stools
− Large firm stools
− Episodes of abdominal pain
− Fecal soiling
− Palpable stool on physical
exam
Bowel Management
Medications
1. Bowel clean out with
Enemas/suppositories
2. Stool softeners
3. Laxatives
Bowel Management
Dietary
1. Increase Fluids
2. Increase Fiber
3. Reduce Dairy Intake
Fiber Facts & Therapy
Fiber is found in grains, cereals, fruits,
veggies, nuts, seeds and legumes.
FIBER RDA’S
1-3 yo needs 8-10g/day
4-6 yo needs 12-14g/day
7-10 yo needs 14-16g/day
Become an expert label reader!
Behavior Modification
for Bowel/Bladder
1. Dietary (remember these tips)
• Avoid bladder irritants such as
•
•
•
•
•
Caffeine, Chocolate, Citrus
Avoid excessive dairy intake
Avoid heavily sugared foods
Increase dietary fiber
Increase water intake
Decrease constipating foods
Behavior Modification
2. Hygiene Techniques
• Be aware of mistakes
• Girls: wipe front to back
• Use sufficient amount of toilet paper
• Avoid “scrubbing” or “dabbing”
• Change underwear when wet or
damp
• Butterfly rinse for girls
Behavior Modification
3. Voiding Techniques
• Proper posture for girls and boys
•
•
•
•
(see handout for posture review)
Timed voiding, timed stooling
Double voiding when necessary
Slow down, relax
Visualization exercise
Behavior Modification
4. Positive Reinforcement
• Stress overall goals and
objectives
• Always be positive
• Start with rewards for attempts
then advance to the goals
• Keep a calendar
Make success your target:
Success
Consistency
Compliancy
Commitment
GOAL
Follow the 3 C’s