Dr. Horsburgh - New England TB Consortium
advertisement

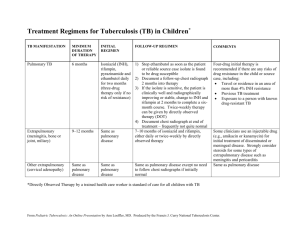
Overview • • • • • • • • Case Presentation Diagnosis Treatment – Induction phase Treatment – Continuation Phase Treatment Monitoring Assessment of Transmission Outcome References Case Presentation 18 y.o Hispanic female presents with 2 day hx of postpartum normal vaginal delivery and abnormal CXR. No cough, mild fever, no unexpected weight loss PPD 25 mm by history. Case Presentation - 2 • PMH: Pt is G1P1, otherwise unremarkable • FMH: Mother alive and well living in El Salvador; father unknown health status. 1 sib living in El Salvador A/W. • Social: Lives alone in bedroom room apt in 3family house. Rents apartment.Works as babysitter. Marital status is single though does have BF. Medical coverage is Medicaid. Immigration status undocumented Case Presentation - 3 • Meds: Tylenol 1gm PRN pain • Substance Abuse: Denies smoking, ETOH, and IVDU • Allergies: none known Physical Exam Pt sitting in bed in precaution room. In NAD, breathing comfortably. VS: WT 108 lbs, T 99.5 (F) HR 98-Pulse Reg--Resp18 BP 104/60 Resp: Symmetric chest wall motion. Neg for retractions or use of accessory muscles. No dullness noted on percussion. No palpable tenderness on palpation. BS with normal air movement, neg for rales and wheezes Labs • • • • • • Hematocrit 40.8 MCV 84 WBC 6.0 Platelets 453 AST 22 Alk Phos 180 • • • • • Creat 0.6 Serum Ca 9.9 PCO2 36.9 O2 sat 100 Sputum smear – x3 pending Chest Radiograph and CT • CXR suggestive of cavity lesion in LUL and RUL otherwise heart normal size. Diaphragm slightly elevated secondary to heightend uteral placement. Film suggestive of active process of pulmonary tuberculosis. • CT confirms cavity opacity in RUL Differential Diagnosis • Tuberculosis • Bacterial Pneumonia • Carcinoma Diagnosis • CXR abnormal but not necessarily diagnostic. • Sputum smears may be – or + depending on the level of infectiousness • May need bronchoscopy with bronchial washings or lavage • Biopsy may be warranted to confirm Diagnosis - 2 • Culture is gold standard but takes 3-6 weeks to grow in solid media, 12-28 days with liquid media • Smear is strongly suggestive but could be due to nontuberculous mycobacteria • Nucleic acid amplification can rule TB in but not out • TB skin test not sensitive or specific • In-vitro interferon gamma-based tests similar to TB skin test Case Presentation - 4 • Smears: 2+/1+/neg • HIV serology - negative Treatment - Induction Phase Because of the relatively high proportion of adult patients with tuberculosis caused by organisms that are resistant to isoniazid, four drugs are used in the induction phase for the 6-month regimen to be maximally effective. – – – – Isoniazid Ethambutol Rifampin Pyrazinamide 5-10 mg/kg day 15-20 mg/kg day 10 mg/kg day 20-25 mg/kg/day Case Presentation - 5 Our patient: Daily therapy with – – – – Isoniazid Ethambutol Rifampin Pyrazinamide 300 mg p.o. (1 pill) 800 mg p.o. (2 pills) 600 mg p.o. (2 pills) 1000 mg p.o. (2 pills) Other issues: intermittent regimens, combination pills Management • • • • DOT- directly observed therapy Self- Administered therapy Case Management Mandatory Confinement? Assessment of Transmission • • • • How long to isolate the patient? Source case? Transmission to household contacts? Transmission in the workplace? Case Presentation - 6 Initial sputum culture results from our patient: “M. tuberculosis” Isoniazid Ethambutol Rifampin Pyrazinamide Sensitive Sensitive Sensitive Sensitive Treatment – Continuation Phase Because of the relatively small number of organisms remaining after 2 months of intensive phase treatment, most patients with tuberculosis can be placed on continuation phase treatment after 8 weeks of induction. Induction Phase usually lasts 4 months (18 weeks) and can be give daily or twice weekly – Isoniazid – Rifampin 5-10 mg/kg day 10 mg/kg day Treatment Monitoring • Visit Schedule: q 2wk during induction q month during continuation • Adherence monitoring • Efficacy monitoring Weight, temperature 2 month and 6 month films monthly smear and culture • Toxicity monitoring Skin rash, LFTs, Nausea, Color vision Case Presentation - 7 Sputum culture results from our patient after 2 months of induction phase therapy: “No Growth” Outcome • Patient received induction and continuation therapy (2+4=6 months) and was cured • All household members received TST and chest radiograph if TST+. There we no active cases, but the 2 persons with TST+ received INH for treatment of LTBI • Baby received INH until follow-up TST 3months later was negative References 1. Horsburgh CR, Burman WJ. Tuberculosis Treatment: Theory and Practice. In: Therapy of Infectious Diseases, ed Baddour L, Gorbach SL. Philadelphia PA; Saunders, 2003: 529-46. 2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Treatment of Tuberculosis, American Thoracic Society, CDC, and Infectious Diseases Society of America. MMWR 2003;52(no. RR-11):1-80. 3. Horsburgh CR, Feldman S, Ridzon R. Quality standards for the treatment of tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis 2000;31:633-9.