GP HOMEOPATHIC PRESCRIBING
advertisement

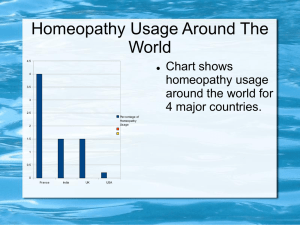
GP HOMEOPATHIC PRESCRIBING Dr Tim’s Magic Box Objective To introduce and encourage homeopathic dispensing in Primary Care setting Current situation in NHS homeopathy nationally 9 NHS Hospital Consultants 34 NHS Hospital Clinical Assistants / Specialist Doctors 692 GP with homeopathic training Homeopathy in NHS Primary Care Delivery options: Homeopathic advice only Homeopathic FP10 prescription issued Homeopathic medicine dispensed Homeopathic dispensing Benefits to: Patients Practitioners NHS hospitals Faculty of Homeopathy Benefits to Patients Immediate treatment – no delay in first aid and acute situations Effective alternative to conventional medicine – no treatment / failed treatment / contraindicated / side-effects Patient education – scope of homeopathy Holistic approach Pharmacy not involved Pharmacy associated problems Most pharmacists don’t have homeopathic knowledge Unreliable information / advice on homeopathic usage Don’t stock full range of medicines / potencies Have to make special order for medicine – takes time and effort for patient Pharmacy problems Incorrect advice given to patient Fobbed off with an incorrect potency / another OTC remedy / herbal alternative / conventional alternative Pt looses heart / gives up / reaches for OTC conventional medicine Net effect: Missed homeopathic opportunity Benefits to practitioner Personal satisfaction – ease suffering particularly with failed conventional treatment More effective practitioner – more to offer patients – homeopathy complements conventional treatment Knowledge utilisation Learning opportunity Reinforcing homeopathic knowledge Benefits to NHS hospitals Increased referral rates from primary care for more complex problems that require more than 10 minutes Support of NHS homeopathic hospitals indirectly supports teaching centres that are linked to the hospitals Benefits to the Faculty of Homeopathy Retention – increased use of homeopathy leads to reduced disuse / disinterest / disengagement Recruitment – increased patient demand for homeopathy encourages training of our colleagues. Personal success stories shared with colleagues may also lead to pursuit of training Why don’t more practitioners dispense homoeopathic medicine? Fear of the unknown. Never had time to research it / think it through. Setting it up – what medicines / bottles / labels. Where from? What cost? Who pays? Time constraints – 10 minutes. Prefer FP10 – issue and out! Too much to explain in too little time. Just not possible in 10 minutes. Homeopathic medicine dispensed in 10 minutes - LIVE! GP / Patient / history / diagnosis Key notes / specific condition / modalities Homeopathic medicine decided Offer homeopathic or conventional treatment – ‘nothing to loose’ / ‘conventional fall back’ etc Record notes – HRX / RHRX Write / print prescription Print label Print instruction sheet Make-up homeopathic medicine Make up homeopathic medicine Pill bottle – 7 gram – pre-filled with pillules Magic Box – index - medicating potencies Add potency – 2 drops / shake / chat – instructions / frequency / stop advice Give instruction sheet to patient Give bottle of pillules to patient Label – from dispensary or apply directly Review – make appointment for 4 weeks How are you going to set-up your dispensary? To be considered: Medicines Box Pillules Bottles Labels Instruction sheet Medicines Many or few? Suggested ‘start-up’ box of 30 medicines – based on: Cost – to make it affordable Basic ‘must have’ medicines Gives scope to add further medicines according to personal perceived need Medicine choice justified Common medicines and conditions as demonstrated by my 12 months audit National 15 GP study of Primary Care homeopathy Gut instinct with review of my 252 potencies – medicines and potencies that I wouldn’t be without! Dr Tim’s Magic Box medicines Aconite 30c Allium Cepa 30c Arg Nit 30c Arnica 30c Ars Alb 30c Belladonna 6c Belladonna 30c Carcinosin 30c Cocculus 30c Colocynth 30c Cup Met 30c Gelsemium 30c Hayfever 30c Hep Sulph 30c Ignatia 30c Lachesis 6c Lachesis 30c Lycopodium 30c Dr Tim’s Magic Box medicines Mag Phos 30c Mix Grass Pollen 30c Nat Mur 30c Nux Vom 30c Phosphorus 30c Pulsatilla 30c Total 30 medicines Rhus Tox 6c Rhus Tox 30c Silica 30c Staphysagria 30c Sulphur 6c Thuja 6c Comments on choice of medicines Polycrests – all there! Potencies – more than one potency in some e.g. Belladonna 6c / 30c All familiar medicines – no high brow (Lac Meerkcat) or small medicines (Teucrium) Most covered in first year of homeopathic training to PHCC level Medicating potency Dropper bottle – containing potency with 95% alcohol Quantity – 5ml = 100 droplets = 50 bottles of each medicine dispensed (2 drops each bottle) Cost: £4.65 - £7.00 Dispensing box Box – better than loose. Quicker to select and pick-out Move between surgeries / practices / home Choice of materials: - Cardboard box with holed insert - £4.84 for box of 28. - Plastic box with handle – £34.50 for box of 58. - Wooden box - £40 for box of 70. Pillules Pillules 3mm or 4 mm diameter. Suggest 4mm as patients find this size easier to tip a single pillule into the cap of the bottle. 3mm are too small and fiddly. Less wasted. Less chance of patient taking more than one which adds to confusion on dosage. Tablets don’t medicate so easily when shaken compared with pillules. Cost: £12 for bag of 1kg. Bottles 7 gram size. Brown glass for sun protection. White cap. Contain 50 pillules (4mm diameter). Easy to handle for the patient to tip one single pillule out into the cap. Easy for me to handle to medicate while in conversation with the patient. Cost: £70 for tray of 405 bottles. Bottles - preparation Pre-fill bottles – at home or surgery receptionist Fill with care – no contamination of the unmedicated pillules. Use funnel to channel pillules into bottles. Judge with eye – neck of bottle = 7 grams = 50 pillules Labels Dispensary practice – print label in dispensary. Label printer – stand alone label printer on desk in consulting room. Sheet of pre-printed labels with spaces for ‘name’, ‘medicine / potency’, dosage frequency / surgery address & phone number Avery labels size 63.5mm x 38.1mm wraps around 7 gram bottle neatly. Longer labels can be folded to leave a flap. Instruction sheet Instruction sheet - 2 sections: - basic instructions for taking medicine - general information about homeopathy Write your own or use mine Download it from the Faculty website Save it as a shortcut icon on your desktop - 2 clicks and it’s printed Another version with instructions on how to make up LM potencies available Instruction sheet – reasons for use Too much information for me to give in the limited 10 minute consultation. Too much information for patient to take in within a 10 minute consultation. Patient can read and re-read instructions at their own leisure. Instructions in clear plain English – no confusion. Pitched at basic level. Instruction sheet – basic instructions for taking medicine Aggravation reactions and how to manage it. Practical aspect of not touching pills. Clear advice about antidoting medicine with coffee and toothpaste. Contact details for any queries or adverse reactions. Clear advice on timing of taking medicine with respect to meal times. Practical advice on how to give to a baby and child. Instruction sheet – general information about homeopathy Evidence base awareness. Facts about safety profile of homeopathy. Conditions treated by homeopathy. Subtle advert about homeopathy. Increases exposure and stimulus for patient to learn more about homeopathy. Patient able to share handout with other family members and friends. The bottom line – what does it cost?! Without a box £292. With a cardboard box £302. With a wooden box £332. Tax deductible. Who pays? You (= £332) or Practice (4 partners = £83 each or 6 partners = £55.33). Sell your case to your partners – saving on conventional medicine spend / good for patient’s perception of the practice / off-loading heart sink patients to you. Summary – benefit to patients Benefits to patients: Immediate – ideal for first aid / acute situations. Pharmacy not involved. Effective alternative to conventional treatments. Increased exposure to homeopathy – more aware of its capabilities. Holistic approach to medical care. Summary – benefits to practitioners Increased use = increased learning Increased use = knowledge maintenance – no disuse atrophy Increased use = increased experience = increased effectiveness as a homeopath Increased use = increased job satisfaction and personal rewards Summary – benefits to NHS Homeopathic hospitals Increased use = increased referrals – supports business case for hospitals. Increased use = generates need for postgraduate education – supports training centres. Summary – benefits to Faculty of Homeopathy Member retention – increased usage prevents disuse atrophy / builds personal experience / benefits patients and GP – net effect is continued use of homeopathy and hence member retention. Member recruitment – increased patient awareness of homeopathy leads to increased patient demand for homeopathy - may encourage GP to undertake homeopathic training. Member recruitment – homeopathic case successes shared with GP colleagues – may encourage GP to undertake homeopathic training. What now?! Buy your own Magic Box / pillules / bottles. Use my list of potencies or use it as a suggestion list and adapt it to your instinctive needs. Download the patient instruction sheet. Go forward, go ahead – go dispensing. Think benefits. Think recruitment. Think retention. I give you…… Dr Tim’s Magic Box …….Thank you