“The Remains of the Day”
or,
why constipation is important
to you…
Interns 2008
outline
•
•
•
•
•
Case studies
Types of constipation
Assessment
Treatment
The importance of PR!
Mrs BM
• 84 yr old, Lives alone, care package 2X week
• Presents on Christmas Eve - daughter found her
confused + cooking breakfast at 4pm
• “difficult historian”
– no complaints, wants to “leave this airport.”
• Hx HTN, OA, T2DM, mild cognitive impairment
• Meds:
–
–
–
–
Paracetamol
Gliclizide MR 30mg od
Perindopril plus 5/1.25mg
Diltiazem CD 180mg od
Mrs BM…
• o/e
– Confused, looks dehydrated, Bsl 7.3
– AMTS 7/10
– Afebrile, p=90, bp 120/70
– cvs, resp, cns, abdo exam nad
– msu: +WCC, glu+
Mrs BM…
•
ED Assessment:
– Likely UTI + Acopia
•
Plan:
– Admit Medics
– MSU,bloods
– Trimethoprim
Mrs BM…
• MSU- no bacteria, no growth
• Bloods: Na 134, Ur 18, Cr 89, FBC nad
• Refuses to eat or drink
• Feels nauseous – given dolesetron by 2ndon
• Commenced on iv fluids
Mrs BM…
• Next medical review on 27/12
–
–
–
–
–
Still confused ++
Picking at bottom (dirty fingernail sign!)
Still not eating
3x dolesetron given for nausea
incontinent
• No BM since admission? How many days prior?
• Abdo soft, but distended
• PR – empty rectum but “ballooned”
Mrs BM…
• Further hx:
– GP had commenced Diltiazem CD 2weeks
prior for HTN
– Very hot over Christmas – decreased oral
intake
Mrs BM
•
•
•
•
•
•
Dolesetron and diltiazem ceased
Given aperients (more on this later)
Large BM x3
Improvement in continence
Improvement in mental function
Stint on 3K:
– d/c home with previous level of care
What have we learned so far?
• Constipation can cause delirium
• Constipation can cause urinary
incontinence
• “poo on fingers” often means constipation
• Ca+ blockers can cause constipation
• Dehydration can cause constipation!
• PR PR PR PR PR
Mr PR
•
•
•
•
•
59 year old Professor of engineering
Admitted for R total hip joint replacement
PMx- OA R hip, L knee, ex-smoker 10yrs
Meds – aspirin only – withheld at present
Pre-op bloods normal – FBC, UE
Mr PR….
• Post-operatively:
– Pain: PCA and then tramadol and oxcodone
SR 20mg bd
– Nurse prescribed C+S given daily
– Refuses to use bed pan.
– Refuses to use commode by bed – 4 bedded
room.
Mr PR…
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Day 4 post op – no BM yet
Grumpy+++
Refuses PR intervention – undignified!
Finally on day 5 – small BM
Abdo discomfort continues
PR- still evidence of loading
Aperients increased to regular
Mr PR…
• Transfer to rehab -periodic constipation
continues
• RMO decides to investigate further:
– Ca 3.28!
– PTH elevated
– Confirmed primary hyperparathyroidism
What have we learned so far?
• Always co-prescribe aperients with opiates
• Hospitals are undignified! – this can cause
constipation
• If constipation persists – always
investigate!
• PR PR PR PR PR
Mr BO…
• 74 yr old, lives “with mates”.
• Presents with fall and prolonged lie
• PMx:
– ETOH: cirrhosis, portal HTN
– T2DM – poor control
– Smoker +++
• Meds:
– Propranolol 40mg
– Thiamine
Mr BO…
• No fractures
• Mildly elevated CK – treated with iv fluids,
IDC inserted to monitor output
• Probable LRTI – commenced on oral abs
Mr BO…
• Difficult to manage – always wanting a
smoke, noisy friends
• No BM for 4/7 then some watery
diarrhoea, further BNO 2/7 then more
diarrhoea
• Needing supervision to mobilise – falls risk
• Found next to bed on the floor, unable to
stand up
Mr BO…
• RMO called to examine:
– No obvious injury
– Decreased power both lower legs
– Hypo reflexic
– Odd pattern of decreased sensation to soft
touch
– PR:
• No anal tone
• Soft faeces loading rectum
Mr BO…
• Repeat Abdo USS – confirmed likely multifocal HCC
• Rapid deterioration on the ward transferred to hospice soon thereafter
What have we learned so far?
• Watery diarrhoea after a period of NBO
often indicates overflow diarrhoea
• Constipation can indicate other problems..
• PR PR PR PR PR PR
The learning bit…
“Normal” bowel habit
• Varies from person to person
• Most people empty their bowels between 3
times a day and 3 times a week
Constipation
(2+ for at least 3months during the last year)
– Straining in 25% of movements
– Feeling of incomplete evacuation after
25%
– Sense of anorectal obstruction /
blockade in 25%
– Manual manoeuvres to help in 25%
– Hard or lumpy stools in 25%
– Stools less frequent than 3 per week
Subtypes
• IDIOPATHIC
• Slow Transit Constipation
• Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
• Combination Syndromes
• Normal Colonic Transit Constipation
• SECONDARY
• Primary Diseases of the Colon / Rectum
• Irritable Bowel Syndrome
• Peripheral Neurogenic
• Central Neurogenic
• Non-Neurogenic
• Drugs
Idiopathic…
• Slow transit constipation
– Slower than normal movement from proximal
to distal colon and rectum
– Colonic inertia vs uncoordinated motor
activity?
– ? enteric nerve plexus dysfunction
• Pelvic floor dysfunction
– Functional defect in coordinated evacuation difficulty evacuating contents from rectum
– Probably acquired / learned dysfunction rather
than organic / neurogenic
Idiopathic…
• Combination syndromes
• Normal Colonic Transit Constipation
– Misperception of bowel habit
– Often psychosocial stresses
Secondary
• Primary diseases of colon/rectum
• Benign stricture, malignancy, proctitis, anal
fissure
• IBS
• DRUGS
SECONDARY …
• Peripheral neurogenic
– Hirschsprung’s, autonomic neuropathy, Diabetes,
pseudo-obstruction
• Central neurogenic
– Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury
• Non-neurogenic
– Hypothyroidism, hypercalcaemia,
panhypopituitarism, pregnancy, anorexia nervosa,
systemic sclerosis
DRUGS ASSOCIATED WITH
CONSTIPATION
• ANALGESICS
– Opiates!!! (this includes tramadol)
• ANTICHOLINERGICS
– Antispasmodics, antidepressants,
antipsychotics
• CATION-CONTAINING
– Iron supplements, antacids,
• NEURALLY ACTIVE
– Ca+blockers, 5HT3 antagonists
Hospital causing constipation
•
•
•
•
•
•
Decreased exercise/mobility
Hospital food (Not eating enough fibre)
Not drinking enough fluid
Lack of privacy
Limited toilet access
Depression / grief / anxiety
“please review Mr Strain,BNO 4/7”
HISTORY
• SYMPTOMS (Nature / Onset / Duration)
• Frequency
• hard stools?
• satisfaction
• Straining/extra help required?
• Bloating, pain, malaise
• BOWEL PATTERN (Usual and current)
• BOWEL REGIME (Usual and current)
• Aperients/PR intervention/ frequency, dose
• IDENTIFICATION OF CONTRIBUTING FACTORS
ALARM…..
•
•
•
•
•
•
Haematochezia
Weight loss
Family history of CRC or IBD
Anemia
Positive FOBT
Acute onset of constipation in elderly
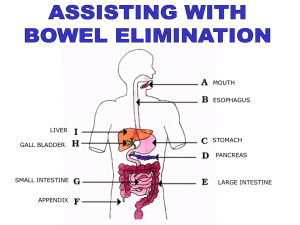
EXAMINATION
• PERINEAL / ANAL EXAMINATION
• Perianal skin, anal reflex, squeeze,
simulated evacuation, mucosal prolapse
• PR!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
• Sphincter tone (resting, squeezing),
masses, tenderness, expel finger
• PV
• Rectocele
• ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION
INVESTIGATIONS
• BLOOD TESTS
– FBP, TSH, Calcium, Glucose, Creatinine
• RADIOGRAPHY
– Abdo XR
– RPH imaging guidelines: DO A PR FIRST
– only use to: diagnose constipation or ? obstruction
•
ENDOSCOPY
• Flexible sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy
•
SPECIALISED TESTS
• Colonic transit (radiopaque marker) studies, barium defecography,
anorectal manometry, balloon expulsion test
Treatment
•
•
•
•
•
Good habits
Pelvic floor exercises
Diet
Remove ppt factors
aperients
The
Call
to
Stool!
DIET
• INSOLUBLE FIBRE
• Speeds up bowel motions
• eg. Multigrain wheat, corn and rice cereals,
bran, fibrous vegetables, skins of fruits and
vegetables
• SOLUBLE FIBRE
• Turns into gel and firms up loose stools
• eg. Oats, barley, rye, legumes, peeled fruits
and vegetables
Fibre supplements
•
•
•
•
•
Ispaghula (Fybogel)
Psyllium (Metamucil)
Guar gum (Benefibre)
Sterculia (Normafibe)
Methylcellulose
• Recommended dietary fibre = 20 – 35 g/day
• Water intake must be increased according to
manufacturers instructions when taking fibre
supplements
MEDICATIONS
• Appropriate use of aperients
• Only commence if simple measures (fibre / fluid /
exercise / review of medications) not adequately
controlling constipation
• Only take for short periods of time
Aperients
• BULK FORMING
• STOOL SOFTENERS
• OSMOTIC
• STIMULANT
• SUPPOSITORIES & ENEMAS
BULK FORMING
• Add bulk to the stool
• Absorb water and increase faecal mass
• Soften stool and increase frequency
• Ispaghula (Fybogel)
• Psyllium (Metamucil)
• Guar gum (Benefibre)
• Sterculia (Normafibe)
• Methylcellulose
• Calcium polycarbophil
• Not helpful in opioid induced, may worsen incipient
constipation
STOOL SOFTENERS
• Soften the stool
• Lower surface tension of stool allowing water to
more easily enter stool
• Few side effects
• Less effective than laxatives
• Eg.
• Docusate sodium (Coloxyl)
OSMOTIC
• Attract water into the bowel
• Osmosis keeps water within intestinal lumen
• Improve stool consistency and frequency
•
•
•
•
•
Lactulose (Actilax, Duphalac, Genlac, Lac-dol)
Sorbitol (Sorbilax)
Polyethylene glycol (Movicol, Golytely, Glycoprep)
Glycerol (Glycerol / Glycerin suppositories)
Magnesium sulfate (Epsom salts)
• Lactulose can take up to 3 days
• Can get bloating, colic, wind!
STIMULANT
• Increase intestinal motor activity
• Alter mucosal electrolyte,fluid transport
• Bisacodyl (Bisalax, Durolax)
• Senna
• Castor oil
• Cascara
• 6-12 hour latency
• Good in opioid with stool softener
• Excessive use may cause hypokalemia,
protein losing enteropathy, salt overload
“PR intervention”
• Always with oral aperient
• Faecal impaction/cord
compression/neurogenic
• PR!
– soft poo + “lax” rectum= bisacodyl
– hard poo = glycerine
– If palpable in abdo = glycerine, then
phosphate. May need to repeat
Summary
• PR!
• Constipation can indicate an underlying
problem – rule this out.
• Opioids are not the only offending drug
• The elderly can develop delirium with just
constipation.
• Hospitals are bad for your bowels.
• Never prescribe PR intervention without
oral.
Oh, and PR!