Systems explanations - Systems and Patterns
advertisement
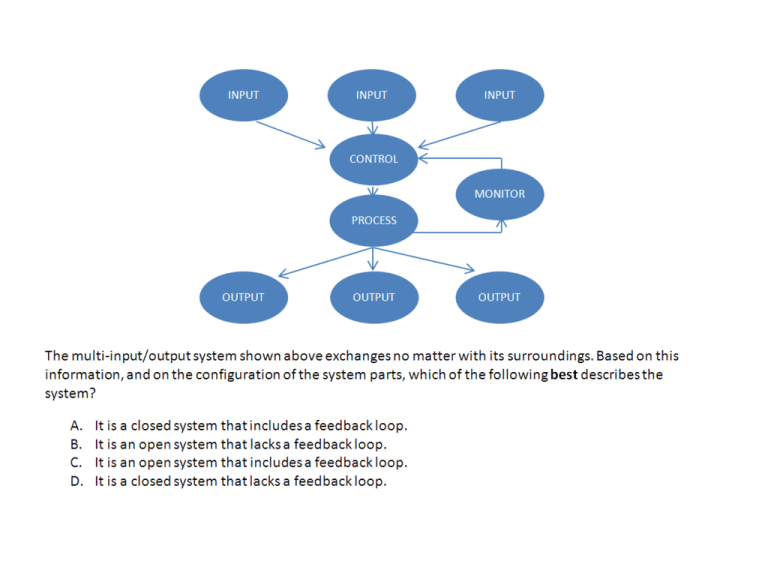
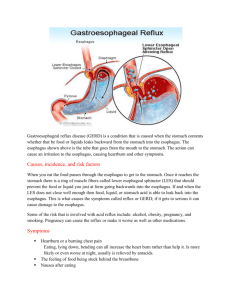
A system is made up of interrelated parts that work together to perform a single task. There are thousands of systems at work every day in society, in machines, and in our own bodies. An example of a system is the digestive system, which includes the stomach and the intestines. These organs and others work together to digest food. Systems can also be made up of interrelated processes. For example, energy production in plants is a system that consists of two main, interrelated processes - photosynthesis and respiration. A closed-loop system is a system with feedback that can change its processes based on the feedback. It is the opposite of an open-loop system. Change in one part of a system affects the whole system. Since all the parts are dependent on each other, the system processes could come to a stop. An example of this is a car. Change in just one part, like the battery failing, means the car will not start or run, even though the other parts of the car are running smoothly. The raw material that is added to a system is known as the input. For example, the input for the digestive system is food that is eaten. The finished product or waste that forms as a result of a process is known as the output. For example, the output of the digestive system is energy and wastes. When the output of a system comes back to influence the subsequent functioning of that system, feedback occurs. There are two main types of feedback:Positive feedback occurs when the output of a system amplifies subsequent outputs of the system. Negative feedback occurs when the output of a system causes subsequent outputs to decrease. What do the lunar cycle, bird migration, and cell mitosis have in common? • They are all natural events that occur in a pattern. • They are all included in the discipline called biology. • None of them are predictable. • None of them are studied by scientists today. All of the natural events in the list have a predictable recurring pattern. In fact, most natural events occur in patterns. Scientists often look for patterns when studying a new phenomenon. In a production system that makes cars, the bumper division produces an output of _______ that becomes an input to the assembly division. energy material information electricity The output of the bumper division is bumpers for the cars. Bumpers are a form of material. The bumpers are then put on the cars by the assembly division. Sending an e-mail is an example of a system with multiple parts. An e-mail program takes the input from the keyboard and changes it into a computer language output. The output language goes through the internet system and finds the account it was sent to. The message becomes the input for another e-mail program which changes it into an output of text that the recipient can read. What is the primary type of input and output that is used in an e-mail system? The primary input and output of an e-mail system is information. The information in the email is changed into different forms as it travels through the system. Energy is used in the process, but it is not the primary form of the input and output. System input is the raw material that is put into a system for processing. In the case of the digestive system, food is the input. The output is energy and waste. The system process is the digestion itself, including chewing, chemical breakdown of the food in the stomach, and nutrient absorption in the intestines. A system is a set of interrelated parts. The outputs from one part of a system can become inputs to other parts of the system. For example, an e-mail system takes the input from a keyboard and changes it into a computer language. The output form of the message becomes an input to the internet as it travels to the account it was sent to. This becomes the input for the other person's email program, which changes it into an output of text that the recipient can read. Inputs and outputs in systems may include material, energy, or information. Change is a variable. It can come as a result of new knowledge and better technology. Or it can happen due to the malfunctioning of a machine or a broken part. It can happen as a result of feedback that a system receives. All systems deal with change. Change in one part of a system affects the whole system. Input: Process: Feedback? Process: Process: Mouth and esophagus, large intestine, small intestine, stomach, liver and pancreas Output: POSITIVE or NEGATIVE? Celiac disease is a digestive disorder caused by the abnormal response of the immune system to a protein called gluten, which is found in certain foods. People with celiac disease have difficulty digesting the nutrients from their food because eating things with gluten damages the lining of the intestines over time. Some of the symptoms are diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. The disease can be managed by following a gluten-free diet. Gastritis and peptic ulcers. Under normal conditions, the stomach and duodenum are extremely resistant to irritation by the strong acids produced in the stomach. Sometimes, though, a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori or the chronic use of certain medications weakens the protective mucous coating of the stomach and duodenum, allowing acid to get through to the sensitive lining beneath. This can irritate and inflame the lining of the stomach (a condition known as gastritis) or cause peptic ulcers, which are sores or holes that form in the lining of the stomach or the duodenum and cause pain or bleeding. Medications are usually successful in treating these conditions. Cystic fibrosis is a chronic, inherited illness where the production of abnormally thick mucus blocks the ducts or passageways in the pancreas and prevents its digestive juices from entering the intestines, making it difficult for a person to properly digest proteins and fats. This causes important nutrients to pass out of the body unused. To help manage their digestive problems, people with cystic fibrosis can take digestive enzymes and nutritional supplements. Hepatitis is a viral infection in which the liver becomes inflamed and can lose its ability to function. Some forms of viral hepatitis are highly contagious. Mild cases of hepatitis A can be treated at home; however, serious cases involving liver damage may require hospitalization. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common intestinal disorder that affects the colon. When the muscles in the colon don't work smoothly, a person can feel the abdominal cramps, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea that may be signs of IBS. There's no cure for IBS, but it can be managed by making some dietary and lifestyle changes. Occasionally, medications may be used as well. Esophagitis (pronounced: ih-saf-uh-jeye-tus) or inflammation of the esophagus, is an example of a noncongenital condition. Esophagitis is usually caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a condition in which the esophageal sphincter (the tube of muscle that connects the esophagus with the stomach) allows the acidic contents of the stomach to move backward up into the esophagus. GERD can sometimes be corrected through lifestyle changes, such as adjusting the types of things a person eats. Sometimes, though, it requires treatment with medication. Occasionally, esophagitis can be caused by infection or certain medications. congenital - meaning people are born with them noncongenital - meaning people can develop them after birth Tracheoesophageal fistula (pronounced: traykee-oh-ih-saf-uh-jee-ul fish-chuh-luh) and esophageal atresia (pronounced: ih-safuh-jee-ul uh-tree-zhuh) are both examples of congenital conditions. Tracheoesophageal fistula is where there is a connection between the esophagus and the trachea (windpipe) where there shouldn't be one. In babies with esophageal atresia, the esophagus comes to a dead end instead of connecting to the stomach. Both conditions are usually detected soon after a baby is born — sometimes even beforehand. They require surgery to repair. congenital - meaning people are born with them noncongenital - meaning people can develop them after birth Input: Process: Feedback? Process: Process: Output: POSITIVE or NEGATIVE? Bread Rippage (BR) is a common problem with today’s store brand breads. The problem manifests itself by having large holes form in the bread while you’re trying to spread peanut butter on the bread. Crunchy style peanut butter can contribute to BR. Sticky Fingers occurs when you get jelly/peanut butter on your hands. It is most often caused by not using a knife to spread, or using too short of a knife, or trying to get the last bit of peanut butter out of an empty jar. It can effect the quality of your sandwich or feature sandwiches. Loss of Jelly is when gobs of jelly fall from the sandwich. If left untreated, it can further lead to sticky fingers. Open Face Disorder is when the two slices of bread are layered backwards, so the jelly and peanut butter are on the outside of the bread instead of the inside. Very bad.