Thrombin generation in two families with MYH-9-related platelet disorder
Eva Zetterberg, MD, PhD1, Margareta S Carlsson Alle, MD, PhD2, Jari Nivala, MD3, Juliane Najm, PhD4, Andreas Greinacher, MD5
1Department
of Hematology and Coagulation, Skane University hospital, Malmö, Sweden; 2Department of Hematology, Växjö Central hospital, Växjö, Sweden; 3Department of Pediatrics, Karlstad, Sweden; 4Institute for Human Genetics,
Greifswald, Germany; 4 Institute of Immunology and Transfusion Medicine, Greifswald, Germany
Corresponding author:
Eva Zetterberg, Department of Hematology and Coagulation, Jan Waldenströms gata 14, plan 3b, 205 02, Malmö, Sweden. Phone: +46 40337436; Fax:+46 40336255; e-mail: eva.zetterberg@med.lu.se
Methods
Thrombin generation was performed on
frozen platelet rich plasma using the
calibrated automated thrombogram (CAT)
method (Fig 1). ETP was compared between
patients diagnosed with MYH-9 related
platelet disorder and a reference material
consisting of 40 healthy individuals.
Results
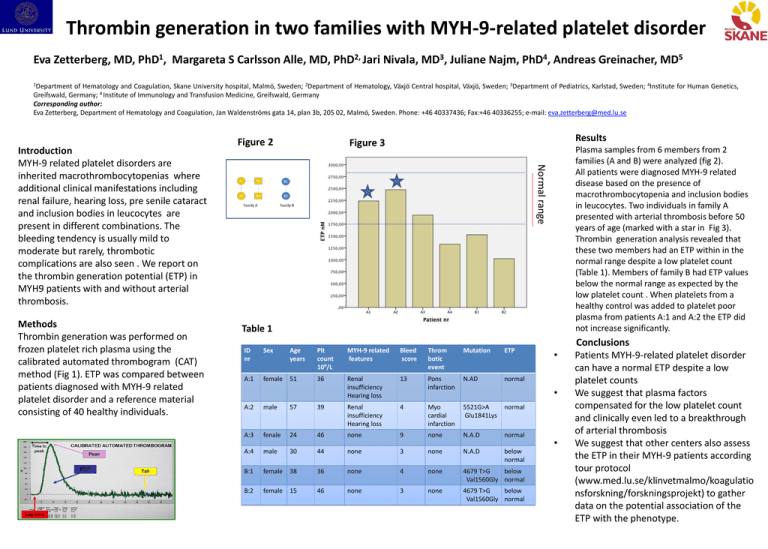
Figure 3
Plasma samples from 6 members from 2
families (A and B) were analyzed (fig 2).
All patients were diagnosed MYH-9 related
disease based on the presence of
macrothrombocytopenia and inclusion bodies
in leucocytes. Two individuals in family A
presented with arterial thrombosis before 50
years of age (marked with a star in Fig 3).
Thrombin generation analysis revealed that
these two members had an ETP within in the
normal range despite a low platelet count
(Table 1). Members of family B had ETP values
below the normal range as expected by the
low platelet count . When platelets from a
healthy control was added to platelet poor
plasma from patients A:1 and A:2 the ETP did
not increase significantly.
Normal range
Introduction
MYH-9 related platelet disorders are
inherited macrothrombocytopenias where
additional clinical manifestations including
renal failure, hearing loss, pre senile cataract
and inclusion bodies in leucocytes are
present in different combinations. The
bleeding tendency is usually mild to
moderate but rarely, thrombotic
complications are also seen . We report on
the thrombin generation potential (ETP) in
MYH9 patients with and without arterial
thrombosis.
Figure 2
Table 1
ID
nr
Sex
Age
years
Plt
count
109/L
MYH-9 related
features
Bleed
score
Throm
botic
event
Mutation
ETP
A:1
female
51
36
Renal
insufficiency
Hearing loss
13
Pons
infarction
N.AD
normal
•
•
A:2
male
57
39
Renal
insufficiency
Hearing loss
4
Myo
cardial
infarction
5521G>A
Glu1841Lys
normal
A:3
fenale
24
46
none
9
none
N.A.D
normal
A:4
male
30
44
none
3
none
N.A.D
below
normal
B:1
female
38
36
none
4
none
4679 T>G
below
Val1560Gly normal
B:2
female
15
46
none
3
none
4679 T>G
below
Val1560Gly normal
•
Conclusions
Patients MYH-9-related platelet disorder
can have a normal ETP despite a low
platelet counts
We suggest that plasma factors
compensated for the low platelet count
and clinically even led to a breakthrough
of arterial thrombosis
We suggest that other centers also assess
the ETP in their MYH-9 patients according
tour protocol
(www.med.lu.se/klinvetmalmo/koagulatio
nsforskning/forskningsprojekt) to gather
data on the potential association of the
ETP with the phenotype.












