Pharmacology
advertisement

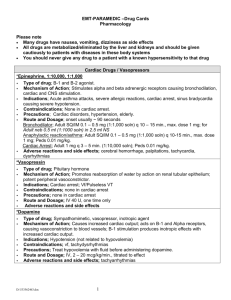
Gimme ‘da DRUGS, man! During the transport of an ACS patient, you notice that after giving nitroglycerin, their blood pressure drops to s*&#! (S*&#! = 50/palp). As you wonder “how did nitroglycerin drop it that low” you give a fluid bolus but also grab the Dopamine. “How does Dopamine work? How do I give it? What are the side effects?” You ponder, noticing a bit late that your patient has been unconscious for the past 10 seconds, in V-fib. Things just went from S*&#! to F*&#!... Generic Name/Trade Name: different names depending on who is making it. Examples: acetaminophen/Tylenol, fentanyl/Sublimaze, hydromorphone/Dilaudid. Mechanism of Action: how it works in the body Pharmacokinetics – how it is absorbed, distributed, and eliminated from the body Dosage/Route – how much and where (oral, rectal, nasal, IV, IM, subcutaneous) Indications/Contraindications – what its used for, what will prevent you from giving it. Adverse effects – things that might go wrong if you give it Therapeutic levels – range of serum levels in which drug will have its predicted value LD50 – level at which drug will kill 50% of the patients given the drug Metabolism – how the body transforms the drug to make it inert and ready for removal Excretion – how the drug exits the body Liver/fecal Kidney/urine Combination Right Drug Right Patient Think Mass Casualty situations Right Dose Have a reference handy Right Time Right Route Right Documentation Time, who gave it, what happened!! Receptor A protein made by the cell, nestled in the cell wall that acts as a signal sentinel. Acts in response to this signal in a certain way Usually by a second messenger system The structure of the receptor is such that it can be stimulated, overstimulated, or blocked from acting. The second messengers cause the production of enzymes Stimulate a receptor epinephrine, dopamine, Narcotics, Benzos, succinylcholine, albuterol Block a receptor lidocaine, aspirin, Narcan, Vecuronium, atropine, adenosine, amiodarone, diphenhydramine Directly effect body chemistry/osmolarity electrolytes, bicarb, NaCl, mannitol Act as an enzyme or catalyst tPA, thiamine, cyanocobalamin Block an enzyme Act as substrate for a chemical reaction Mucomyst, nitroglycerin, oxygen, glucose Kill Bugs - antibiotics Sympathetic Alpha (1, 2) Constricts blood vessels, dilates pupils Beta 1 – increases heart rate 2 – dilates bronchioles, arterioles Parasympathetic Muscarinic Relaxes smooth muscle (except bronchioles) Decreases heart rate, electrical conduction Constricts pupils GABA Causes a decrease in neuronal activity Opioid Block pain reception in the spinal cord Causes euphoria (mu receptor) Acetylcholine Allows for transmission of nerve impulse to a muscle group – contracts muscle Dopamine Poorly understood, neuronal signaling and cognition Aspirin (Ecotrin, Bayer) Action: Thromboxane A2 inhibitor, causes platelet function inhibition Dosage: 324mg oral chewed Indications: Cardiac chest pain Contraindications: Allergy, GI bleeding Side Effects – bleeding, GI upset Nitroglycerin (EMT can assist patient with his/her own, AEMT and medic can give without prior Rx) Effect: vasodilator, chest pain reliever Dosage: 0.4mg sublingual Q 15 min x3 Indications: chest pain Contraindications: hypotension, allergy Side Effects: Headache, hypotension, syncope, cardiac arrest Albuterol (Proventil) Effect: Dilates smooth muscle in bronchioles (B2) Dosage: 1-2 puffs per MDI PRN (max three doses); AEMTs and Medics – 1 ampule neb prn, max 3 Indications: Asthma or COPD exacerbations Contraindications: none Side Effects: jitteriness, tachycardia, arrhythmia, sweating, anxiety Epinephrine (EpiPen, EpiPen Jr) Effect: A1, A2, B1, B2 receptor agonist – vasocontricts, relaxes bronchiole smooth muscle, increases heart rate Dosage: EMTs: EpiPen (0.3ml) or EpiPen Jr (0.15ml) Dosage: AEMTs: 0.3ml 1:1000 IM, or 0.15ml for 15-30kg Dosage: Medics: as above, or 0.1-0.5mg iv 1:10,000 for anaphylaxis, 0.1mg/kg, max 1mg IV Q5 min for arrest Indications: Anaphylaxis, severe asthma (medical control), cardiac arrest Contraindications – none Side Effects: arrhythmia, hypertension, MI, jitteriness Oxygen Effects: acts as a metabolic substrate for respiration, energy production Dosage: 2-15lpm via NC (max 6lpm), or oxymask Indications: hypoxia, respiratory distress, stroke like syndromes Contraindications: open flame Side Effects: hyperoxia indicated in free radical formation and increased cell damage. Dextrose/Glucagon Reviewed in Diabetic Emergencies Lecture Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) Reviewed in Anaphylaxis Lecture Naltrexone (Narcan) Effects: opioid receptor antagonist Dosage: 0.4mg IV Q5 min until desired effect, max 2mg Indications: altered mental status, narcotic OD Contraindications: alert patient Side Effects: pain, agitation, vomiting, injury to EMT if patient not restrained. Benzodiazepines (diazepam/Valium; medazolam/Versed) Effects: GABA receptor agonist – increase seizure threshold, sedating effects Dosage: Valium (long acting) .1-.2mg/kg IV, IM or PR (gel) max 5-10mg x1 dose Versed (medium acting) .02-.05mg/kg max 4mg x1 Indications :Seizures, acute severe agitation, bath salts Contraindications: respiratory depression, sedation, high risk airway, allergy Side Effects: miosis, respiratory depression, need for intubation Narcotics (morphine; fentanyl) Effects: opioid agonist – provides pain relief Dosage: Morphine 0.1mg/kg IV/IM max 10mg for pain Fentanyl – 0.5-1 mcg/kg iV max 50mcg x1 SLOW Medical control for any further dosing Indications: acute traumatic pain, cardiac pain (morphine only) Contraindications: abdominal pain, allergy, respiratory depression or altered mental status Side Effects: Chest Wall Rigidity syndrome, respiratory depression, hypotension Zofran Effect: Reduction of nausea through inhibition of serotonin 5-HT3 receptor Dosage: 4mg IV/ODT for Adults and Children 6 and older 2mg IV/ODT children 2-6 1mg IV children 6 months-2 years Indications: nausea and vomiting Contraindications: allergies Side effects: may prolong QT, headache Phenergan Effects: reduces nausea and vomiting via dopamine receptor antagonism Dosage: 25mg IM for adults only. Pediatric use not permitted Indication: nausea and vomiting Contraindication: sedation, allergy Side Effects: respiratory depression, extrapyramidal symptoms (dystonic reaction), anxiety, hypotension Haldol Effects: sedation and reduction of psychotic symptoms via dopamine receptor antagonism Dosage: 2.5mg-5mg IM/2mg IV Indication: acute psychosis, severe agitation, second line to maxing out your benzos for bath salts. Contraindications: allergies, prolonged QT syndrome Side Effects: sedation, Torades de Pointe, ventricular tachycardia, dystonia. Ketamine Effect: produces dissociative state through limbic system interaction Dosage: 1-2mg/kg IV or 3-4mg/kg IM Indications: induction agent Contraindications: Theoretical – increased ICP, increased IOP, allergy Side effects: laryngospasm, emergence reactions, excessive drooling Paralytics (Rocuronium/Vecuronium) Effect: inhibits release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction causing paralysis Dosage: Vecuronium: 0.1mg/kg IV Rocuronium: 1mg/kg IV Indications: paralytic agent for RSI Contraindications: difficult airway, insuffient expertise in airway management Adverse Reactions: death Solu-Medrol Effects: corticosteroid - reduces inflammation and immunity through multiple messengers and interactions Dosage: 1mg/kg IV, max 125mg IV Indications: asthma, COPD, anaphylaxis Contraindications: allergy Side Effect: hyperglycemia, jitteriness, immunosuppression, renal impairment, GI bleeding Vasopressin Effect: hormone – constricts blood vessels and improves cardiac contractility Dosage; 40 units x1 dose in lieu of first epi for cardiac arrest. Indications: cardiac arrest Contraindications: none Side effects: none in prehospital setting Lidocaine Effects: Sodium Channel Blockade, inhibiting nerve conduction for pain, and delaying ventricular automaticity Dosage: V-tach/V-fib – 1mg/kg IV x1 IO needle pain – flush IO tubing with lidocaine and push through with first normal saline flush Indications – v-tach/v-fib, IO injection site pain Contraindications: allergy Side effects: complete heart block, ventricular arrest, seizures MARK I Kit Effects: Reverses the effects of organophosphate poisons Dosage : 1 kit, repeat in 5 min as needed Contains: Atropine 1mg 2-PAM Chloride 600mg Indications: organophosphate poisoning, WMD event Contraindications: none in this setting Side Effects: blurred vision, headache, dizziness, nausea, tachycardia Magnesium Sulfate Effect: relaxes smooth muscles in bronchioles, uterus, stabilizes cardiac membranes Dosage: 1-2 gm IV in adults over 20 minutes for asthma (medical control required), 1-2gm IV push for Torsades Indications: severe asthma, Torsades, preterm labor Contraindications: hypermagnesemia Side Effects: paralysis, respiratory depression Amiodarone Effect: Antiarrhythmic – multiple mechanisms Dosage: 150mg IV for V-tach, 300mg IV for V-fib arrest Indications: V-tach, V-fib Contraindications: allergy, AV block, pregnancy, breastfeeding Side Effects: lung fibrosis, AV block, Torsades with other QT prolonging medications Atropine Effect: antagonizes muscarinic receptors in parasympathetic nervous system Dosage: 0.5mg-1mg IV Indication: Symptomatic Bradycardia Contraindications: none Side Effects: dry mouth, tachycardia, jitteryness Hydroxocobalamin Effect: reverses cyanide toxicity by combining with cyanide to make Vitamin B12 Dosage:5gm IV Indications: cyanide Toxicity Contraindications: caution for hemodialysis patients Side Effects: none Tetracaine Effect: anaesthetizes eye nerve ending through sodium channel blockade Dosage: 1-2 gtts per eye, repeat PRN Indications: eye trauma Contraindications: allergy to agent, open globe Side Effects: increasing tearing. Burning Adenosine Effects: AV nodal blocking agent Dosage: 0.05-0.1mg/kg up to 6mg IV RAPID push, max 12mg Indications: SVT Contraindications: wide complex tachycardia with abberancy, WPW Side Effect: asystole (short lived), increased HR with WPW.