Sutter AIM Project Readmission HEN Presentation
advertisement

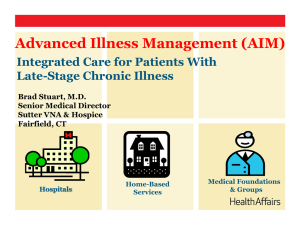
Advanced Illness Management Sutter Health Lois Cross RN BSN ACM Sutter Health crossl@sutterhealth.org Sutter Health Serving more than 100 cities and towns in Northern California & Hawaii with: • • • • • • • • • • • • 25 acute care hospitals (multiple facilities do transplants) 3 Patient Transfer Centers Ambulatory Surgery Centers Urgent Care Facilities & Care Centers 5,000 physician members of the Sutter Medical Network (5 Foundations, 4 IPAs) Approximately 48,000 employees Home health, hospice & long-term care services Medical research and training $2 million a week in charity care 5 Regions & 6 Boards of Directors Culturally diverse population Competitive environment w/ heavy Kaiser presence & multiple Academic centers A Missing Link? HF “Curative” Treatment COPD DM etc Advanced Illness Management (AIM) ? Comfort Care Goals of Program • Patient Centered • Evidence Based • Patient experience is important across time and all settings • Support patient that may be actively pursuing curative treatments • Coordinate care around patient’s goals to improve patient well being and quality of life • Reduce avoidable hospitalizations, ED visits • Reduce physician practice burden • Provide improved access to quality comprehensive end of life care for patient and family Key Elements – Patient (caregiver) Support – Individualized Care Plans • Patient-centered: patient’s care goals, that may change as illness progresses • Curative and comfort • Psychosocial and spiritual • Access to decision support & advice • Advance care planning – Care Coordination Across Health System • • • • • Team approach with providers PCP relationship is critical to success Coordinate care over an extended period of time Integrated with inpatient palliative care Data driven continuous improvement 5 Team Members • AIM Care Liaison • AIM Home Health Team RN/SW/PT/OT • Transitions Nurse • Office Based Case Manager 6 Changing the Focus of Care EHR • Patient Registry HOSPITALS • Emergency Dept. • Hospitalists • Inpatient palliative care • Case managers • Discharge planners 911 • Telesupport • Care Liaisons HOME-BASED SERVICES • Home health • Hospice MEDICAL OFFICES • Physicians • Office staff • Transitions Team • Case Managers • Telesupport New AIM staff & services CRITICAL EVENTS • Acute exacerbation • Pain crisis • Family anxiety AIM 2.0 Eligibility and Care Processes • Eligibility • Enrollment requires: – Identified PCP – Utilizes Sutter hospital or SMN physician • Clinical criteria: – End stage chronic illness, or – Would not be surprised at death in next 12 months, or – Clinical, functional, or nutritional decline, or – Eligible for hospice, but not ready • 5 Pillars of Care – “Red Flag” symptom management • Customized treatment + comfort care • Home crisis management plan – Medication management – Follow-up visits – Ongoing advance care planning – Personal health record Staff Training • • • • • • Pillars Symptom management Motivational Interviewing Teach Back Advanced Care Planning Cultural Issues 9 Outcome Measures • Adherence to model supports patient centered goals and evidence based practices – Measured in terms of completion of pillars at key times and places • Patient Experience – Engagement via crisis planning, use of personal health record, and satisfaction surveys. • Provider Experience- Satisfaction surveys; (Advisory Committee) • Utilization and cost of all health services – Hospital, physician, home health, hospice, snf, etc. • Improvement in number of referrals to and days of care provided by hospice to an AIM patient Program Evaluation Methodologies • Pre / Post utilization and cost data 30 days, 90 days, 180 days - quarterly • Comparative analysis with Dartmouth Atlas Data Base -quarterly • Comparative analysis with FFS Medicare non Sutter Health patient population – final results pending • Concurrent control group- under consideration Results- What do the trends look like? • Descriptive Statistics • Utilization Trends • Cost Trends General Description of Population Total Admissions Current Enrollees 1720 Diagnosis 44% Geriatric Frailty 39% Cancer 34% HF 19% COPD 16% Neurologic AIM LOS Median: 43 days Mean: 65.5 days Payer Mix* 51% Medicare FFS 21% Medicare Cap 12% Commercial FFS 8% MediCal 5% Dual Eligible Referral Source MD Office=37% Hospital= 35% SCH=24% ~320 54%: 2 or more conditions Advanced Illness Indicators 68% Hospice eligible 30% Self-rated health “poor” 31% Self-rated health “fair” *Exclusive category, no patient overlap 90-Day Pre/Post Utilization Summary % Reduction in Utilization Year 2 2011 Current Rolling 12 Months Q2 2011 to Q1 2012 Number of Patients Year 1 2010 Sacramento 181 229 170 Percent Change in Hospitalizations -58% -59% -62% Percent Change in ED Visits -38% -40% Number of Patients -14% Roseville* 64 270 194 Percent Change in Hospitalizations -33% -51% -52% Percent Change in ED Visits -17% 4% Number of Patients -23% Consolidated 245 499 364 Percent Change in Hospitalizations -53% -54% -56% Percent Change in ED Visits -16% -28% -21% 14 Hospital Care Intensity 90 Day Pre/Post AIM Enrollment Year 1 2010 Number of Patients Percent Change in ICU Days ALOS (Days) Number of Patients Percent Change in ICU Days ALOS (Days) Number of Patients Percent Change in ICU Days ALOS (Days) Year 2 2011 Sacramento 181 229 -81% -80% -1.8 -1.0 Roseville* 64 270 -25% -87% -1.0 -0.4 Consolidated 245 499 -75% -84% -1.6 -0.6 Current Rolling 12 Months Q2 2011 to Q1 2012 170 -100% -1.2 194 -25% 0.3 364 -81% -0.2 15 Medical Group Utilization Impact % Change in Utilization Year 1 2010 Year 2 2011 Current Rolling 12 Months Q2 2011 to Q1 2012 30-Day Number of Patients Percent Change in MD Visits # Percent Change in Telephone Encounters # 354 657 584 -24% -14.29% -15.95% 2% 27.56% 25.09% 245 499 364 -19% -3.95% -3.88% 16% 26.24% 29.29% 178 322 219 -12% -5.10% -1.39% 16% 36.24% 41.13% 90-Day Number of Patients Percent Change in MD Visits # Percent Change in Telephone Encounters # 180-Day Number of Patients Percent Change in MD Visits # Percent Change in Telephone Encounters # 16 Dartmouth Atlas Comparison (External and Historical Benchmarking) 35 Sutter Sacram ento 15 20 25 30 Before AIM Q1 2012 10 Sutter Ros eville 5 Interm ountain Health Care AIM Pilot 0 Hospital days per decedent, last six months of life Hospital Days Per Decedent Last 6 Months of Life 2010- Q1 2012 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 Year of death 17 40 Before AIM 30 Sutter Ros eville 20 Sutter Sacram ento 10 Interm ountain Health Care (2003 - 2007 average) AIM Pilot Q1 2012 0 Physician visits per decedent, last six months of life Dartmouth Atlas Comparison (External and Historical Benchmarking) Physician Visits Per Decedent Last 6 Months of Life 2010-Q1 2012 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 Year of death 18 AIM 2.0 Financial Impact Current Roling 12 months 2010 2011 Q1 2011-Q12012 Net Impact Net Impact Net Impact Payers (Hospital, MD Visits, Home Care) Number of Patients Charges Billed to Payers Charges Billed to Payers per Patient Hospital Costs Hospital Costs Per Patient All Costs All Costs Per Patient 245 499 364 ($842,489) ($2,457,651) ($1,848,342) ($3,439) ($4,925) ($5,078) Hospital Portion ( Inpt., ED, Obs) ($1,568,712) ($2,935,567) ($2,122,709) ($6,403) ($5,883) ($5,832) Sutter Total Costs (Hospital, Physician Visits, Home Health, Hospice, Unreimbursed AIM) ($966,470) ($1,435,907) ($815,918) ($3,945) ($2,878) ($2,242) Opportunities Infrastructure • Every geographic area looks different • Incorporating other agencies/hospitals Hiring the right team members Physician Engagement Reports Education IT-Just In Time communication • EPIC • Home Care Home Base Team Integration 20