VSPER Structures - Riverside Local School District
advertisement
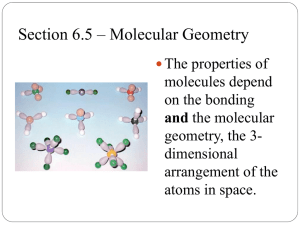
VSPER Structures Chapter 6 Section 5 Molecular Geometry Help to determine the properties of molecules Molecular polarity- the uneven distribution of molecular charge VSPER Theory • “valence shell, electron pair repulsion” • Repulsion between the sets of valence- level electrons surrounding an atom causes these sets to be orientated as far apart as possible Using VSPER Theory • Step one- Draw the Lewis Dot structure for the compound CBr • Step two- Be sure to arrange the atoms so they are the farthest distance apart 4 VSPER and Molecular Geometry Molecular Shape: Linear Atoms bonded to the central atom: 2 Lone pair of electrons: 0 Type of molecule: AB2 Example Formula: Carbon Dioxide VSPER and Molecular Geometry Molecular Shape: Bent Atoms bonded to the central atom: 2 Lone pairs of electrons: 1 Type of Molecule: AB2E Example: Water VSPER and Molecular Geometry Molecular Shape: Trigonalplanar Atoms bonded to central atom: 3 Lone Pairs of electrons: 0 Type of molecule: AB3 Example: AlCl3 VSPER and Molecular Geometry Molecular Shape: Tetrahedral Atoms bonded to central atom: 4 Lone Pairs of electrons: 0 Type of molecule: AB4 Example: CH4 VSPER and Molecular Geometry Molecular Shape: Trigonal-pyramidal Atoms bonded to central atom: 3 Lone Pairs of electrons: 1 Type of molecule: AB3E Example:PH3 VSPER and Molecular Geometry • • • • • Molecular Shape: Trigonal-bipyramidal Atoms bonded to central atom: 5 Lone Pairs of electrons: 0 Type of molecule: AB5 Example: NbBr5 VSPER and Molecular Geometry Molecular Shape: Octahedral Atoms bonded to central atom: 6 Lone Pairs of electrons: 0 Type of molecule: AB6 Example: SF6