Atomic Theory: History, Models, and Particles
advertisement

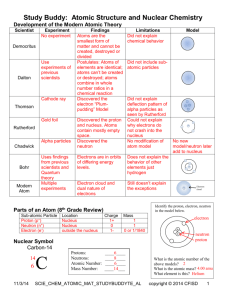
John Dalton William Crookes J.J. Thomson Ernest Rutherford ATOMS Early Theories About ATOMS Ancient Greeks- 4 Materials: (2500 years ago) -Earth -Fire -Air -Water -Ex. Wood= Earth+Fire Early Theories About ATOMS Democritus (Greek thinker) – All matter is made up of Atoms “Cannot be divided” solid spheres(No one believed him) (930 BC) 1808 John Dalton -Proved that matter is made up of Atoms - Different elements have different masses 1808 - John Dalton (By putting substances together to form new substances and taking them apart chemists discovered that ALL matter is made of elements) -Element – matter made of atoms of only one kind (periodic table of elements) 1870 - William Crookes -Used a cathode ray tube to show streams of particles 1897 - J.J. Thomson -Discovered the Electron (opposite side) - Bent Crookes stream with a magnet did this with many gases and many elements Plum Pudding model http://www.aip.org/history/electron/jjsound.htm -The Nuclear Atomic Model 1911 - Ernest Rutherford Used by modern scientists 1911 - Ernest Rutherford -The Nucleus – the small central core of an atom where most of the mass is located -protons & neutrons - positive charge -(electrons found in a cloud around it) Electron Cloud - -Region around the nucleus in which the electrons travel Dalton Thomson Rutherford Dalton Thomson Rutherford Atomic Particles-The basic building blocks of atoms Particle charge found Electron - negative outside nucleus Proton + positive inside nucleus Neutron No charge inside nucleus Proton Neutron Electron Size of Atomic Particles-Sooooo small that scientists use: Atomic Mass Unit (u) – A unit used to express the masses of atomic particles and atoms (1u=1.66 x 10-27Kg) Electron Proton Neutron 0 u (1/1836) 1u 1 u (1837/1836) Scientific Models -Used when objects can’t be studied directly Ex. Stars, Atoms -Many experiments -(how do atoms behave under different conditions) Atomic Number - The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Element #of protons # of electrons Hydrogen 1 1 Oxygen 8 8 Sulfur 16 16 Gold 79 79 In a normal atom positive charges (proton) cancel out negative charges (electrons) Electrons in motion 1913 –Niels Bohr – electrons can follow only certain orbits Electron Arrangement Energy Level – A region around an atomic nucleus in which electrons move Ex. He + Ex. C Nucleus 2 8 18 32 + Symbols of Elements - Berzelius (Swedish Scientist) Atomic Symbol – 1 or 2 letters used to represent an atom of an element 1st letter – ALWAYS CAPITALIZED 2nd letter (if there is one) – ALWAYS lower case - Based on the element name (sometimes the Latin name) The Periodic Table of Elements Symbols of Elements Hydrogen 1 H 1.008 Name of Element Atomic Number Symbol Atomic Mass The Number of Particles in a Nucleus Protons = Electrons Mass Number = Protons + Neutrons Mass Number – The sum of the protons and Neutrons in an atom (different atoms have different mass #’s) Element Atomic Mass # Proton Neutron Electron # # # # Lithium 3 7 3 4 3 Boron 5 11 5 6 5 Nitrogen 7 14 7 7 7 10 20 10 10 10 Neon Isotopes- Atoms whose nuclei contain the same # of protons, but different #s of Neutrons Ex. Hydrogen-1, Hydrogen-2, Hydrogen-3 (deuterium) (tritium) + + + Atomic Mass- The average of all the masses of the isotopes of a particular element -Round to the nearest whole #= Mass #