Radioactive Decay
advertisement

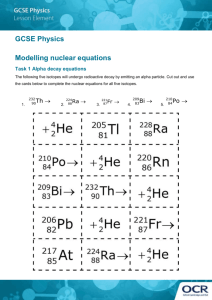
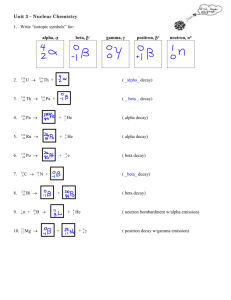
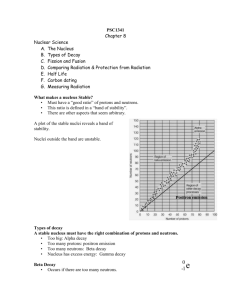
Radioactive Decay Radioactive Decay Radioactive Decay: • Some unstable atoms try to regain stability by losing energy. They lose energy by emitting radiation. • These elements continue to undergo radioactive decay until they are stable Radioisotopes: Types of isotopes are capable of radioactive decay Stable versus Unstable • Stable: not likely to decay • Unstable: will decay eventually • Different Isotopes have different degrees of stability Eg. Carbon-12 = Stable Carbon-13 = Stable Carbon-14 = Unstable All three are found in the human body Three Types of Radiation Alpha Radiation: A stream of alpha particles Alpha Particles: positively charged atomic particles. The largest of the three types What is it made of: The alpha particle is made of the same particles as a helium atom (2 protons, 2 neutrons) Equations for alpha decay Equations where atoms lose alpha particles - Three Types of Radiation Beta Radiation: Caused by the flow of beta particles Beta Particle: an electron During Beta Decay: A neutron becomes a proton and an electron. This proton stays in the nucleus while the electron leaves Equations for beta decay • p Equations for beta decay • p Three Types of Radiation Gamma Radiation: Rays of high energy, short wavelength radiation. Has almost no charge and no mass. Gamma Decay: The redistribution of energy within the nucleus. Equations for gamma decay Equations for gamma decay