Chapter 4
advertisement

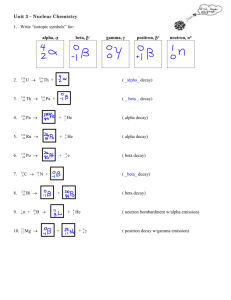
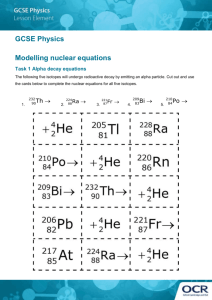
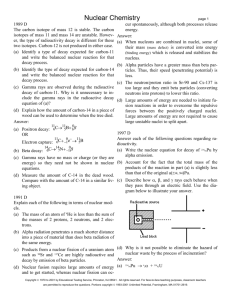
Chemistry for Changing Times, 11th edition John W. Hill and Doris K. Kolb Chapter 4: Nuclear Chemistry: The Heart of the Matter James A. Noblet California State University San Bernardino, CA 2007 Prentice Hall Most of our exposure to ionizing radiation is from natural sources, the majority of which is due to this element: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Radium Uranium Radon Plutonium Carbon-14 Most of our exposure to ionizing radiation is from natural sources, the majority of which is due to this element: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Radium Uranium Radon Plutonium Carbon-14 When an electron is emitted during a radioactive decay process, it is referred to as: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Alpha decay Beta decay Gamma decay Delta decay Sigma decay When an electron is emitted during a radioactive decay process, it is referred to as: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Alpha decay Beta decay Gamma decay Delta decay Sigma decay Which of the following types of radiation has the greatest penetrating power? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Alpha Beta Ultraviolet X-ray Gamma Which of the following types of radiation has the greatest penetrating power? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Alpha Beta Ultraviolet X-ray Gamma If you have 16 g of a radioactive isotope, how much will be left after three half-lives? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1g 2g 4g 6g 8g If you have 16 g of a radioactive isotope, how much will be left after three half-lives? 1 general formula n , 2 w heren no. of half - lives 1 1 1 1 1 3 2 2 2 2 8 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1g 2g 4g 6g 8g The nuclear reaction transforming gold-179 into iridium-175 is an example of what type of decay? 179 79 Au Ir ? 175 77 1. Alpha 2. Beta 3. Gamma 4. Positron 5. Electron capture The nuclear reaction transforming gold-179 into iridium-175 is an example of what type of decay? 179 79 Au Ir He 175 77 4 2 1. Alpha 2. Beta 3. Gamma 4. Positron 5. Electron capture