File

By the end of this unit:
You will be able to demonstrate that you have developed the ability to:
Derive the equation y = mx + b for a line given two distinct non-vertical points
(8.EE.5)
Derive the equation y = mx + b for line through the origin and the equation y = mx + b for a line intersecting the vertical axis at b
(8.EE.6)
Explain why the slope m is the same between any two distinct points on a non-vertical line in the coordinate plane using similar triangles
(8.EE.6)
Slope of a Line:
In skiing, slope refers to a slanted mountain side.
The steeper the slope is, the higher its difficulty rating will be. In math, slope defines the “slant” of a line. The larger the absolute value of the slope is, the “steeper”, or more vertical the line will be.
Slope
Notes
Linear Equations:
Linear equations have constant slope
For a line on a coordinate plane, to find the slope we use the ratio: rise over run
Rise is the number of units moved up or down
Run is the number of units moved right or left
Slope can be… positive negative zero undefined
Mr. Slope
https://www.youtube.com/w atch?feature=player_embedd ed&v=JLxA2v0pjKY
The slope is… positive
The slope is… negative
The slope is… zero
The slope is… undefined
SLOPE
FOLDABLE
Exploring
Slope -
Climbing
Stairs
Using Slope and
Intercepts
X – Intercept
Where the line crosses the x-axis
Y = 0
y – Intercept
Where the line crosses the y-axis
X = 0
Slope Intercept Form
Slope
Intercept Form
Foldable
HTTP://MATHEQUALSLOVE.BL
OGSPOT.COM/2012/11/NEW-
YMXB-FOLDABLE.HTML
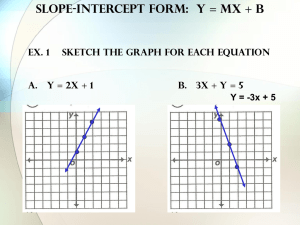
Slope Intercept Form
Y = m x + b