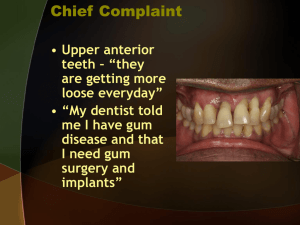
ANTERIOR TOOTH
SELECTION
SIZE OF THE TEETH
• Selection of the size and the teeth is a
problem in three dimension .
• First we have to consider whether to use
porcelain or acrylic teeth.
SIZE OF THE FACE
• The average width of the maxillary central
incisor is estimated to be one sixteenth of
the face measured between the zygoma.
• The size of the maxillary central incisor is
important for they are the most prominent
teeth in arch as individual is viewed from
frontal position.
• “the tribute tooth indicator” is useful in
determining the maxillary central incisor.
SIZE OF THE MAXILLARY ARCH
• The mold selector can be used to make
measurement of the maxillary cast.
• Accurately contoured occlusion rims are
required
• The mold selector is used in the selection of
anterior teeth .The measurments are made from
the midline on the maxillary occlusion rim to the
distal of the cuspid eminence
• Measure the distance from the distal of one
cuspid eminence to the distal of the other with a
flexible.
MAXILLARY MANDIBULAR
RELATION
• Any disproption in size between thr
maxillary and mandibular arches influence
the length, width, and the position of the
teeth.
• In instances of protruded mandible, the
mandibular anterior teeth are frequently
larger than normal. If the mandible are
retruded the mandibular anterior teeth are
frequently smaller.
INCISAL PAPPILAE & THE
CUSPID EMINENCE OR THE
BUCCAL FRENUM
• If the cuspid eminence are visible, a line can be
placed on the cast at the distal termination of the
eminence.
• If the cuspid eminence are not visible the
attachment of the buccal frenum can be used. A
line placed slightly anterior to the frenum
attachment will be distal of the eminence.
• Measure the distance from the distal of one
cuspid eminence to the distal of the other with a
flexible.
CONTOUR OF THE RESIDUAL
RIDGE
• The artificial teeth should be placed to
follow the contour of the residual ridges
that existed when the natural teeth were
present.
• The loss of contour as a result of
resorption, accident or surgery makes this
a difficult task.
THE VERTICAL DISTANCE
BETWEEN THE RIDGES
• The length of the teeth is determined by
the available space between the existing
ridges.
• When the space is available, it is more
esthetically acceptable to use a tooth long
enough to eliminate the display of the
denture base
THE LIP
• When the lips are relaxed and apart the
labial surface of the maxillary anterior
teeth support the upper lip.
• The incisal edge extends inferior to or
slightly below the lip margin.
Length
• The length of the upper six anterior teeth
is normally such that the neck of the teeth
will overlap the anterior ridge by 2-3mm
• Cervically up the incisive edges of the
centrals will show below the relaxed lip.
HARMONY
• The face length is taken from supra orbital
ridge line to inferior border of the chin.
• Breadth is the distance between the
zygomatic process
• The length is greater than width would
indicate teeth of htose proportions,
irrespective of their shape.
BERRY’S BIOMETRIC INDEX
• Used to derive the length of central incisor
using zygomatic width or the length of the
face.
• Width of the maxillary central
incisor=zygomatic width/ 16
=length of the face/20
POUNDERS FORMULA
• To determine the length and width of
central incisor using the zygomatic width
and length of face respectively.
WIDTH
• Most satisfactory way of selecting teeth
width
• Choose a set which are wide enough to
allow the canines to be mounted on the
canine eminence when set up.
GOLDEN PREPORTION
• G.P for each patient is measured as follows
• The width of the central incisor was multiplied by
62% and compared with the width of central
incisor is in G.P to the width of lateral incisor.
• In comparing with the width of lateral incisor
multiplied by 62% with the width of adjacent
canine it can be determined if the width of lateral
incisor is in golden proportion to the width of
canine.
PHYSIOLOGICAL
• The facial musculature contributes to
esthetics of the patient
• Increasing the thickness of the denture
base in the labial and the buccal sulci can
produce a puffy appearance.
PSYCHOLOGICAL
• A patient with a +ve self evaluation shows
a broad smile up the one width a negative
self evaluation shows a tight lipped small
smile
• The campers line the psychological plane
of orientation
BIOMECHANICAL
• The teeth should be placed such that they
fulfil the biomechanics of the denture.
• The teeth should be set in the neutral
zone.
COLOUR OR SHADE
• Colour is described by means of
• hue
• Chrome
• Value
FORM OF THE ANTERIOR TEETH
•
The form of the teeth should be coformed to
contour of the face as considered from the
labial, mesial, distal and incisal aspect
• The general outline of the tooth should
conform to the general outline of the face when
viewed from frontal aspect.
• Three factors are used as guides in the
selection of anterior teeth for form.
1. Sex
2. The form and contour of the face
3. Age
THE FORM AND CONTOUR OF
THE FACE
•
According to Leon Willians classification
face
• Three types
1. Square
2. Tapering
3. Ovoid
SEX
• Dentogenic concept : sex, personality, age
, are the factors which determine the form
of anterior tooth