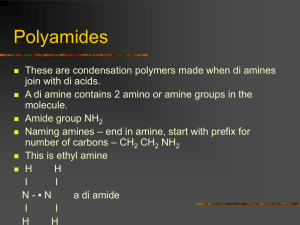
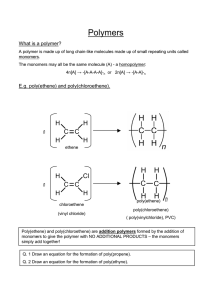
Plastics & Synthetic Fibres: Chemistry Presentation
advertisement

Plastics and Synthetic Fibres Intermediate 2 Chemistry Unit 2(d) Examples of plastics Examples of plastics • • • • • • • • Polythene [poly(ethene)] Polystyrene Perspex PVC Nylon Bakelite Formica Silicones PVC [poly(vinyl chloride)] Nylon Bakelite Formica Silicones Where do plastics come from? • Crude oil – Fractional distillation – Cracking • Alkenes Uses related to properties • • • • Flexible Watertight Shatter-proof Light Non-biodegradable • Can’t be broken down by living things. • “Biopol” is a recently developed biodegradable plastic. Other problems with plastics • Low density • Durable • Burn or smoulder to give off toxic fumes – Carbon monoxide – Hydrogen chloride – Hydrogen cyanide Types of plastic • Thermoplastic – Can be reshaped on heating • Thermosetting plastic – Cannot be reshaped on heating Chemistry of plastics • Plastics are examples of polymers – These are long chain molecules made from smaller molecules joining together • These smaller molecules are called monomers • There are two types of polymer: – Addition polymer – Condensation polymer Addition polymers Addition polymers • Like all polymers, these are made from monomers. • For an addition polymer, these monomers always have a C=C • These join together in a reaction called addition polymerisation. – view animation 1 2 + 3 1 2 … + … … … MONOMERS 3 POLYMERS 1 … H C H 2 H C H + H C H 3 H C H + MONOMERS H C H 1 H C H … H C H 2 H H H H C C C C H H H H POLYMERS 3 H C H Naming polymers • The name of the polymer is made by taking the name of the monomer, putting brackets around it, and adding “poly” in front – Poly(ethene) is made from ethene; – Poly(vinyl chloride) is made from vinyl chloride. Naming practice • Name the polymer made from: – Propene – Chloroethene • Name the monomer used to make: – Poly(heptene) – Poly(phenylethene) Drawing polymers, monomers and the repeating unit C=C H H C6H5 H H H C6H5 H H H C6H5 H Poly(phenylethene) Condensation polymers • What type of molecule is produced from an alkanol and alkanoic acid? – Esters • Polyesters are made from similar molecules. Polyesters Monomers • Must have two functional groups per molecule – For polyesters, they are a diol and a diacid OH OH C CH 2 CH 2 OH O C C CH 2 CH 2 O O C O O CH 2 O CH 2 HO O O Condensation polymerisation • The joining up of two molecules, producing water, is condensation. • Because giant molecules are made, this is condensation polymerisation. • Specifically with a diol and a diacid, a polyester is produced. Polyamides • Are produced when an amine group reacts with a carboxyl group. Amides • Formed when an amine reacts with an alkanoic acid. H N O C H OH R amine R 1 carboxylic acid R H O N C amide An AMIDE group R 1 Polyamides • Are condensation polymers. • Formed when a diamine reacts with a diacid. Recently developed plastics • Kevlar – Very strong • Poly(ethenol) – Water soluble • Biopol – Biodegradable Kevlar Kevlar Poly(ethenol) Poly(ethenol)