Appendicular Skeleton- Hind Limb
•
Connected to the axial skeleton at sacroiliac joint
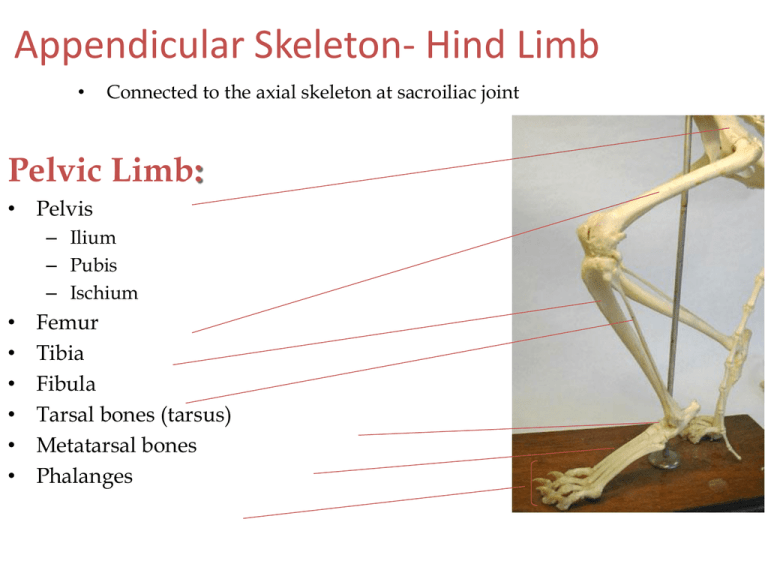
Pelvic Limb:
• Pelvis
– Ilium
– Pubis
– Ischium
•
•
•
•
•
•
Femur
Tibia
Fibula
Tarsal bones (tarsus)
Metatarsal bones
Phalanges
• May be referred to as the os coxae
• Develops as three separate bones on each
side that fuse into a solid structure.
• 2 sides halves join at the pelvic
______________.
• Socket of ball and socket joint is the
______________.
• Bones are:
– _____________
• Cranial most bone of pelvis
• “Wings of the ilium” or hips in
dogs and cats.
• Tuber coxae are “points of the hip”
in cattle and horses
– _____________
• Most caudal pelvic bone
• Tailbone is ischial tuberosity.
– _____________
• Smallest of the pelvic bones
Pelvis
Femur
• Long Bone of thigh
• Articulates proximally with the ___________
and distally with the ___________ and
____________
• On proximal end is the ball portion of ball
and socket joint, called the head.
• Proximal end also contains the greater
_______________ where muscles attach.
• Distal end contains the medial and lateral
condyles which form the _____________
(knee)
– The trochlea is at the distal end in between the
condyles and contains a groove that the patella
fits in.
– Like the humerus, there are palpable medial
and lateral epicondyles
• Kneecap is largest ___________ bone in the body.
• Formed in the distal tendon of the ____________ femoris
muscle on the cranial aspect of the stifle joint.
• Helps to protect tendon as it passes down over the trochlea of
the femur.
• Patellar luxation: when trochlear groove is not deep enough to
contain patella so it slips in and out of place.
–
–
–
–
Usually will cause brief episodes of lameness which can correct.
May hear or feel “popping” in and out of place.
Found in small, toy breeds most prevalently.
Can be surgically corrected.
Patella
Fabellae
• Two small __________ bones located in
the proximal gastrocnemius (calf muscle).
– Located cranial to the femoral condyles.
• Not present in cattle or horses.
• Main weight bearing bone of the
lower leg (shinbone).
• Forms stifle joint proximally with
femur.
• Forms ___________ (ankle) distally
with tarsal bones.
• Tibial _______________ continues
distally down the femur as the tibial
crest.
– Where patellar tendon attaches.
• Medial __________ is medial to
distal articular surface and is called
“knob” of ankle.
Tibia
Fibula
• Consists of proximal extremity, shaft, and
distal extremity.
• Does not support significant weight.
• Thin, but complete, in dogs and cats.
Horses and cattle do not have shaft of
fibula.
• Forms lateral ____________ at distal end.
• aka ankle or “hock”
• Consists of two rows of tarsal bones
(similar to carpal bones in wrist).
– Proximal row is named and distal row is
numbered.
– Proximal row: tibial tarsal (with
____________), fibular tarsal (with
____________), and central tarsal bone
• Calcaneal tuberosity forms the point
of the hock. Site of attachment for
tendon of the gastrocnemius muscle (aka
___________ tendon)
Tarsal Bones
Metatarsal
Bones
• Almost identical to
metacarpals
– exception: dogs and
cats usually only
have metatarsals II –
V
• Horses/Cattle same
as front leg.
Almost identical to
phalanges on
thoracic limb
exception: dogs and
cats usually only
have digits II – V
Horses/Cattle
same as front leg.
• Bones that form in soft organs (__________)
• Are not found in every animal
• Examples
– os cordis: in heart of cattle and sheep that supports the valves
– os penis: in penis of dogs, beaver, raccoons, and walruses that partially
surrounds the urethra
– os rostri: in nose of swine that strengthens snout for rooting/digging
Visceral Skeleton
• Junctions between bones
• Can be moveable or immovable.
• Arthro and articular refer to joints.
Joints
• 3 Types of joints:
– Fibrous Joints (____arthroses)
• Immovable; joined by fibrous tissue
• Found in sutures of skull bones,
splint bones in horses
– Cartilaginous Joints (_______arthroses)
• Slightly moveable; rocking motion
• Vertebral disks between vertebrae,
Pelvic and mandibular symphisis
– Synovial Joints (___arthroses)
• Freely moveable
• Shoulder, stifle, elbow, etc
Characteristics of Synovial Joints
– Have Articular surfaces on
bones
• Articular (__________) cartilage
covering articular surfaces
– Fluid-filled joint cavity (joint
space)
– Enclosed by a joint
____________
• Synovial membrane- outer
membrane that produces:
– Synovial fluid- lubricates joint
surfaces
– Ligaments – fibrous
(__________) connective tissue
that join bones to other bones.
Synovial Joint Movements
• Flexion and Extension
– Opposite movements
– Increase (extension) or decrease (flexion)
angle between two bones
• Adduction and Abduction
– Opposite movements
– Move an extremity toward (Adduction) or
away from (Abduction) medial plane
• Rotation
– Twisting movement of a part on its own
axis
• Circumduction
– Movement of an extremity so that the
distal end moves in a circle
Types of Synovial Joints
•
Hinge Joints
– One joint surface swivels around another
– Only capable of flexion and extension
•
Gliding Joints
– Rocking motion of one joint surface
on another
– Primarily capable of flexion and
extension
– Abduction and adduction possible in
humans not dogs/cats
•
Pivot Joints
– One bone pivots (rotates) on another
– Only capable of rotation
•
Ball-and-socket joints
– Allow for all joint movements










