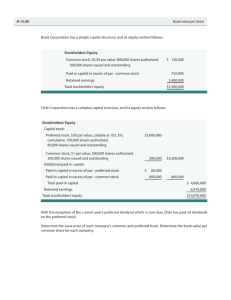
Corporation –an artificial being created by operation of law having
advertisement

Corporation –an artificial being created by operation of law having the right of succession and the powers, attributes and properties expressly authorized by law or incident to its existence. ARTIFICIAL BEING LEGAL PERSONALITY RIGHT OF SUCCESSION CORPORATE OWNERSHIP LIMITED LAIBILITY TRANSFERABILITY OF INTEREST Distinctions between Partnership and Corporation • Corporation 1.Created by law 2. Requires at least 5 incor porators to be organized Partnership created by mere agreement of the parties may be organized by only 2 3. Capital raising ability is limited By the profitableness in which Funds of stockholders are employed capital raising ability is limited by the # of partners 4. Creditors of corp cannot claim the personal assets General partners have unlimited liability of the stockholders 5. There is continuity of business life. 6. Can only be dissolved with the consent of the state It has a limited life. May be dissolved at any time by the will of the any or all the partners Advantages…. greater amount of capital Limited liability Transferability of shares of stocks Continous existence Centralized management Standard creation Disadvantages …. • Subject to governmental control and supervision • Heavy taxation • It is more costly to organize • Complicated formation • Stockholders have little voice in the conduct of the business Types of Corporation Public corporation Private corporation Stock corp and non – stock corp Government Owned or Controlled Corp Domestic Foreign Close Open Kinds of Stocks AS to value Par Value – one which has a fixed valuemstated on the certificate of stock and in the articles of incorporation. No Par Value - one without a designed value stated in the stock cerificate but it can not be sold at less than P5.00 as provided in the Corporatin Code of the Philippines. As to Right….. • Common stock – an ordinary stock issued by a corporation entitling the owner to a pro rata dividend without priority or preference over any other stockholders. • Preferred Stock – a class of stock with preferential rights or claims over the common stock Legal capital – refers to the minimum permanent investment which can not be distributed to the stockholders in the lifetime of the corporation. This is called the TRUST FUND DOCTRINE/ Illustration ! ! ! • X Corp issued 1,000 shares of stock with a par value of P100 in exchange for P120,000 cash. • X Corp issued 1,000 shares of no par value stock in exchange for P120,000 cash. Rights of the Stockholders Right to share in the corporate profits at the discretion of the Board of Directors Right to vote and to attend annual stockholders’ meetings Right to share in the distribution of assets upon liquidation of the business Right to purchase additional shares of stock whenever there is an increase in the authorized capital stock. This is called pre-emptive right Incorporation Requirement: • The law permits any number of natural persons, not less than 5 and not more than 15, to form a private corporation. • At least 25% of the authorized capital stock must be subscribed and at least 25% of these subscriptions must be paid. Note: the corp code does not mention any minimum authorized number of shares for as long as the paid up capital is not less than P5,000. • A corporation should file its Articles of Incorporation with the SEC, duly signed and acknowledged by all incorporators . Terms to Remember Authorized Capital Stock –represents the maximum # of shares or amount the corporation may issue a stated in the articles of incorporation approved by the SEC. • Stock Subscription- an agreement to purchase stock and states the number of shares being subscribed, the subscription price, term of payment and call dates. • Capital Stock – this represents the amount paid in by the stockholders whether in cash , property or service and for which a certificate of stock is issued as evidence of stock ownership. Certificate of Stock – a written evidence of the holder’s ownership of shares. • Unissued Capital Stock – difference between the authorized capital stock and the outstanding capital stock. • Subscsription Receivable - amount of contract price collectible from the subscriber. • Paid up Capital Stock – the portion of the subscribed or outstanding capital stock that is paid. Accounting for stock transaction! • Authorization – recording the maximum number of shares corp is authorized to issue. This is called authorized capital stock. a • Sale – when a SH buys and pays immediately in full, the stocks are considered sold and a stock certificate is issued. • Subscription –a subscriber enters into a contract to buy a number of shares . A down payment is usually required with the balance payable on fixed dates. • Collection of subscription – the subscription may be paid by the stockholders in cash property, service or in the form of business. • Issuance of Certificate – issued once subscription is fully paid. 2 methods of recording • Memorandum entry method • Journal entry method Things to remember! • Asset contributions may be in the form of cash, property, or service • Properties must be recorded at its fair market value or the fair market value of the stock to be issued whichever is clearly determinable • Services must be recorded at its billed price • Capital stock and Subscribed Capital Stock must be recorded at the par value. Stocks are issued only when the stocks are fully paid for