Work and Energy: Physics Presentation on Work
advertisement

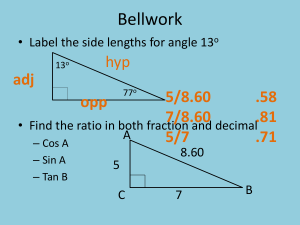
Work and Energy Section 1 Unit 3 Lesson 1: Work Goals: •Recognize the difference between the scientific and ordinary definitions of work. •Define work by relating it to force and displacement. •Identify where work is being performed in a variety of situations. •Calculate the net work done when many forces are applied to an object. Work and Energy Section 1 Bellringer • List five examples of things you have done in the last year that you would consider work. • Based on these examples, how do you define work? Work and Energy Section 1 Work • Work is done on an object when a force causes a displacement of the object. • Work is done only when components of a force are parallel to a displacement. Work and Energy Section 1 Work • In physics, work is the magnitude of the force (F) times the magnitude of the displacement (d) in the same direction as the force. • W = Fd • What are the SI units for work? – Force units (N) distance units (m) – N•m are also called joules (J). • How much work is 1 joule? – Lift an apple weighing about 1 N from the floor to the desk, a distance of about 1 m. Work and Energy Work Section 1 • Pushing this car is work because F and d are in the same direction. • Why aren’t the following tasks considered work? – A student holds a heavy chair at arm’s length for several minutes. – A student carries a bucket of water along a horizontal path while walking at a constant velocity. Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A 20.0 kg suitcase is raised 3.0 m above a platform by a conveyor belt. How much work is done on the suitcase? Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A 20.0 kg suitcase is raised 3.0 m above a platform by a conveyor belt. How much work is done on the suitcase? • 5.9 x 102 J Work and Energy Work • How would you calculate the work in this case? – What is the component of F in the direction of d? • F cos – If the angle is 90°, what is the component of F in the direction of d? • F cos 90° = 0 – If the angle is 0°, what is the component of F in the direction of d? • F cos 0° = F Section 1 Work and Energy Work Section 1 Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • How much work is done on a vacuum cleaner pulled 3.0 m by a force of 50.0 N at an angle of 30.0O above the horizontal? Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • How much work is done on a vacuum cleaner pulled 3.0 m by a force of 50.0 N at an angle of 30.0O above the horizontal? • 130 J Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A tugboat pulls a ship with a constant net horizontal force of 5.00 x 103 N and causes the ship to move through a harbor. How much work is done on the ship if it moves a distance of 3.00 km? Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A tugboat pulls a ship with a constant net horizontal force of 5.00 x 103 N and causes the ship to move through a harbor. How much work is done on the ship if it moves a distance of 3.00 km? • 1.50 x 107 J Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A weight lifter lifts a set of weights a vertical distance of 2.00 m. If a constant net force of 350 N is exerted on the weights, what is the net work done on the weights? Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A weight lifter lifts a set of weights a vertical distance of 2.00 m. If a constant net force of 350 N is exerted on the weights, what is the net work done on the weights? • 7.0 x 102 J Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A shopper in a supermarket pushes a cart with a force of 35 N directed at an angle of 25O downward from the horizontal. Find the work done by the shopper on the cart as the shopper moves along a 50.0 m length of aisle. Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A shopper in a supermarket pushes a cart with a force of 35 N directed at an angle of 25O downward from the horizontal. Find the work done by the shopper on the cart as the shopper moves along a 50.0 m length of aisle. • 1.6 x 103 J Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • If 2.0 J of work is done in raising a 180 g apple, how far is it lifted? Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • If 2.0 J of work is done in raising a 180 g apple, how far is it lifted? • 1.1 m Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A bumble bee has a mass of about 0.3 grams. Suppose the bee does 0.04 J of work against gravity, so that it ascends straight up with a net acceleration of 1.0 m/s2. How far up does it move? Work and Energy Section 1 Practice Problem • A bumble bee has a mass of about 0.3 grams. Suppose the bee does 0.04 J of work against gravity, so that it ascends straight up with a net acceleration of 1.0 m/s2. How far up does it move? • Answer Work and Energy Work is a Scalar Section 1 • Work can be positive or negative but does not have a direction. • What is the angle between F and d in each case? Work and Energy Section 1 Homework Due Next Class Work and Energy Section 1 Ticket Out • Determine whether work is being done in each of the following examples a. A train engine pulling a loaded boxcar initially at rest. b. A tug of war that is evenly matched c. A crane lifting a car • Choose one of the examples above and explain your answer.