Investing in Stocks Chapter Sixteen

Investing in Bonds
Objectives
Describe bonds and how they are used by corporations and investors.
Describe the major characteristics of bonds.
Differentiate among the four general types of bonds.
Objectives
Describe what the investor should consider before investing in bonds, particularly the current yield and yield to maturity.
List the advantages and disadvantages of investing in bonds.
Descriptive Terms for Bond Features
., REVIEW BOOK: Personal Finance.
Retrieved Oct 1, 2009 from http://www.flatworldknowledge.com/node/50890
.
Language of Bond Investing
Registered and bearer
Zero-coupon
Callable
Warrants
Convertibility
Language of Bond Investing
Indenture
Face value, coupon rate, maturity date
Secured and unsecured
Senior and subordinated
Interest Income
Assume you purchase $1,000 corporate bond issued by AT&T Corporation. The interest rate for this bond is 6.70%. The annual interest is $67 as shown below:
Dollar amount of annual return = Face value x interest rate
= 1,000 x 6.7%
= 1,000 x .067
= $67.00
Types of Bonds
Corporate bonds
U.S. government securities
Treasury bills, notes, and bonds
Federal agency issues
Municipal Bonds
Approximate Bond Value
Assume you purchase a Verizon Communications bond that pays 5.5% interest based on a face value of $1,000 until maturity in 2017. Also assume new corporate bond issues of comparable quality are currently paying 7%. The approximate market value of your Verizon bond is $786 calculated as follows:
Dollar amount of annual interest = $1,000 x 5.5% = $55
Approximate market value = Dollar amount of annual interest
Comparable interest rate
= $55
7%
= $786
Current Yield
Current yield = current annual income current market price
= $55
$786
= 7%
State and Local Government
Securities
Municipal Bonds
General Obligation Bonds
Revenue Bonds
Effective Yield of a Tax-Free
Investment
Not paying tax effectively increases your rate of return
you get to keep all of your profits, instead of only a portion
1 r
taxbracket
100
Example: 28% tax bracket, 5% rate of return
.
05
1
.
28
100
= 6.94%
What is the Yield or Rate of Return on a
Financial Investment?
Annualized Percentage Change:
1
new
old old
1 n
1
100
Example: original price=$20/share, current price=$100/share, stock held for 9 years
Comparison of Taxable vs Tax
Exempt Investments
Tax-
Exempt
Yield
4%
5%
6%
7%
15%
Tax
Rate
25%
Tax
Rate
28%
Tax
Rate
33%
Tax
Rate
35%
Tax
Rate
4.71% 5.33% 5.56% 5.97% 6.15%
5.88% 6.67% 6.94% 7.46% 7.69%
7.06% 8.00% 8.33% 8.96% 9.23%
8.24% 9.33% 9.72% 10.45% 10.77%
What is the Yield or Rate of Return on a
Financial Investment?
1
100
20
20
1
9
1
100
=19.58%
Bond Price Calculation
Assume that a bond has a price quote of 84. The actual price for the bond is $840, as calculated below:
Bond price = Face value (usually $1,000) x bond quote
= $1,000 x 84 percent
= $1,000 x .84
= $840
Bond Ratings
A plus sign (“+”) following a rating indicates that it is likely to be upgraded, while a minus sign (“-“) following a rating indicates that it is likely to be downgraded.
., REVIEW BOOK: Personal Finance.
Retrieved Oct 1, 2009 from http://www.flatworldknowledge.com/node/50890
.
Considerations Before Investing in
Bonds
Susceptibility to certain risks
Credit
Callability
Inflation
Interest rate
Considerations Before Investing in
Bonds
Premiums and discounts
Current yield
Yield to maturity
Tax-equivalent yields
When to sell
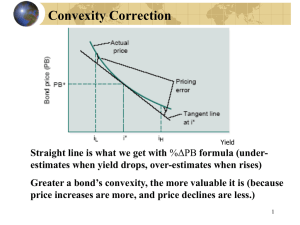
Bond Prices, Bond Yields, and Interest
Rates
., REVIEW BOOK: Personal Finance.
Retrieved Oct 1, 2009 from http://www.flatworldknowledge.com/node/50890
.
Yield to Maturity
Effective Yield of a Tax-Free
Investment
Not paying tax effectively increases your rate of return
you get to keep all of your profits, instead of only a portion
1 r
taxbracket
100
Example: 28% tax bracket, 5% rate of return
.
05
1
.
28
100
= 6.94%
Advantages of Investing in Bonds
Pay higher interest rates than savings
Offer safe return of principle
Have less volatility than stocks
Offer regular income
Require smaller initial investment
Disadvantages of Investing in Bonds
No hedge against inflation
Can be quite volatile
Compounding is almost impossible
Subject to investors tax rate
Poor marketability
Bond Characteristics and Risk
., REVIEW BOOK: Personal Finance.
Retrieved Oct 1, 2009 from http://www.flatworldknowledge.com/node/50890
.