Week 2A
advertisement

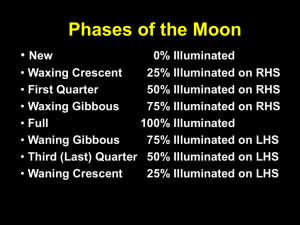
Week 2 Earthly Phenomena: Seasons Lunar Phases Solar and Lunar Eclipses Tides Reading: E2, E3, 5.2 (12 pages) Quick Quiz 1) If new Moon fell on March 2nd, what is the Moon's phase on March 14th? A) waxing crescent B) first quarter C) waxing gibbous D) full E) waning crescent 2) Only people in the Moon's umbral shadow can see a total solar eclipse. T/F 3) What will occur when the full Moon is on the ecliptic? ) A) a total lunar eclipse B) a total solar eclipse C) a partial solar eclipse D) an annular lunar eclipse E) a partial lunar eclipse if the Moon is at perigee • Rotation of the Earth • Revolution (orbit) of the Earth • Revolution (orbit) of the Moon • Rotation of the Moon Rotation of the Earth Earth’s rotation around its axis: • Causes night and day (Solar day = average time between consecutive “noontimes”). • Causes (apparent) motion of the stars Rotation of the Earth Earth’s rotation around its axis: • Causes night and day (Solar day = average time between consecutive “noontimes”). • Causes (apparent) motion of the stars Revolution (Orbit) of the Earth • The revolution of the Earth around the Sun defines the year (365.2425 days). • Earth’s motion around the Sun traces a path on the Celestial Sphere called the ecliptic. • The Earth’s revolution around the Sun also causes the seasons. How? TPS: What causes the seasons? A. The changing distance between the Earth and the Sun? B. The 23.5 degree tilt of the Earth’s axis? Hint: Although it is Winter in the Northern Hemisphere right now, it is Summer in the Southern Hemisphere. Spring in Northern Hemisphere Fall in Southern Hemisphere Winter in Northern Hemisphere Summer in Southern Hemisphere NP SP Summer in Northern Hemisphere Winter in Southern Hemisphere Fall in Northern Hemisphere Spring in Southern Hemisphere Why exactly? The Sun is lower in the sky in the Winter. The light from the Sun is diluted. Short Winter days mean less overall light shining on that part of the Earth. Summer Winter Earth as Seen from the Sun North American Summer North American Winter Equinoxes – Sun crosses the celestial equator (twice – Spring and Fall) Solstices – Sun’s farthest northerly or southerly position (Summer or Winter) Ecliptic – Path that the Sun follows in the sky Seasons • Ecliptic is plane of Earth’s path around Sun; at 23.5° to celestial equator • Northernmost point (above celestial equator) is summer solstice; southernmost is winter solstice; points where path cross celestial equator are vernal and autumnal equinoxes Seasons • Combination of day length and sunlight angle gives seasons • Time from one vernal equinox to next is tropical year “Path of the Sun” Revolution of the Moon The Moon’s revolution around the Earth causes: • Lunar phases • Eclipses • Tides Lunar Phases What causes the phases of the Moon? Is this crescent Moon caused by A. Sunlight shining mostly on the “far side” of the Moon? B. The shadow of the Earth? Months The Moon takes about 29.5 days to go through whole cycle of phases – synodic month Phases are due to different amounts of sunlit portion being visible from Earth Time to make full 360° around Earth, sidereal month, is about 2 days shorter First quarter Waxing gibbous Waxing crescent Full Moon New Moon Waning gibbous Third quarter Waning crescent First quarter Waxing crescent New Moon Waning crescent First quarter Waxing gibbous Waxing crescent Full Moon New Moon Waning gibbous Third quarter Waning crescent Name of Phase Fraction Illuminated (Apparent) Side Illuminated Rises Sets New Moon 0 None 6am 6pm Waxing Crescent ¼ West (Right) 9am 9pm First Quarter ½ West (Right) Noon Midnight Waxing Gibbous ¾ West (Right) 3pm 3am Full Moon 1 All 6pm 6am Waning Gibbous ¾ East (Left) 9pm 9am Third Quarter ½ East (Left) Midnight Noon Waning Crescent ¼ East (Left) 3am 3pm Lunar Phases Movie