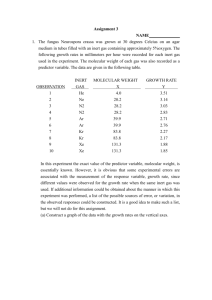
Simple Linear Regression: Model, Estimation, and Analysis
advertisement
Topic 3: Simple Linear Regression Outline • Simple linear regression model – Model parameters – Distribution of error terms • Estimation of regression parameters – Method of least squares – Maximum likelihood Data for Simple Linear Regression • • • • Observe i=1,2,...,n pairs of variables Each pair often called a case Yi = ith response variable Xi = ith explanatory variable Simple Linear Regression Model • • • • Yi = b0 + b1Xi + ei b0 is the intercept b1 is the slope ei is a random error term – E(ei)=0 and s2(ei)=s2 – ei and ej are uncorrelated Simple Linear Normal Error Regression Model • • • • Yi = b0 + b1Xi + ei b0 is the intercept b1 is the slope ei is a Normally distributed random error with mean 0 and variance σ2 • ei and ej are uncorrelated → indep Model Parameters • β0 : the intercept • β1 : the slope • σ2 : the variance of the error term Features of Both Regression Models • Yi = β0 + β1Xi + ei • E (Yi) = β0 + β1Xi + E(ei) = β0 + β1Xi • Var(Yi) = 0 + var(ei) = σ2 – Mean of Yi determined by value of Xi – All possible means fall on a line – The Yi vary about this line Features of Normal Error Regression Model • Yi = β0 + β1Xi + ei • If ei is Normally distributed then Yi is N(β0 + β1Xi , σ2) (A.36) • Does not imply the collection of Yi are Normally distributed Fitted Regression Equation and Residuals • Ŷi = b0 + b1Xi – b0 is the estimated intercept – b1 is the estimated slope • ei : residual for ith case • ei = Yi – Ŷi = Yi – (b0 + b1Xi) e82=Y82-Ŷ82 Ŷ82=b0 + b182 X=82 Plot the residuals Continuation of pisa.sas Using data set from output statement proc gplot data=a2; plot resid*year vref=0; where lean ne .; run; vref=0 adds horizontal line to plot at zero e82 Least Squares • Want to find “best” b0 and b1 • Will minimize Σ(Yi – (b0 + b1Xi) )2 • Use calculus: take derivative with respect to b0 and with respect to b1 and set the two resulting equations equal to zero and solve for b0 and b1 • See KNNL pgs 16-17 Least Squares Solution b1 (X X )(Y Y ) (X X ) i i 2 i b 0 Y b1 X • These are also maximum likelihood estimators for Normal error model, see KNNL pp 30-32 Maximum Likelihood Yi ~ N 0 1X i , 2 1 Y X i 0 1 i 2 2 1 fi e 2 L f1 f 2 f n (likelihood function) Find 0 and 1 which maximizes L Estimation of σ2 2 ˆ ( Yi Yi ) e i 2 s n2 n2 SSE MSE df E s s Root MSE 2 Source Model Error Corrected Total dfe Analysis of Variance Sum of Mean DF Squares Square F Value Pr > F 1 15804 15804 904.12 <.0001 11 192.28571 17.48052 12 15997 Root MSE Dependent Mean Coeff Var 4.18097 R-Square 0.9880 693.69231 Adj R-Sq 0.9869 0.60271 s Standard output from Proc REG MSE Properties of Least Squares Line • The line always goes through (X, Y) • ei (Yi (b0 b1 X i )) Yi b0 b1 X i nY nb0 nb1 X n((Y b1 X ) b0 ) 0 • Other properties on pgs 23-24 Background Reading • Chapter 1 – 1.6 : Estimation of regression function – 1.7 : Estimation of error variance – 1.8 : Normal regression model • Chapter 2 – 2.1 and 2.2 : inference concerning ’s • Appendix A – A.4, A.5, A.6, and A.7