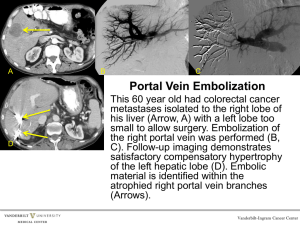
splanchnology
Chapter 4 Introduction
1. The concept and function
Splanchnology is a subject that studies the shape,
structure and position of the organs of viscera.
Viscera includes alimentary system, respiratory system,
urinary system and genital system.
funtion: The main functions of the viscera are to fulfil
the metabolism and maintain the life of species.
The main functions of alimentary system are to ingest
the food, to secrete enzymes, to absorb the products of the
digestive action, and to eliminate the unused residues.
The respiratory system is to carry out the gas exchanges -- supply of oxygen for living cells and remove of carbon
dioxide resulting from cell metabolism.
The primary function of urinary system is to keep the
body in homeostasis by removing and restoring selected
amount of water and solutes, excreting the various wastes.
The functions of genital system are to produce germ
cells (ovum and sperm) and to secrete some hormones.
2. General structure of viscera
porta hepatis
mucosa
(submucosa)
tubular
organs
renal hilum
muscular coats
serosa
Parenchymatous organs
The visceral surface of the liver
hilum/porta
The
hilum view
of right
lung
The
anterior
of the
left kidney
3. The reference lines of thorax
the anterior median line
the sternal line
the midclavicular line
the parasternal line
the anterior axillary line
the midaxillary line
the posterior axillary line
the scapular line
the posterior median line
The 4 abdominal regions
right upper abdomen
left upper abdomen
right lower abdomen
left lower abdomen
4 The abdominal regions (9 region )
epigastric
left hypochondriac
right hypochondriac
right lumbar
right inguinal
(right iliac)
umbilical
left lumbar
left inguinal
(left iliac)
hypogastric/pubic
Chapter 5 Alimentary/digestive system
alimentary
canal
mouth/oral cavity
pharynx
esophagus
duodenum
stomach
small intestine
jejunum
large intestine
ileum
salivary glands
alimentary liver
gland
Pancreas
Small gland
The upper/lower alimentary canal
1. The oral cavity
Palate
oral vestibule
oral cavity proper
Palatopharyngeal
The opening arch
of
the parotid duct
Palatoglossal arch
1) Lips
2) Cheek
3) Palate:
Palatine tonsil
Hard palate
Soft palate
Uvula
Palatine glands
tongue
Isthmus of fauces
Tonsillar fossa
4) Palatine tonsile
Sublingual gland
Submandibular gland
Parotid gland
Parotid duct
5) The teeth/dentes
deciduous teeth (20):
incisors 2,
canine 1,
molars 2
permanent teeth (32):
incisors 2
canine 1
premolars 2
molars 2~3
The basic structure of teeth
enamel
The shape :
dentine
crown, neck and root
Dental cavity :
cavity of crown, root canal
cement
The tissue :
dentine, enamel, cement
and dental pulp
The periodontal structure:
periodontal membrane,
alveolar bone and
gums/gingiva.
gums
periodontal membrane
6) The tongue
The shapes:
apex, body, root of tongue
The mucous membrane:
filifirm papillae
fungiform papillae
vallate papillae taste bud
foliate papillae
The muscle:
intrinsic muscle
extrinsic muscle:
styloglossus
hyoglossus
genioglossus
frenulum of tongue
the
theopening
openingof
of
auditory
auditorytube
tube
2. The pharynx
1) Position
nasopharynx
2) Parts
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
3) Communication
nasopharynx
nasal cavity
tympanic cavities of the middle ear
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
oral cavity
laryngeal cavity
esophagus.
The
Thesagittal
sagittalsection
section
of
ofthe
theskull
skulland
andneck
neck
The anterior wall of pharynx
First constriction
3. Esophagus
Esophagus
Cervical part
1) The position
Trachea
Aortic arch
2) The position
of the three constriction
Principal bronchus
Second constriction
constriction
position
Thoracic aorta
the beginning (commencement)
the first Thoracic
partborder of 6th C
or lower
or the level of cricoid cartilage
Third constriction
the intersection
with left bronchus
Abdominal
part
the second or the level of the sternal angle
or thevena
lower
border of the 4th T
Inferior
cava
the esophageal hiatus
the third
or the lever of the 10th T
The esophagus and its relationships
the distance
from incisor
15cm
25cm
40cm
4. Stomach/gaster
cardia
cardia
1)the shape
two orifices:
two curvature:
two surface:
lesser
lesser
curvature
curvature
angular
angular
incisure
incisure
pylorus
pylorus
2)the parts
cardiac part
fundus of stomach
body of stomach
pyloric antrum
pyloric part
pyloric canal
greater curvature
greater curvature
3)The position
In middle full
left hypochondriac region
epigastric region,
hypochondriac
region
epigastric
region
hypochondriac
region
and umbilical region;
cardia on the left of the eleventh
thoracic vertebra,
umbilical
region
pylorus on the right of the first
lumbar vertebra.
The position of stomach
4)The relation of stomach
The anterior surface:
The L part is contact with diaphragm
The R part is relation with the left
and quadrate lobes of live and the
anterior abdominal wall.
The posterior surface:
It is relation with the spleen, the
diaphragm, the left suprarenal gland,
the upper part of the left kidney, the
splenic blood vessels, the pancreas,
the left colic flexure, the transverse
colon and its mesocolon. These
structures form the stomach bed.
5)the musculature and inner
surface of stomach
The musculature:
The wall of stomach has three layer
muscle. The outer is longitudinal,
the middle circular, the inner
lesser curvature
oblique and incomplete. At the
angular incisure
pylorus, the middle circular muscle
thicken and form a muscular ring --- pylorus
the pyloric sphincter. It can control
the pylorus open and close.
The inner surface:
When the stomach is empty, the
mucosa form many ridges and rugae.
But the mucosa of pyloric part is
smooth. Gastric neoplasm and
ulcers, the mucous pattern will be
changed and become radiological.
cardia
greater curvature
5. the small intestine
superior part
descending part
duodenum
horizontal part
jejunum
ascending part
ileum
The mesentery
6. the large intestine
1) parts
caecum
vermiform appendix
colon
rectum
anal canal
about 1.5 m long
2) The characteristics of
the cecum and colon
colic bands
haustras of colon
epiploic appendices
3) The cecum and the
vermiform appendix
The position of appendix
retrocecal and retrocolic
in 65.28%
pelvic in 31.01%
subcecal in 2.26%
pre-ileal in 0.4%
post-ileal in 1.0%
higher and left position
McBurney’s point
transverse mescolon
4) colon
right colic
flexure
left colic
flexure
ascending colon
transverse colon
parts
descending colon
sigmoid colon
sigmoid mescolon
5) rectum
sacral flexure
two flexures
perineal flexure
Ampulla of rectum
Transverse folds of rectum
6) the anal canal
anal column
anal valves
anal sinuses
inner surface
dentate line
anal pecten
white line
sphincter ani internus
sphincter
Columnar epithelium
Stratified columnar epithelium
sphincter ani externus
Stratified squamous epithelium
7. The alimentary gland
1) salivary gland
Minor gland
Opening of parotid duct
parotid gland
Major gland
submandibular gland
sublingual gland
sternocleidomatoid
masseter muscle
Opposite the crown of second upper molar
8. liver/hepar
The liver is the largest
gland in our body.
Food processing factory
1. Functions
1) produce bile
2) synthesis
glycogen
Nutrients, vitamins, mineral, and other
albumin
products of digestion(include the poison)
3) detoxification
1) The position
R. triangular lig.
hepatic portal
Caudate
lobe v.
diaphragm
inferior vena cava
L. triangular
lig.
bare
area
right hypochondriac region
epigastric regions
left hypochondriac region
beneath the diaphragm
coronary lig.
L. lobe
hypochondriac
epigastric common
bile duct
region
region
portalobe
Left
hepatis
Right lobe
R. lobe
hypochondriac
region
behind the ribs
falciform lig.
2) The shapes
superior surface/
diaphragmatic surface:
inferior surface/
visceral surface:
proper hepatic a.
hepaticgallbladder
quadrat
duct
lobe
systic duct
lig. teres hepatis
gallbladder
3) The lobe of liver
diaphragm
R. triangular
lig.
L. triangular lig.
caudate lobe
On the superior surface:
coronary lig.
right lobe
left lobe
R. lobe
L. lobe
On the inferior surface:
L. lobe
R. lobe
falciform lig.
right lobe,
left lobe
quadrate lobe
caudate lobe.
lig. teres hepatis
quadrate lobe
gallbladder
9. The gallbladder and
the biliary ducts
fundus of gallbladder
body of gallblader
neck of gallbladder
cystic duct
right and left hepatic duct
common hepatic duct
common bile duct
10. The drainage of the bile
hepatocyte
bile canaliculi
intralobular bile ductules
R. hepatic duct
L. hepatic duct
common hepatic duct
common bile duct
Cystic duct
gallbradder
hepatopancreatic ampulla
Major duodenal papilla
11. The Pancreas
position
head
parts
neck
body
tail
exocrine part
function
endocrine part