13.7 day 1 Tangent Planes
advertisement
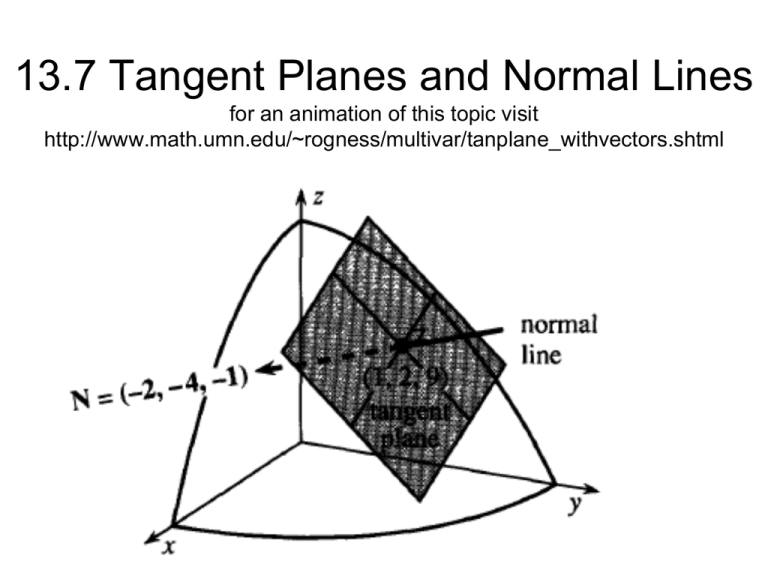
13.7 Tangent Planes and Normal Lines for an animation of this topic visit http://www.math.umn.edu/~rogness/multivar/tanplane_withvectors.shtml Recall from chapter 11: • • • • • • Standard equation of a plane in Space a(x-x1) + b(y-y1) + c (z – z1) = 0 parametric form equations of a line in space: x = x1 + at y = y1 +bt z = z1 +ct symmetric form of the equations of a line in space x-x1 = y – y1 = z – z1 a b c Example 1 For the function f(x,y,z) describe the level surfaces when f(x,y,z) = 0,4 and 10 Example 1 solution For the function f(x,y,z) describe the level surface when f(x,y,z) = 0,4 and 10 For animated normal vectors visit: http://www.math.umn.edu/~rogness/math2374/paraboloid_normals.html OR http://www.math.umn.edu/~rogness/multivar/conenormal.html Example 2 Find an equation of the tangent plane to given the hyperboloid at the point (1,-1,4) Example 2 Solution: Example 3 Find the equation of the tangent to the given paraboloid at the point (1,1,1/2) Example 3 Solution: Find the equation of the tangent to the given paraboloid at the point (1,1,1/2). Rewrite the function as f(x,y,z) = -z Example 4 Find a set of symmetric equations for the normal line to the surface given by xyz = 12 At the point (2,-2,-3) Example 4 Solution Find a set of symmetric equations for the normal line to the surface given by xyz = 12 At the point (2,-2,-3) One day in my math class, one of my students spent the entire period standing leaning at about a 30 degree angle from standing up straight. I asked her “Why are you not standing up straight? “ She replied “Sorry, I am not feeling normal.” Of course that students name was Eileen. - Mr. Whitehead