Math 6C - Chapter 12 Quiz - SOLUTIONS
advertisement
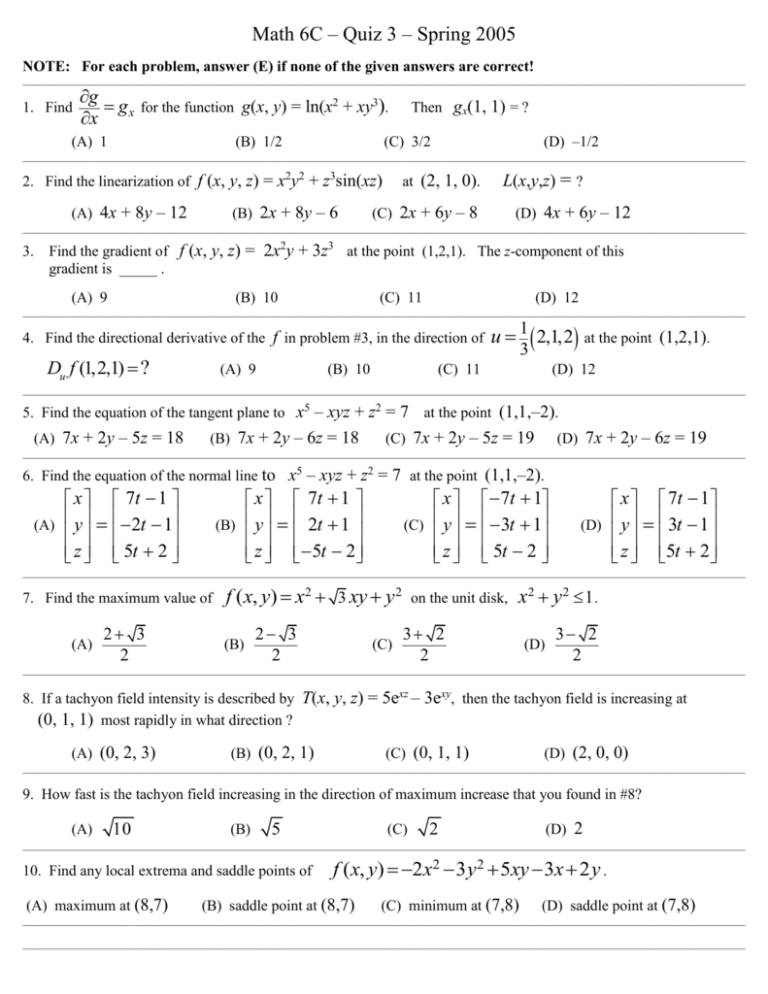
Math 6C – Quiz 3 – Spring 2005 NOTE: For each problem, answer (E) if none of the given answers are correct! ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Find g gx x for the function g(x, y) = ln(x2 + xy3). (A) 1 (B) 1/2 Then gx(1, 1) = ? (D) –1/2 (C) 3/2 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ at (2, 1, ). 2. Find the linearization of f (x, y, z) = x2y2 + z3sin(xz) (A) 4x + 8y – 12 (B) 2x + 8y – 6 L(x,y,z) = ? (C) 2x + 6y – 8 (D) 4x + 6y – 12 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Find the gradient of f (x, y, z) = 2x2y + 3z3 at the point (1,2,1). The z-component of this gradient is _____ . 3. (A) 9 (B) 10 (C) 11 (D) 12 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Find the directional derivative of the f in problem #3, in the direction of Du f (1,2,1) ? (A) 9 (B) 10 u 1 2,1,2 at the point (1,2,1). 3 (C) 11 (D) 12 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Find the equation of the tangent plane to x5 – xyz + z2 = 7 (A) 7x + 2y – 5z = 18 (B) 7x + 2y – 6z = 18 at the point (1,1,–2). (C) 7x + 2y – 5z = 19 (D) 7x + 2y – 6z = 19 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Find the equation of the normal line to x5 – xyz + z2 = 7 at the point (1,1,–2). x 7t 1 (A) y 2t 1 z 5t 2 x 7t 1 (B) y 2t 1 z 5t 2 x 7t 1 (C) y 3t 1 z 5t 2 x 7t 1 (D) y 3t 1 z 5t 2 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Find the maximum value of (A) 2 3 2 f ( x, y) x2 3 xy y 2 (B) 2 3 2 (C) on the unit disk, x2 y 2 1 . 3 2 2 (D) 3 2 2 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. If a tachyon field intensity is described by T(x, y, z) = 5exz – 3exy, then the tachyon field is increasing at (0, 1, ) most rapidly in what direction ? (A) (0, 2, ) (B) (0, 2, ) (C) (0, 1, ) (D) (2, 0, ) ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. How fast is the tachyon field increasing in the direction of maximum increase that you found in #8? (A) 10 (B) 5 (C) 2 (D) 2 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Find any local extrema and saddle points of (A) maximum at (8,7) f ( x, y) 2x2 3 y2 5xy 3x 2 y . (B) saddle point at (8,7) (C) minimum at (7,8) (D) saddle point at (7,8) ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Find the tangent plane to the surface defined by (A) 1 y (B) z G( x, y) 2x2 y e xy 1 x y (C) 1 x y z=? at (1,0,1). (D) 1 x y ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. Find the equation of the tangent plane to the implicit surface defined by at the point (1,1,1). (A) x 6 y 3z 4 x 5 y 3z 4 (B) x2 3xy 2 z3 1 x 5 y 3z 4 (C) (D) x 6 y 3z 4 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ f (2,3) 4 and f '(2,3) 0 0 . Further suppose that the Hessian of f evaluated at (2,3), 13. Suppose that f xx f yx f xy 2 3 . f yy 3 1 (A) relative maximum One can conclude that at the point (2,3,4), the graph of f has a . . . (B) relative minimum (C) saddle point (D) point of inflection ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Suppose that g xx g yx g (2,3) 4 and g '(2,3) 0 0 . Further suppose that the Hessian of g evaluated at (2,3), g xy 5 3 . g yy 3 4 (A) relative maximum One can conclude that at the point (2,3,4), the graph of g has a . . . (B) relative minimum (C) saddle point (D) point of inflection ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ g ( x, y) 2 2x 2 y x2 y 2 15. Find the absolute maximum value of by the x and y axes and the line y = 9 – x. (A) 2 over the triangle in Quadrant I bounded (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 16. Find the equation of the tangent plane to (A) 4 y (B) g ( x, y) 2 2x 2 y x2 y 2 4 x y (C) at the point (1,1). 4 x (D) z=? 4 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Find the greatest value that 2 y2 . f ( x, y) xy attains over the closed elliptic disk x 1 8 2 (B) –1 (A) 2 (C) –2 (D) 4 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 18. Find the greatest value that (A) 3 f ( x, y) 3x 4 y attains on the closed unit disk x2 y 2 1 . (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 9 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 19. Find the minimum distance from the surface at (A) 10 (B) xyz 1 to the origin. 5 (C) 3 (D) 2 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 20. What’s the largest possible product n positive numbers can have, given that their sum is 1? (A) 1 n (B) 1 nn (C) n 1 n2 (D) n 1 nn ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________