Elasticity
advertisement

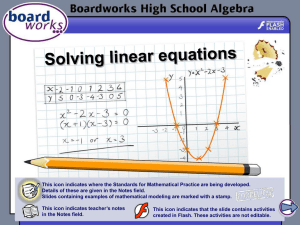
Elasticity 1 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Changing shapes Forces can make objects change their speed or their direction when they are in motion. They can also make objects change shape. Stretching forces can change the shape of objects, making them longer and thinner. Compression forces can squash objects, making them smaller. 3 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Elastic or plastic? In physics, materials are described as having either elastic or plastic properties. Most materials display both properties, depending on how much they are deformed. Plastic materials change shape permanently when they are deformed by an external force. Elastic materials return to their original shape once the external force is removed. 4 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Elastic potential energy A stretched or compressed material, like the spring in a jack-in-the-box when the lid is closed, has elastic potential energy (EPE) stored in it. EPE is the energy stored in a body due to a load causing a deformation. According to the law of conservation of energy, no energy is created or destroyed when a spring is compressed. Therefore the work done in compressing the spring is equal to the EPE stored in it, plus any energy released as heat and sound. 5 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Slingshot science 6 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Investigating springs 7 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Results plastic region force (N) break point limit of proportionality elastic limit elastic region extension (cm) If a spring is stretched far enough, it reaches the limit of proportionality and then the elastic limit. The elastic limit is a point beyond which the spring will no longer return to its original shape when the force is removed. 8 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Hooke’s law The limit of proportionality is a point beyond which behaviour of an elastic material no longer conforms to Hooke’s law: The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied, provided its limit of proportionality is not exceeded. F e or F = ke original length where k is a constant. x F 9 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Elasticity calculations 10 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 11 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Glossary 12 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Anagrams 13 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012 Multiple-choice quiz 14 of 14 © Boardworks Ltd 2012



![Direction_and_Scale[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005432475_1-80ce3065f13008250a8cdec135db9846-300x300.png)