Capacitor2 - WordPress.com
advertisement
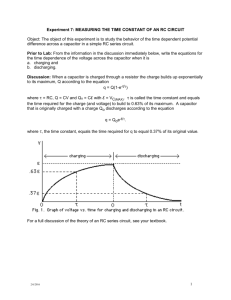
Capacitors in a Circuit emf Resistors series parallel Circuit problems Capacitors in a circuit Reading Question Electrical power is 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. P = IV P = Ed P = I2R P = qV None of the above. Two or more of the above. Reading Question Electrical power is 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. P = IV P = Ed P = I2R P = qV None of the above. Two or more of the above. Reading Question What property of a real battery makes its potential difference slightly different than that of an ideal battery? 1. Short circuit 2. Chemical potential 3. Internal resistance 4. Effective capacitance 5. Inductive constant Reading Question What property of a real battery makes its potential difference slightly different than that of an ideal battery? 1. Short circuit 2. Chemical potential 3. Internal resistance 4. Effective capacitance 5. Inductive constant Reading Question In an RC circuit, what quantity is represented by the symbol 1. Period 2. Torque 3. Terminal voltage 4. Time constant 5. Coefficient of thermal expansion Reading Question In an RC circuit, what quantity is represented by the symbol 1. Period 2. Torque 3. Terminal voltage 4. Time constant 5. Coefficient of thermal expansion Reading Question The equivalent resistance for a group of series resistors is 1. less than any resistor in the group. 2. equal to the smallest resistance in the group. 3. equal to the average resistance of the group. 4. larger than any resistance in the group. 5. larger than any resistor in the group. Reading Question The equivalent resistance for a group of series resistors is 1. less than any resistor in the group. 2. equal to the smallest resistance in the group. 3. equal to the average resistance of the group. 4. larger than any resistance in the group. 5. larger than any resistor in the group. Student Workbook emf emf Student Workbook Resistors in Series R R1 R2 R3 V V1 V2 V3 IR IR1 IR2 IR3 R R1 R2 R3 Resistors in Parallel 1 1 1 1 R R1 R2 R3 I I1 I 2 I 3 V V V V R R1 R2 R3 1 1 1 1 R R1 R2 R3 A Problem A Problem Class Question What is the potential at points a to e ? 1. Va = 0, Vb = -4 V, Vc = -10 V, Vd = -12 V, Ve = -20 V 2. Va = -20 V, Vb = -16 V, Vc = -10 V, Vd = -8 V, Ve = 0 V 3. Va = 20 V, Vb = 16 V, Vc = 10 V, Vd = 8 V, Ve = 0 V 4. Va = -4 V, Vb = -6 V, Vc = -2 V, Vd = -8 V, Ve = 0 V 5. Va = 4 V, Vb = 6 V, Vc = 2 V, Vd = 8 V, Ve = 0 V Class Question What is the potential at points a to e ? 1. Va = 0, Vb = -4 V, Vc = -10 V, Vd = -12 V, Ve = -20 V 2. Va = -20 V, Vb = -16 V, Vc = -10 V, Vd = -8 V, Ve = 0 V 3. Va = 20 V, Vb = 16 V, Vc = 10 V, Vd = 8 V, Ve = 0 V 4. Va = -4 V, Vb = -6 V, Vc = -2 V, Vd = -8 V, Ve = 0 V 5. Va = 4 V, Vb = 6 V, Vc = 2 V, Vd = 8 V, Ve = 0 V Light light light Class Question Rank in order, from brightest to dimmest, the identical bulbs A to D. 1. A = B = C = D 2. A > B > C = D 3. A > C > B > D 4. A > C = D > B 5. C = D > B > A Class Question Rank in order, from brightest to dimmest, the identical bulbs A to D. 1. A = B = C = D 2. A > B > C = D 3. A > C > B > D 4. A > C = D > B 5. C = D > B > A Another Problem What is the current in the 600 W resistor? Student Workbook Student Workbook Ground Student Workbook Voltage Measurement To measure the potential difference or voltage across an element we connect the two voltage leads to the ends of the element. Voltage Measurement What is the effect of connecting a voltmeter (DMM) to an element? This is the resistance of the voltmeter (DMM). This resistance is more like 10 MW If 10 MW and 1kW 1 1 1 R 999.9W R R1 R2 Voltage Measurement What about measuring the voltage of a old battery? I V 8.50V ?A R 17 W Vemf Vr VR 9V Vr 8.50V Vr r ?W I Current Measurement To measure the current through an element we break the circuit and place the current meter (DMM) in the circuit so that current flows through the meter. Ideal Ammeter Ideal Ammeter V Rs Rs = 0 for an ideal ammeter Charging a Capacitor Kirchhoff’s Rules Discharging a Capacitors Write Kirchhoff’s voltage equation for discharging a capacitor. Q IR 0 C and dQ I dt The charge on the capacitor decrease while the charge through the resistor increases. dQ dq dt dt dQ 1 Q0 dt RC dQ 1 dt Q RC Integrate the equation Q t Q0 t dQ 1 dt Q RC 0 Q (t ) t ln Q RC 0 Q (t ) Q0e t RC Discharging a Capacitor Write the equation for current and voltage for a discharging capacitor. Q(t ) Q0e t RC dQ I (t ) dt Q0 I (t ) e RC t RC I 0e t RC Use the definition of capacitance and the charge equation to find the equation for the voltage across the capacitor. Q Q C or V V Q0 V (t ) e C t RC V0e t RC Charging a Capacitor Are the graphs for a charging capacitor the same? Discuss this. Discuss these equations in your group and make sure you all understand and can explain these equations in terms of the characteristic of the capacitor. Charging a Capacitor Now lets see a charging capacitor. For times less than one time constant For times greater than a few time constant Capacitors in a Circuit Now lets see what effect a capacitor has in a circuit? For times less than one time constant For times greater than a few time constant Student Workbook Student Workbook Student Workbook Student Workbook
![Sample_hold[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005360237_1-66a09447be9ffd6ace4f3f67c2fef5c7-300x300.png)