CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Session 3
Types & Measurements of
Risk, Standard Deviation,
Beta, CAPM
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Session Details
Module
2
Chapter(s) 1, 2, 3
LOs
2-3
Calculate a weighted average return. Also
calculate the standard deviation and mean
return of a single asset, and understand how
the range of returns is calculated within one,
two, and three standard deviations.
2-4
Calculate coefficient of variation, and
understand its application.
2-8
Calculate required return using the capital
asset pricing model (CAPM), and understand
its application.
3-2
Risk
• Standard deviation: variability
• Beta: volatility
Total Risk
Standard Deviation
(Variability)
Systematic Risk
Beta
(Volatility)
Unsystematic Risk
3-3
Standard Deviation (Normal Distribution)
M (mean/average return) = 10%
σ (standard deviation)
= 15%
68% of returns
95% of returns
99% of returns
-3 σ
-2 σ
-1 σ
- 35%
- 20%
- 5%
Mean Return
10%
+1 σ
+2 σ
+3 σ
25%
40%
55%
2-4
Standard Deviation
• For normally distributed returns, calculate the standard
deviation range, add and subtract the standard
deviation amount from the mean return.
Example: Mean return of 10%, Std deviation of 15%
• One standard deviation: 10 + 15 = +25, and
10 – 15 = – 5
• Two standard deviations: 25 + 15 = +40, and
– 5 – 15 = – 20
• Three standard deviations: +55 to -35
3-5
Standard Deviation Concepts
• Normal distribution
• Skewness (security
•
•
•
returns are positively
skewed)
Kurtosis
Leptokurtic
Platykurtic
3-6
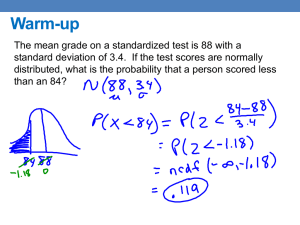
Standard Deviation Question
Scorpio Inc. has a mean return of
19%, and a standard deviation of
25.
What is the probability that the
stock will have a return greater
than 19% if the returns are
normally distributed?
3-7
Standard Deviation Question
Libra Inc. has a mean return of
11%, and a standard deviation
of 9.
Assuming the returns are
normally distributed, what is the
probability that the stock will
have a return greater than
20%?
3-8
Standard Deviation of a Single Asset
Use the calculator!
(rn r)
2
n 1
3-9
Calculating Standard Deviation
Single Asset (2)
• Formula #4 on diagram
• Calculation is simple on
the 10BII+ or 12C
Assume Acme Industries has
the following annual returns:
• + 15%
• + 22%
• - 7%
• + 10%
What is the standard deviation and mean return?
3-10
Calculating Standard Deviation
Single Asset (2)
Keystrokes are:
1, SHIFT, P/YR
15, ∑+
22, ∑+
7, +/-, ∑+
10, ∑+
SHIFT, 8
(g, “.” on 12C)
Answer = 12.36
For the mean return the keystrokes would be:
SHIFT, 7
(g, “0” on 12C)
Answer = 10%
3-11
Coefficient of Variation
Risk per unit of return
CV
σ
x
3-12
Coefficient of Variation Example
CV(A) = 6%/10% = 0.60
CV(B) = 9%/12% = 0.75
B has a higher mean, but also has a higher CV, which
means you take higher risk per unit of return.
Asset A
Asset B
Std Dev.
6%
9%
Mean.
10%
12%
Remember that you can easily calculate both standard
deviation and mean return for a single asset with your
financial calculator, as we did previously.
3-13
Beta Coefficients
• Measures the volatility of a stock (or portfolio)
•
relative to the market (a benchmark); so, the
greater the correlation, the more accurate beta
becomes.
Since R-squared measures systematic risk, it
can be used to determine beta
reliability; generally you are looking
for an R-squared of 70 or higher
in order for beta to be considered
reliable.
β
3-14
Beta
Beta of 1 means the asset has the same
volatility as the benchmark.
What would be the approximate price movement
of the Acme Fund if it has a beta of .85, and the
benchmark it is being compared to has a return of
15%?
Answer: 15% x .85 = 12.75%
What if Acme’s beta were 1.25?
Answer: 15% x 1.25 = 18.75%
3-15
Weighted Average Using Beta
What is the weighted beta of the following portfolio?
• $40,000 in AAA, beta of 1.2
• $20,000 in TTT, beta of 0.9
• $15,000 in ZZZ, beta of 0.8
Shortcut on 10BII+ calculator:
1.2, INPUT (ENTER on 12C)
40,000, ∑+
.9, INPUT
20,000, ∑+
.8, INPUT
15,000, ∑+
SHIFT, 6 (g, 6 on 12C)
Answer = 1.04
3-16
The Capital Asset Pricing Model
• CAPM also has a micro component that looks at
•
individual stock returns – the Security Market
Line – SML
This micro component is also used to help value
stocks
r rf (rm rf )β
3-17
The Capital Asset Pricing Model
The risk-free rate is 3.5%, and the market’s
expected return is 8%. Your stock has a beta
of 1.1.
What is the required return?
• r = 3.5 + (8.0 – 3.5)1.1
• r = 3.5 + 4.95
• r = 8.45
What is the market risk premium?
• 4.5% (8.0 – 3.5)
3-18
Required Return Calculations
What is the required return for the following
securities? The risk-free rate is 4%, and the
market return is 8%.
Fund
Beta
Triad
0.9
Triangle
1.1
Trapeze
2.0
Tango
1.4
Tangent
1.0
Required
Return
3-19
Question 1
Jake wants to know the beta coefficient for his portfolio of
stocks, shown below:
Current Market
Value
Beta
Alto Associates
$33,000
1.1
Bolero Enterprises
$12,500
1.0
Cactus Co.
$45,000
0.9
Dire Straights Int’l
$29,000
1.6
Stock
What is the beta coefficient for Jake’s portfolio?
a. 1.14
b. 1.19
c. 1.23
d. 1.28
3-20
Question 2
Triad Industries has a mean return for the
past five years of 12%, with a standard
deviation of 9%.
Assuming the returns are evenly distributed,
what is the probability that Triad will have a
return greater than 21%?
a. 3%
b. 12%
c. 16%
d. 24%
3-21
Question 3
Your client has narrowed his choice down to the following
three mutual funds, and wants your opinion concerning
which one to choose based on the fund that will provide the
lowest amount of risk per unit of return.
Fund
Mean
Return
Standard Deviation
ABC
8%
12
DDD
10%
14
EFG
7%
10
Which fund should your client choose?
a. Fund ABC
b. Fund DDD
c. Fund EFG
3-22
Question 4
A mutual fund you are considering has a beta of
0.75, a standard deviation of 11, a correlation
coefficient of .90 with the Russell 2000, an Rsquared of .65 with the S&P 500, and an
expected return of 12%.
Which one of the following is the fund’s
coefficient of variation?
a. .92
b. 1.09
c. 1.15
d. 1.25
3-23
Question 5
The current return of the market is 11%. The
current market risk premium is 7%, and the
risk-free rate is 4%.
If the beta of your stock is 1.1, what is your
required return?
a. 7.30
b. 11.70
c. 12.10
d. 16.10
3-24
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Session 3
End of Slides
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.