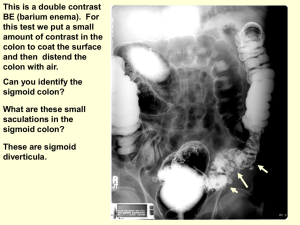
Exploring_the_equine_abdomen - veterinaryanatomy
advertisement

We examine the gastrointestinal tract of a donkey in dorsal recumbency (on its back) much as one might do this in abdominal surgery. For the exposure that we use in this presentation, the incisions are different and, as the specimen is preserved, the midventral abdominal incision is much larger than it would be were we actually performing the surgery. Exploration of the viscera would not be markedly different in a horse. See the presentation, “Equine Abdominal Topography”, for review. 1. Cut along long axis. R 2. Cut along transverse axis (at leve of last rib). L epidermis subcutaneous c.t. (superficial fascia) dermis The skin is made up of two layers, a superficial epithelial layer, the epidermis, which is thin, and the dermis, which is a much thicker layer of connective tissue on which the epidermis rests. The epidermis is usually pigmented and probably no more than 100 microns thick.The dermis is the deeper layer of the skin, continuous with the underlying subcutaneous tissue (superficial fascia). Different from the fairly uniform epidermis, the thickness of the dermis is variable and depends on the area of the body. In the case of the abdomen, the dermis is thin ventrally, perhaps two to four millimeters thick on average, and becomes gradually thicker as the dorsal midline is approached. Ventral body wall. At the sternal end of your longitudinal incision, make a stab incision through the ventral body wall. Go only Use the blunt end of hemostatic forceps to push through the peritoneum to enter the abdominal cavity. Now put your finger through the hole that you’ve made and lift the abdominal wall away from the viscera. You’re still not through the peritoneum. You’re looking at the internal lamina of the rectus sheath. Now you’ve carefully cut through the internal lamina and the peritoneum and you’re looking at abdominal viscera. Lifting the body wall away from the viscera, cut along your longitudinal and transverse incisions to expose Abdominal viscera exposed: cecum L R Right parts of large colon. Left parts of large colon. large colon, right parts cecocolic fold large colon, left parts cecocolic fold right ventral colon left ventral colon jejunum desc/sigmoid colon cecocolic fold. Lift up on the apex of the cecum to demonstrate the cecocolic fold. cecocolic fold ??? Pull on the apex of the cecum to demonstrate the cecocolic fold. The fold extends from the lateral tenia of the cecum to the right ventral colon. cecocolic fold ??? Draw the cecum away from the viscera as shown. ??? must be the right ventral colon. jejunum ileum cecum The cecum is turned back, to the right, to show the ileocecal fold. ileocecal fold The ileocecal fold extends from the dorsal tenia of the cecum to the ileum. As a matter of definition, the ileojejunal junction is where the ileocecal fold ends. RTRT VENT VENT COL COL LEFT VENT LT VENT COL COL CECUM CECUM Follow Followthe theleft leftparts partsofofthe thelarge largecolon coloncaudally. caudally. Note Notethat thatthey theycurve curvetotothe theright rightororenter enterthe thepelvic pelvic inlet. inlet.Find Findthe thepelvic pelvicflexure flexureand anddraw drawititout. out. RT VENT COL LT VENT COL CECUM Follow the left parts of the large colon caudally. Note that they curve to the right or enter the pelvic inlet. Find the pelvic flexure and draw it out. LT VENT COL LT DORS COL Pelvic flexure single tenia, mesentery left dors colon no haustra left vent colon with haustra left parts of large colon rt dors col rt vent col cecum Pelvic flexure and left parts of the large colon drawn to the right with the cecum out of the body cavity. coils of jejunum (no teniae) desc/sigmoid colon (with teniae) cecum cecum Pelvic pelvicflexure flexure Cecum, pelvic flexure, right leftView parts,from and athe little of theside. right parts of large colon drawn out of abdomen, right view. From: Anatomie des Pferdes, W. Ellenberger, H. Baum; 1897. Verlagsbuchhandlung Paul Parey Left Side Right Side right ventral colon sternal flexure diaphragmatic flexure cecum left ventral colon jejunum small colon Coils of jejunum moved out of the way to show the ileum joining the base of the cecum. ileocecal junction Following the jejunum to the jejunum duodenojejunal flexure at the cranial end of the duodenocolic fold. ascending duodenum jejunum ascnd duod duodenojejunal flexure transv colon desc colon coils of small colon leading to the rectum right dorsal colon mesocolon of desc/sigmoid colon jejunum Replace coils of small colon…. right ventral colon cecum transv colon right dorsal colon jejunum Replace coils of jejunum ventral to coils of small colon… Replace left parts of large colon ventral to jejunal coils… Replace the cecum.