Radial Surveying
advertisement
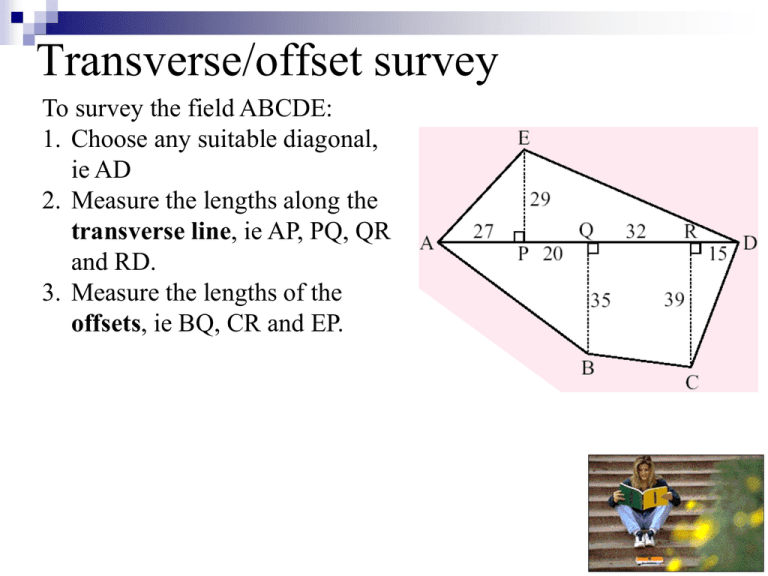
Transverse/offset survey To survey the field ABCDE: 1. Choose any suitable diagonal, ie AD 2. Measure the lengths along the transverse line, ie AP, PQ, QR and RD. 3. Measure the lengths of the offsets, ie BQ, CR and EP. Field diagrams When in the field doing the survey the surveyor sketches the information as a field diagram. To complete a field survey: 1. Start at one end of the transverse line 2. Write down the cumulative distances of the offsets from the starting point 3. Write down the lengths of the offsets. 4. Units are not shown. 20+27=47 Plane table radial survey When doing a plane table radial survey you normally: •Place a table towards the middle of a field •Mark a point towards the middle of the paper. •From this point draw a line towards each corner of the field •Measure the distance from the point towards the middle of the paper to each corner of the field Note •The angles at which the lines are drawn are important as this is used in doing an accurate scale drawing, •It is called a radial survey as all lines “radiate” out from the centre. •The point O is often used as the centre point Example 1 The diagram shows the results of a radial survey of a field ABCD A D 23m 87º 28m 19m 68º 81º 33m C O B Compass radial survey A compass radial survey is similar to a plane table survey: •Stand towards the middle of a field, •Take a compass bearing of each corner of the field, •Measure the distance from the point you are standing to each corner of the field Note •Only very rarely is one of the corners directly north, •Often the angle asked for involves the corners just to the left and right of due north. Example 2 The diagram shows the results of a radial survey of a field EFG G 318º N E 053º 49m 29m O 35m F 197º Today’s work There are two ‘fields’ marked on the oval. •Create a radial and compass survey/diagram of each of the ‘fields’. •On ‘field 1’ use radiating lines (and protractors) and the navigational compass. •On ‘field 2’ use the giant protractor and the iphone. •Use your surveys to find the area of the ‘fields’. •Equipment: pencils, rulers, rubbers, paper. Example 1 The diagram shows the results of a radial survey of a field ABCD a) Find the size of BOC. A D b) Calculate the length of BC. c) Calculate the area of triangle OBC. 23m 87º 28m a) BOC = 360 68 81 87 19m 68º 81º 33m O = 124º C x B b) a 2 b2 c 2 2bccos A x2 332 192 2 33 19 cos124 Just type it in. x2 2151 2 x 46 4m c) Area = ½absinC = ½ 19 33 sin124 = 259·9m2 Example 2 The diagram shows the results of a radial survey of a field EFG a) Find the size of GOE. G 318º N b) Calculate the length of GE. E 053º c) Calculate the area of triangle GOE. a) NOE = 53º 49m NOG = 360 318 29m = 42º O GOE = 53 + 42 35m = 95º b) a 2 b2 c 2 2bccos A x2 492 292 2 49 29 cos 95 x2 3489 7 x 59 1m c) Area = ½absinC = ½ 49 29 sin95 = 707·8m2 F 197º Today’s work Exercise 6G pg 197 #2a, 3a, 4, 5,