ANSWER
advertisement
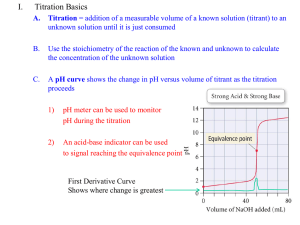
Acids and Bases Jeopardy Acid Calculations Base Calculations Concentration of species Titration Curves Pot Luck 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Final Jeopardy Help (1) Save a duplicate of this template. (2) Enter all answers and questions in the normal view. (view/normal) (3) Change the category headings in the normal view (view/normal) (4) View as a slideshow. (5) Use the home red button after each question. ©Norman Herr, 2003 Acid Calculations-100 • QUESTION: Calculate the pH of a solution containing 0.134 molL-1 hydronium ions • ANSWER: 0.873 Answer Question Acid Calculations-200 • QUESTION: Calculate the pH of 1.35 x 10-9 molL-1 HCl • ANSWER: 6.99 Answer Question Acid Calculations-300 • QUESTION: Calculate the pH of 3.0 x 10-4 molL-1 H2SO4 • ANSWER: 3.22 Answer Question Acid Calculations-400 • QUESTION: Calculate the pH of an acid with a hydroxide ion concentration of 1.38 x 10-10 molL-1 • ANSWER: 4.14 Answer Question Acid Calculations-500 • QUESTION: Calculate the pH of 0.0243 moL-1 ethanoic acid, given Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 • ANSWER: 3.19 Answer Question Base Calculations-100 • QUESTION: Calcuate the pH of 0.1 molL-1 hydroxide ions • ANSWER: 13 Answer Question Base Calculations-200 • QUESTION: Calculate the pH of 0.153 molL-1 KOH • ANSWER: 13.2 Answer Question Base calculations-300 • QUESTION: Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration of a 3.02 x 10-4 molL-1 HCl solution • ANSWER: 3.31 x 10-11 molL-1 Answer Question Base Calculations-400 • QUESTION: If the pH is 8.65, what is the concentration of hydronium ions? • ANSWER: 4.47 x 10-6 molL-1 Answer Question Base calculations-500 • QUESTION: Calculate the pH of a 0.107 molL-1 solution of NH3, given the pKa of the ammonium ion is 9.75 • ANSWER: 11.4 Answer Question Concentration of species-100 • QUESTION: From highest to lowest concentration, what are the species present in a 1 molL-1 solution of H2SO4? • ANSWER: H2O>>H3O+>SO42->OH- Answer Question Concentration of species-200 • QUESTION: From highest to lowest concentration, what are the species present in a 1 molL-1 solution of CH3COOH? • ANSWER: H2O>> CH3COOH>H3O+ =CH3COO->OH- Answer Question Concentration of species-300 • QUESTION: From highest to lowest concentration, what are the species present in a 1 molL-1 solution of NH3? • ANSWER: H2O >> NH3 > OH- = NH4+ > H 3O + Answer Question Concentration of species-400 • QUESTION: From highest to lowest concentration, what are the species present in a 1 molL-1 solution of NH4NO3? • ANSWER: H2O >> NO3- = NH4+ >H3O+ = NH3 > OH- Answer Question Concentration of species-500 • QUESTION: From highest to lowest concentration, what are the species present in a 1 molL-1 solution of HCOONa? • ANSWER: H2O >> HCOO- = Na+ > OH= HCOOH > H3O+ Answer Question Titration curves-100 • QUESTION: The concentration of HPab (a weak acid) solution was determined by titration. A 20.0 mL sample of the HPab solution required 12.0 mL of 0.0500 mol L–1 NaOH to reach the equivalence point. The equation for the reaction occurring is HPab + NaOH → NaPab + H2O Calculate the concentration of the HPab solution. • ANSWER: 0.03 molL-1 Answer Question Titration curves-200 • QUESTION: Explain why the pH at the equivalence point for this titration is less than 7. (Include an equation to support your answer.) • ANSWER: Titration is weak base strong acid. At equivalence point there is the conjugate acid of the weak base which means pH<7 NH3 +HCl→ NH4+ + Cl- Answer Question Titration curves-300 • QUESTION: What is the Ka for the acid shown? • ANSWER: 1.78 x 10-10 Answer Question Titration curves-400 • QUESTION: 20.0 mL of the weak acid HPab (0.03 molL-1) is titrated against 0.05 molL-1 NaOH. The Ka of (Pab-) is 1.2 x 10-5. Its initial pH is 3.22. Using the information above, sketch a curve showing the change in pH against the volume of sodium hydroxide added to the solution in the flask. • ANSWER: Curve has: pH 3.22 at 0mL, 4.92 at 6 mL, and end point pH 8-10 at 12 mL, correct shape Answer Question Titration curves-500 • QUESTION: A titration is carried out – 40.0 mL of 0.0500 mol L–1 NaOH solution is titrated against 0.200 mol L–1 CH3COOH solution. Calculate the pH after 5 mL CH3COOH added. • ANSWER: 12.3 Answer Question Pot luck-100 • QUESTION: The titration curve is for ethanoic acid + NaOH. What is the Ka for ethanoic acid? Show working • ANSWER: pH = pKA at ½ moles base added. So pKa = 5. Ka = 10-5 = 1x 10-5 Answer 14 13 12 11 pH 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 A 2 1 0 2 Question D C B 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Volume of NaOH (mL) Pot luck-200 • QUESTION: The titration curve is for ethanoic acid + NaOH. List the species present in decreasing concentration at point B • ANSWER: H2O>>CH3COOH = CH3COO-=Na+>OH- Answer 14 13 12 11 pH 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 A 2 1 0 2 Question D C B 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Volume of NaOH (mL) Pot luck-300 • QUESTION: Indicator pKa Thymol blue 1.7 Chlorophenol red 6.1 Cresol red 8.3 Choose the best indicator for the titration. Give a reason. • ANSWER: Cresol red – its pKa means it would change colour in the range of the equivalence pint of the titration Answer 14 13 12 11 pH 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 A 2 1 0 2 Question D C B 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Volume of NaOH (mL) Pot luck-400 • QUESTION: Discuss how a buffer solution of pH = 3.3 could be prepared from solutions of 0.01 mol L–1 HNO2 and 0.01 mol L–1 KOH. Include relevant equations in your answer. pKa (HNO2) = 3.3 • ANSWER: Mix 10 mL of HNO2 with 5 mL of KOH.(or equivalent) HNO2 + OH– NO2– + H2O At half neutralisation conc. HNO2 = conc. NO2- and therefore Ka = H3O+ pKa = pH Answer Question Pot luck-500 • QUESTION: An acid base indicator has the formula HIn. It is yellow in the presence of any acid solution and blue in the presence of any base solution. pKa for HIn is 7.0. Using chemical equations explain how such an indicator works. Explain under what conditions and pH the indicator is green. • ANSWER: The indicator HIn is a weak acid and reacts with water as shown in the equation. HIn(aq) + H2O(aq) → In-(aq) + H3O+(aq) The HIn form of the indicator is yellow and the In- form is blue. If acid, i.e. hydronium ions are added to the indicator solution, the position of equilibrium is shifted to the left hand side, forming more HIn and therefore giving an yellow colour. If base is added to the indicaor solution, the hydronium ions will react with it, shifting the equilibrium position to the right, forming more In-, and therefore giving a blue colour. At apH of 7 the concentration of the HIn and the In- will be equal and the colour of the solution will be a mixture of blue and yellow, i.e. green. Answer Question FINAL JEOPARDY • ANSWER: • QUESTION: Answer Question