Amino Acids notes
advertisement
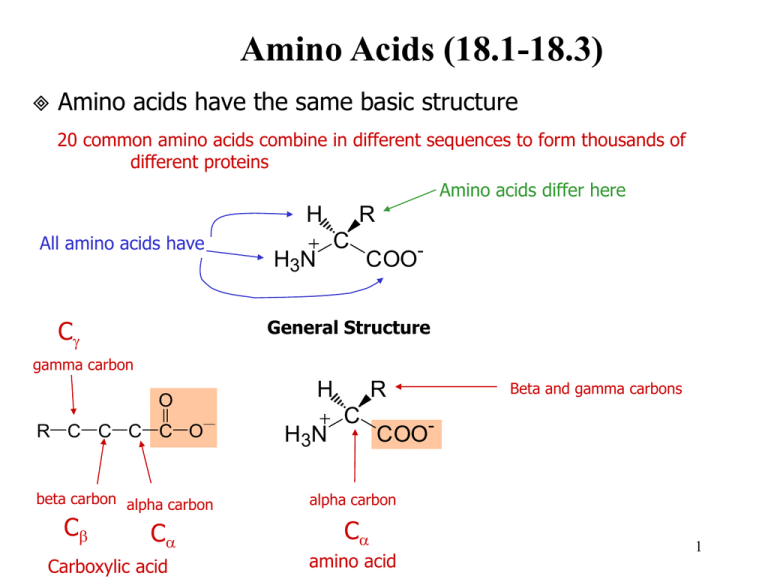
Amino Acids (18.1-18.3) Amino acids have the same basic structure 20 common amino acids combine in different sequences to form thousands of different proteins Amino acids differ here H All amino acids have Cg R C H 3N COO- General Structure gamma carbon O R C C C C O beta carbon alpha carbon Cb Ca Carboxylic acid H H 3N R C Beta and gamma carbons COO- alpha carbon Ca amino acid 1 Which of the following are alpha amino acids and which are not? 2 Classification of Amino Acids Nonpolar amino acids H3N CH C O H3N CH C O O H CH3 glycine alanine CH2 CH3 CH2 CH CH3 CH3 CH3 isoleucine O H3N CH C O methionine HN phenylalanine O O H3N CH C O H3N CH C O O H3N CH C O H3N CH C O CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH3 C O CH2 SH OH OH NH 2 C O cysteine serine asparagine NH2 CH C O H3N CH C O CH2 CH2 CH2 C O C O O aspartic acid (aspartate) CH2 tyrosine OH Polar charged basic amino acids O H3N CH C O O glutamic acid (glutamate) H3N CH C O threonine glutamine O O O CH2 O proline tryptophan O H3N CH C O leucine C O H 2N CH3 Polar H3N charged acidic amino acids O CH2 S Polar uncharged amino acids H3N CH C O CH CH3 CH2 CH2 O CH CH3 valine H3N CH C O CH2 H3N CH C O H3N CH C O O H3N CH C O O O O O arginine O H3N CH C O O CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH CH2 C NH2 NH 3 3 NH lysine histidine NH2 H3N CH C O CH2 N Amino Acid Abbreviations Name Glycine Alanine Valine Leucine Isoleucine Proline Phenylalanine Tyrosine Tryptophan Cysteine Methionine Lysine Arginine Histidine Aspartate Glutamate Asparagine Glutamine Serine Threonine 3-letter Single-letter abbreviation abbreviation Gly Ala Val Leu Ile Pro Phe Tyr Trp Cys Met Lys Arg His Asp Glu Asn Gln Ser Thr G A V L I P F Y W C M K R H D E N Q S T 4 Amino acids are weak polyprotic acids (18.4) both the amino and carboxy groups are protonated at low pH. Carboxy loses proton first and then amino loses at high pH. H H O H H O H N C C O H N C C O H H R H R lower pH “many protons” neutral pH H O H N C C O H R higher pH Amino acids are zwitterions (dipolar) zwitterions have charged residues but are electrically neutral the amino and carboxy charges cancel each other out at neutral pH so aa wo/ charged side chains are uncharged at neutral pH H H 3N R C - Isoelectric point, pI pH where amino acid is electrically neutral depends on the R group also COO 5 Amino Acid pKa’s Amino Acid Alanine Arginine Asparagine Aspartic Acid Cysteine Glutamic Acid Glutamine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Proline Serine Threonine Tryptophan Tyrosine Valine a-carboxylic a-amino acid 2.34 9.69 2.17 9.04 2.02 8.80 2.09 9.82 1.71 10.78 2.19 9.67 2.17 9.13 2.34 9.60 1.82 9.17 2.36 9.68 2.36 9.68 2.18 8.95 2.28 9.21 1.83 9.13 1.99 10.60 2.21 9.15 2.63 10.43 2.38 9.39 2.20 9.11 2.32 9.62 Side chain 12.48 3.86 8.33 4.25 6.00 10.53 10.07 6 Titration of Amino Acids Amino acids have titration curves like diprotic or triprotic acids net charge 0 +1 -1 pK2 X O H2N CH C O Net charge +1 O H3N CH C OH H X H pI X H3N O CH C O H Net charge -1 Net charge 0 pK1 7 Alanine similar to diprotic acid 8 Histidine similar to triprotic acid 9 Amino Acid Questions. Explain in detail with structures and equations where applicable. 1. Given a peptide with the following amino acid sequence, identify the polar amino acids, the aromatic amino acids, and the sulfur-containing amino acids. Val-Met-Ser-Ile-Phe-Arg-Cys-Tyr-Leu 2. Write equations to show the ionic dissociation reactions of the following amino acids: aspartic acid valine 3. Draw the predominant ionized forms of the following amino acids at pH 7: glutamic acid histidine arginine 4. Based on the pKa information for amino acids, is there any amino acid that could serve as a buffer at pH 6? If so, which one(s)? 10 Amino acid questions continued. 5. Sketch a titration curve for the amino acid cysteine; indicate the pKa values for all titratable groups. 11 Amino acids have handedness (18.5-18.6) Chirality - an object or molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image image is chiral your left and right hands are mirror images of each other. They are non-superimposable mirror images. You cannot exactly superimpose your left and right hands. Molecular handedness Molecules with carbon are frequently chiral carbon must have 4 different groups bound to it - called a chiral carbon or chiral center. non-superimposable mirror images - chiral The presence of one chiral carbon always produces a chiral molecule A molecule with more than one chiral carbon may or may not be chiral overall superimposable mirror images - achiral 12 In the type of chiral center we are intersted in, carbon must have 4 different groups attached: The chiral atom that makes the overall molecule chiral Examples: Propane CH3 H C H CH3 Has 2 sets of Chloroethane identical groups attached (the H hydrogens and the methyl groups) achiral Cl C H Has 2 identical atoms attached (the hydrogens) achiral CH3 Amino acids Groups attached to Ca of amino acids H H 3N 1. 2. 3. 4. COOH NH3+ R group NH3+ R C NH3+ - COO Ca H 4 different groups attached in all amino acids except glycine (the R group is hydrogen) CH3 CH3 Ca H COO- COO- Alanine enantiomers 13 Label the chiral center in the following molecules if one is present. NH3 OH O H3C CH C H3C OH C NH3 CH3 Cl H3C H2 C CH H3C H2 C C CH3 Cl H2 C CH3 H3C CH H2 H2 C C CH3 Two of the 20 common amino acids have two chiral carbon atoms in their structures. Identify these amino acids, draw their structures below, and label their chiral centers. 14 Enantiomers - molecules that are non superimposable mirror images of each other Enantiomers have the same name but are distinguished by a prefix R vs. S system most commonly used D vs. L is older nomenclature only L amino acids are in making proteins (L for “Life”) Enantiomers have many identical physical properties: melting and boiling points same pI same solubility in water same density Enantiomers have some physical and chemical properities that differ rotate plane polarized light in opposite directions reactivity with other chiral molecules **biological activity **odors and tastes **activity as drugs 15 Examples of the differing biological activity of enantiomers: CH3 Chiral center CH3 O O Chiral center H2C C H H CH3 L-Carvone (in spearmint) Chiral center C CH2 H3C mirror D-Carvone (in caraway) Chiral center (R)-Limonene (S)-Limonene (smell of oranges) mirror (smell of lemons) 16 Chiral center Chiral center O O H O H N O N HN NH O O O (R)-Thalidomide (sedative) H mirror CO2H CH3 O (S)-Thalidomide (fetal abnormalities) HO2C H H3C H3CO OCH3 (S)-Naproxen (anti-inflammatory) mirror (R)-Naproxen (liver toxin) Must be sold as 97% S enantiomer 17