Input Service
advertisement

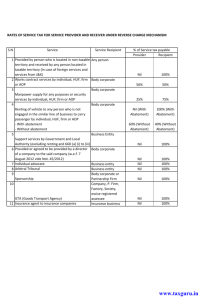
CENVAT - OVERVIEW AS PER NEGATIVE LIST By Bhupendra Agarwal Cenvat Credit – An overview Output o Excisable goods o Taxable services Procurement o Capital goods o Inputs o Input services – Excise duty – Service tax – Excise duty - Excise duty - Service tax # Equivalent paid on import of goods / services Only value addition is taxed as set off given for taxes paid on procurement Only goods / services to be exported AND not the taxes Business – Manufacturer of Goods Cenvat not available if business is EXEMPT: S. No Particulars Availability of Cenvat Credit 1 Fully exempt from ED NO 2 Chargeable to NIL rate NO 3 2% ED # NO 4 Export outside India YES 5 Goods supplied to SEZ Developer / Unit YES 6 Goods supplied to EOU / EHTP / STP YES 7 Goods supplied to Mega Power Project YES * # Notf 1/2011 – CE and 12/2012 – CE (entries at Sl. No. 67 and 128) * Subject to prescribed conditions Business – Provider of service Cenvat not available if business is EXEMPT: S. No Particulars Availability of Cenvat Credit 1 Negative List / Exempt from Service tax NO 2 Not leviable NO 3 Part of the value is exempt NO* 4 Trading in Goods NO 5 Export outside India (including by SEZ Unit) YES 6 Services provided to SEZ Developer / Unit YES 7 Service provider located in Non-Taxable territory (J&K) NO * Conditional exemption – Exemption available only if credit on inputs and input services NOT taken Capital Goods – Definition Capital Goods MEANS the following: S. No Particulars Recipient # A (i) CH 82, 84, 85, 90, 68.02 and 6801.10 Both (ii) Pollution Control Equipment Manufacturer (iii) Components, spares and accessories (i) and (ii) Both (iv) Moulds and dies, jigs and fixtures Both (v) Refractories and refractory materials Manufacturer (vi) Tubes and pipes and fittings Both (vii) Storage Tank Both # To be used in the factory of the manufacturer or for providing output service $ Outside the factory for generation of electricity for captive use of electricity within the factory also eligible Capital Goods – Contd.. Capital Goods MEANS the following: S. No Particulars Recipient # (viii) Motor vehicles and their chassis including dumpers and tippers (excluding falling under tariff headings 8702, 8703,8704,8711) Manufacturer B Motor vehicles (including chassis) designed for transportation of goods registered in the name of service provider Renting of motor vehicle, transport of goods by service provider and Courier agency C Motor vehicles (including chassis) designed to carry passengers registered in the name of service provider Transportation of passengers, renting of motor vehicle, imparting motor driving skills 10 Components, spares and accessories of capital goods which are capital goods for user Manufacturer and Service provider Issues Capital Goods o Used outside the factory - Implications when part of the electricity is either sold to grid / consumers or transferred to other factories Inputs – Definition Inputs INCLUDES the following: S. No Particulars Recipient 1 Used in the factory Manufacturer 2 Cleared with Finished product (accessories) Manufacturer 3 Replacement under free warranty Manufacturer 4 Generation of electricity / steam – captive use Manufacturer 5 Providing output service Service Provider Inputs – Inputs EXCLUDES the following: Contd.. S. No Particulars Recipient 1 LDO / HSD / Petrol Both 2 Construction of building / Civil structure or execution of Works Contract * Manufacturer / Service provider 3 Foundation / Structure for capital goods 4 Capital goods Both 5 Motor vehicles Both 6 Food items, used in guest house etc (personal use of employee) Both 7 No relationship with manufacture Manufacturer * Admissible only for execution of service portion in the Works contract or construction service specified in section 66E(b) Issues Inputs Is consumption of goods necessary in order to be ‘inputs’? Is anything which is not ‘capital goods’ to be treated as ‘inputs’? Treatment of goods used outside the factory (for instance mines, power plant) If motor vehicle excluded, whether cycle can be treated as input? Inputs used in manufacture of capital goods Sector specific Telecommunications Towers Cement / Steel plant (Mines) Input Service – Definition Input Service INCLUDES the following: S. No Particulars Recipient 1 Providing output service Service Provider 2 Manufacture of final product Manufacturer 3 Clearance / Outward transportation of finished products (up to the place of removal) Manufacturer 4 Modernization, renovation or repairs of factory / office / premises Both 5 Others (As specified) Both Input Service – Contd.. Input Service EXCLUDES the following: S. No Particulars Recipient 1. Service portion in the execution of Works Contract Manufacturer/ Service and construction service used for building / civil provider * structure and foundation for support of capital goods 2. Renting of motor vehicles – if motor vehicle is NOT a capital goods Both 3. In relation to Motor vehicles - General insurance, servicing, repairs and maintenance – if motor vehicle is NOT a capital goods Both ** 4. Personal use or consumption of any employee (outdoor catering, beauty treatment, life and health insurance, travel benefits) Both * Specified service provided by service provider are eligible ** Manufacturer of motor vehicle and insurance company eligible in specified cases Issues Why there is a need to give restricted definition to input services when the definition of “Service” including almost everything under the Sun……………. Service to be used by manufacturer / service provider to be termed as input service o Even though the provider of service require to pay service tax even if no services are provided (agreed to be provided, amount received and forfeited) Non – compete fees paid to competitor liable for payment of service tax o Whether Coke / Reebok can take credit for amount paid to Pepsi / Bata for closing their business » Amount paid to rule out competition but not related to manufacture Exempted service Why there is a need to clarify that services exported are not “Exempted service” Trading in goods not specified as “Exempted service” but Rule 6(3) consider the same as exempted service for reversal of Cenvat credit Issues Contd.. No concept of “Capital services” – How to avail credit of input services avail during setting up of the Factory / premises etc No turnover during setting up period hence ratio method can not be applied Implications of deletion of the phrase “Setting up” from the definition of input service Personal use or consumption of employee – distinction between personal and official Conditions for Availing Cenvat Credit Manufacturer Inputs & capital goods On receipt of goods in the factory Duty paying documents received from supplier Service provider Inputs & capital goods On receipt of goods at any place Duty paying documents received from supplier Manufacturer and Service provider Input services Service are received Invoice containing prescribed particulars is received Refund of CENVAT – Specified cases Export of goods / services outside India Service recipient is liable for payment of Service tax Refund not admissible Goods supplied to STPI / SEZ Unit / Developer Goods supplied to Power Plant eligible for excise duty exemption Imported goods where higher duties are paid (ACD plus SAD) Draw drawback / Rebate of duties are claimed Cenvat – service recipient pays ST Specified services – Service tax liability on Service recipient Output service definition excludes services where service recipient is liable to pay service tax As per Rule 3, Cenvat credit admissible to provider of Output service If the services are not “Output service” how service provider is eligible to claim Cenvat credit New Rule 5 B of CCR grants refund of unutilized Cenvat credit when service recipient is liable to pay service tax Without availing credit how to claim refund Input Service Distributor – Concept Manner of Distribution : i.) No credit distribution exceeding ST paid. Ii.) No Credit distribution to Unit – Engaged in Exclusive Manufacture of Exemtped Goods/ Providing of Exempted Services Iii.) Distribution of Full credit to single unit – wholly attributable Iv) Otherwise prorata basis – turnover basis of relevant period No distribution when no turnover for a Unit. Relevent period means :Expl 3(a) : The month prior to the month in which CENVAT Credit distributed. Expl 3(b) : The quarter prior to the quarter in which CENVAT Credit distributed – Special cases – ST paid per Rule 6 of ST Rules 1994 or Rule 8 of CE Rules 2002. Some more …………… Service tax under reverse charge to be paid in Cash and not by Cenvat No payment required to be made where inputs are removed ‘as such’ outside the factory for providing free warranty of final product Partial provision or write-off of CG or inputs also to attract reversal of Cenvat credit Cenvat credit can not be used for payment of service tax as a recipient of service tax Service tax to be paid if services are received from provider located in Jammu & Kashmir (Non-Taxable territory) What if contract is executed in J&K and part of the work sub-contracted to service provider located in J&K who raises invoice on company located in Hyderabad Availing Credit – Optionssssssssss Rule Scheme Rule 6 (1) Credit not allowed on inputs / input services used for exempt business Rule 6 (2) Credit allowed only on input / input services used for taxable business provided separate accounts are maintained for input and input services Rule 6 (3) Where separate accounts are not maintained:- Rule 6 (3) (i) Outright payment on exempt output Pay 6% of exempt business Output service whose part of the value is exempted (condition no credit allowed on inputs and input services), Cenvat credit allowed on payment of 6% of the exempted value 6% payment to be considered as credit not availed for the purposes of such exemption notifications Rule 6 (3) (ii) - Rule 6 (3A) Proportionate credit for taxable business Pay proportionate credit for exempt business (Take full credit and reverse for exempt) Rule 6 (3) (iii) Cocktail - 6(2) for inputs & 6 (3A) for input services Scheme for availing Credit Rule Cocktail Rule 6 (3) (iii) Scheme Loss of proportionate credit on input services exclusively used for taxable business Gain of proportionate credit on common input services and input services exclusively used for exempt business Trading ‘Value’ in the case of ‘Trading’: Difference between purchase and sale value Explanation to to be considered for the purposes of reversal of Cenvat credit Rule 6 (3) and 6 (3A) BFS / NBFC Provider of BFS eligible to avail only 50% of Cenvat credit (Net) Cenvat Credit – Other issues 1. Trading of Securities : Exempted part of Service for the purpose of Cenvat credit – i.) Diff between Selling Price and Purchase Price; or ii.) 1% of Purchase price whichever is more Issue : What if purchase and sale of securities occurs in different years 2. Loans, Deposits and Advances CENVAT Credit not to be reversed with respect to Loans, Advances and Deposits represented by way of Interest or Discount. 3. Banking and Financial Institutions including NBFC 50% of CENVAT Credit(on inputs/input services) availed to be paid every month. THANK YOU