Work,Energy,Power, New0
Work…
In everyday speech work has a very general meaning.
In describing motion in physics, work has a very specific meaning.
Chair Example
Standing Walking
No work is done on the chair
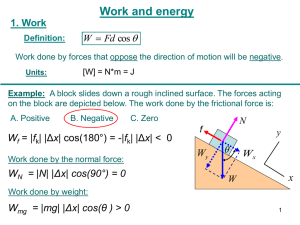
Work is defined as the product of the force applied to cause motion and the distance the object moves in the direction of the force.
Work is done only when components of a force are parallel to a displacement
FORMULA
W = fd
IN DIRECTION OF MOTION
The symbol for work is W
Work has 2 acceptable units
Nm
Joules (J)
JOULE
Lifting an apple about
2ft is a Joule
3 good push-ups is about 1000J
Situations that affect the sign of work
Force is in the direction of motion
Force opposes motion
Force is 90° to motion
Object is not in motion
Positive Work
Negative Work
No Work
No Work
10N
Moves 2m
W = fd
W = 20J of Work
Notice direction of motion is the same as the applied force
10N
How would you solve this? Force applied is NOT in the same direction as the objects motion.
Y
X
60°
2m
Think back to vectors and use the component of the force applied in the direction the object moves.
Y
X
10N
COS θ = adj/ hyp
COS 60° = force parallel to motion
10N
60° force para. =
COS 60° (10N) force para. = 5N
2m w = F(parallel) D
5N (2m) = 10Nm
W = Fd (COS θ)
Always measure angle with horizontal!
The above formula works in every case
θ = 0°
θ = 90°
No work because no motion in direction of force
Pg. 170
Problems
1-4
Section Review p. 171
With your Neighbor, answer questions
2, 3, 4
Section Review Answers
2 the neighbor, twice as much
3 a-negative
B-positive
C- negative
4 a-yes
B- no
C-yes
Energy
The Stuff that makes things move
The ability to do work
Has the units of Joules (J)
There are 2 kinds of mechanical energy
Kinetic Energy
This is the energy associated with an objects motion.
KE depends on mass and velocity
When the object is treated as a particle, the formula for KE is…
KE = ½ mV 2 manipulated
V = 2KE/m M = 2KE/V 2
KE is a scalar quantity
The SI unit for KE is the Joule, yes the same as for work
Look at sample prob. 5B
Page 173
DO practice problems
5B 1-5 on page 174
Work- Kinetic Energy
Theorem
The net work done on an object is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the object
W net
W net
= ΔKE
= KE final
– KE initial fd(cos θ) = ½ mV 2
The KE of an object is equal to the work that moving object can do
This theorem allows us to think of
KE as the work an object can do as it comes to rest, or the amount of energy contained in the moving object
The KE of the moving hammer can do work
KE = Work done (net) fd = ½ mv 2 some of the energy is sound, heat and light (if spark)
Practice Problems 5C p.176 #1 and 4 only
Potential Energy
2.
This is the energy associated with an object due to the position of the object.
1.
STORED ENERGY
There are two kinds of potential energy
GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL
ENERGY
ELASTIC POTENTIAL ENERGY
Gravitational Potential
Energy (PE g
)
The energy associated with an object due to the objects position relative to a gravitational reference
Wh = PE g
= mgh
= mass x gravity x height acceleration gm = w
Has the unit of joules
Elastic Potential Energy
(PE elastic
)
The energy associated with a stretched or compressed elastic object
Spring, bungee cord, rubber band
Elastic Potential Energy
Overhead
(springs)
In both the compressed and stretched example, energy is stored
PE elastic
= ½ KX 2
K = spring constant
X = distance stretched or compressed
Practice Problems
5D 1-3 pg. 180
Conservation of Energy
To say something is conserved is to say it remains constant. Something can change form and still be conserved.
burning log: matter and energy are conserved.
5Kg 5Kg
ASH
Pendulum
Energy is transferred from one form to another
As the pendulum swings,
PE is transferred to KE. As the bob swings upwards
KE is stored as PE
PE = max
KE = min
PE = min
KE = max
PE = max
KE = min
PE = mgh
10M
A falling egg
Mass = .1kg Height = 10m
PE = 10 J
KE = 0 J
PE = 5 J
KE = 5 J
PE = 0 J
KE = 10 J
Mechanical Energy
The sum of Kinetic Energy and
ALL forms of Potential energy associated with an object or group of objects
ME is not a unique form of energy. Its merely a way of classifying energy
ME includes KE and PE
Mechanical Energy
ME is different from non mechanical energy (nuclear, chemical, thermal, internal, electrical)
ME = Σ KE + Σ PE
ME = ½ mv 2 + mgh
(if PE is NOT present, elastic)
Conservation Of
Mechanical Energy
Conservation of Mechanical
Energy can also be written as…
ME i
= ME
½ mv i
2 f
+ mgh i
= ½ mv f
2 + mgh f
True when friction can be ignored
The Law of Conservation of Energy:
The total energy of a closed system is constant.
Often is the case that KE or PE i or PE f that is the case… i or KE will be zero. When f mgh = ½ mv 2
2mgh = v 2 m
V = 2gh h = V 2
2g
Problems p.185
Look at sample problem 5E
Practice problems 5E #s 5,2,1
HOMEWORK!!
28-31, 33, 34a
All on page 195 of packet
Power
This quantity also has a very specific meaning in science that can be confused by common English usage
Power is the rate of doing work
That is to say that power is the rate at which energy is transferred
Power
Power = Work = fd
Time t
Power is work done divided by the time taken to do the work
P = w t
Power is measured in watts (W) J/s
A watt is a small unit, 1 watt is about what is needed to lift a 2N glass of water
.5m to your mouth in 1 second.
Watts
Since watts are so small, we sometimes use Kilowatts
1 KW = 1000W
Watts are metric
Horse power is traditional
1 Horse power = 746 Watts
Watts
Watts are named after
James Watt, the inventor of the steam engine
Practice Problem
An electric motor lifts an elevator that weighs 12000N a distance of 9m in
15sec
What is the motors power in watts?
What is the motors power in kilowatts?
Given Formula
Solution f = 12000N P = fd/t
P = 12000(9) d = 9m
15 t = 15s
A. P = 7200 W
P = ?
B. 7.2 KW
Sample Problem p. 188
Pg. 189
5F
5, 4, 3, 2