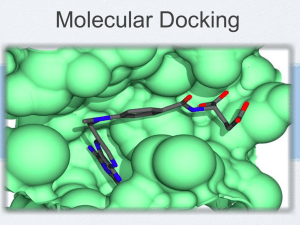
Docking molecules with Vina
advertisement

Docking molecules with Vina Autodock Vina To study molecules they must be docked • Docked molecules bind their enzyme or receptor in a specific conformation • Docked molecules bind with high affinity • The best way to get docked conformation is to use X-ray crystallography • Alternative: use docking software like Vina to predict docked conformation What is docking? • Find the conformation with which a ligand binds a receptor • This information includes full coordinates of all ligand atoms • The docked configuration is the (presumed) lowest energy binding site Steps • 1. get protein structure • 2. create files with protein only • 3. Use a known ligand (not your ligand) to define the ligand binding site • 4. Generate some modified structure files • 5. Use files with docking software • 6. Extract predicted conformation and make new file with protein and target ligand docked Make a folder • Need a place to store many files • Make c:\thesis Get PDB file • • • • • • • • Go to PDB RSCB on web Search for PDB code if unknown Once PDB code is known, download it Use PDB/Tools, download entries and follow instructions You must have Java enabled Change mmCIF to PDB as type of file Change compressed to uncompressed Save in your thesis folder PDB search PDB download PDB info – Protein name PDB – ligand name (HET) PDB coordinates Start with PDB file with protein and ligand (not your ligand) • Make a copy of the PDB file • Split it into only protein and only ligand • Ligand will be used to get coordinates of binding site • Example: beta adrenergic receptor and carazolol • 2rh1.pdb Use wordpad text editor • Copy cau (= carazolol, ligand) from 2rh1 • Paste into a file called car.pdb • REMARK carazolol • • • • • HETATM HETATM HETATM HETATM HETATM 3598 3599 3600 3601 3602 O17 C16 C18 N19 C20 CAU CAU CAU CAU CAU A A A A A 408 408 408 408 408 -33.477 -32.267 -32.478 -33.702 -33.806 10.957 10.230 8.951 8.250 6.805 8.170 8.041 7.225 7.600 7.498 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 50.96 45.65 51.24 54.99 60.13 O C C N C PDB files have 3D structure information including XYZ coordinates of atoms • Also have atom numbers • Residue numbers • Atom types Find the center of the ligand • This will be the center used when you dock your ligand to the receptor • Start with the X coordinate. Add all the X values and then divide by the number of atoms. Record for later • Repeat for Y and Z coordinates • The only purpose of having a ligand at this point is to define the ligand binding site. Find coordinates • • • • • • • • • z y x REMARK carazolol HETATM 3598 O17 CAU A 408 -33.477 10.957 8.170 1.00 50.96 HETATM 3599 C16 CAU A 408 -32.267 10.230 8.041 1.00 45.65 HETATM 3600 C18 CAU A 408 -32.478 8.951 7.225 1.00 51.24 HETATM 3601 N19 CAU A 408 -33.702 8.250 7.600 1.00 54.99 HETATM 3602 C20 CAU A 408 -33.806 6.805 7.498 1.00 60.13 O C C N C Carazolol – no hydrogens Visualizing structures • Try rasmol or raswin • Download at google: rasmol bernstein • Several web tutorials available Adding hydrogens • • • • Hydrogen is rarely found in PDB files But all atoms are needed to dock molecules Solution: add back missing hydrogens We will use Babel OpenBabel • • • • Download openbabel from its web site Install Use the command prompt to run the program Use a full ‘path’, that is a description of the program location • Add hydrogens • On my machine that is (one line): • \lm\downloads\openbabel-2.1.1\babel.exe -ipdb car.pdb –opdb carH.pdb -h Add H Check that hydrogens have been added • • • • • • HETATM HETATM HETATM ATOM ATOM ATOM 20 21 22 23 24 25 C1 C6 C5 H H H CAU CAU CAU CAU CAU CAU 408 408 408 408 408 408 -26.395 -27.717 -28.269 -34.319 -31.904 -31.591 6.432 6.731 7.948 10.255 9.929 8.256 7.689 8.006 7.652 8.260 9.079 7.396 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 C C C H H H Other ligands • Up to now we have been dealing with the ligand found in the PDB file with your receptor/protein • You may wish to try docking that ligand as a control • At some point you will want to deal with other ligands Getting other ligands • To use ligands they must be transferred from the page to PDB format • Some ligands may be present in other files in the protein data bank – try searching • Ligands can be drawn, e.g. with DS Viewer Pro or other software and saved in PDB format • Most ligand files will have to have hydrogens added Add hydrogen to the protein • Repeat ligand procedure, but with protein • We did car.pdb carH.pdb • Now make copy of the protein pdb file with the ligand deleted (e.g. CAU in this example) • (you can delete WAT and other ligands too) • Now, with full path, use babel to add H Add hydrogen to protein • Full path on my machine (yours will differ) • \lm\downloads\babel-2.1.1\babel.exe –ipdb bar.pdb –opdb barH.pdb -h • Result: bar.pdb barH.pdb We’re almost ready to dock • But we need two things: • Torsions • Hydrogen bonds Torsions • The ligand may have rotatable bonds • Benzene can not twist (0 torsions) • Hexane can twist (3 torsions, we’ll ignore rotating methyl groups) • MGLtools calculates these • Vina will twist the ligand to try to find the best fit during docking H bonds • We need to find H bond acceptors and donors • MGLtools also calculates these MGLtools • • • • • MGLtool, ADT, Autodock tools are the same Download from MGLtools site Install Read tutorial Click to open window MGLtools MGLtools We will use MGLtools/Autodock tools for two things: Annotate the ligand(s) Annotate the receptor Autodock / MGL tools • First we will process the ligand to add torsions and H bond information • On left side of ADT screen find ligand menu • Open ligandH.pdb (or other file) • Note: this is the ligand file you want to dock, not the X-yl structure file, unless you are docking it as a control Autodock/MGLtools and ligand • • • • • Select torsion tree Find the ligand torsion ‘root’. Detect root Aromatic carbons: set names Output: Save file as carH.pdbqt It is key that you save the pdbqt file that MGLtools makes ADT and protein/receptor • Find ‘grid’ menu • Macromolecule • Open receptor file with hydrogens (receptorH.pdb) • The file gets processed • Save as ligandH.pdbqt • Do not choose ‘flexible’ ADT receptor refinement • Now the receptor file and ligand file have been saved as .pdbqt files. • These have H bond and torsion information • Look at the ligandH.pdbqt file using wordpad or simpletext • It still looks like a .pdb file, but has extra information added Now we have all of the files that we need to dock a ligand • • • • Let’s check: receptorH.pdbqt ligandH.pdbqt Binding site coordinates Setting up Vina • • • • • • Vina needs to know what you want to do: What receptor What ligand Where the binding site is Where to send out the results This information is placed in a file called config.txt Configuration file, config.txt • Config.txt gives information to Vina as it docks your ligand • The left side of each = is Vina code (don’t change) • The right side of each = is your input • You control the site of binding, the size of the site, and the receptor and ligand Example Vina configuration file out = out_carh.pdbqt receptor = 2rhe.pdbqt ligand = carh.pdbqt center_x = -28 center_y = 9 center_z = 6 size_x = 25 size_y = 25 size_z = 25 energy_range = 4 Download Vina • Web site AutoDock Vina • Install in ‘thesis’ folder, or wherever your config file and .pdbqt files are saved. • Get the right version of Vina for your computer (e.g. PC vs. Mac) Autodock Vina Read manual! Dock ligand • Open command prompt • Make certain that command prompt is pointed to thesis directory/folder • Use the cd command with command prompt or Mac command screen Finding the right directory • If necessary change directory using ‘cd’ • E.g. type ‘cd \thesis’ [without the quotes] for a PC • Or type ‘cd /thesis’ [without quotes] for mac • This assumes that you put all your files in the directory ‘thesis’ on the c:drive or equivalent • Type dir/p [PC] or ls [Mac] to check that your files are present Vina docking To dock, type : vina.exe --config config.txt Vina docking Vina output • It takes a minute or two for Vina to dock • This represents millions of docked positions being analyzed • The output file name is defined by the config file out = outfilename.txt • Each outfile has several models • We usually only care about model 1, the best Output score • We often want to know how tightly a ligand binds • Vina gives an estimate in the output file • Look for Vina Result: x • If x is -10 or less, binding is very tight • If x is -6 to -7 binding is just random, not tight • In between is hard to judge Visualizing a docking • The easiest way is to splice the best ligand model onto the receptor with its ligand removed • Open the outfilename.txt (whatever you called it in config.txt) – the Vina output • Copy from the beginning of model 1 to model 2 [note the residue number of the ligand] • Paste into a copy of the receptor pdb file with the old ligand removed Seeing is believing • Now you can open your new file with receptor and docked ligand using RasWin or another visualization program • Use the residue number of the ligand to select it (e.g. select 480) • Convert to spacefill (e.g. spacefill) • How does it look? Is it in a binding pocked? Next steps • Having a ligand binding model is valuable • Specific contacts can be analyzed • By comparing two or more models and the contacts that they make, patterns of receptor change can be determined • E.g differences between active and inactive receptors or receptor subtypes can be understood