No static solution - Red Hook Central School District
advertisement

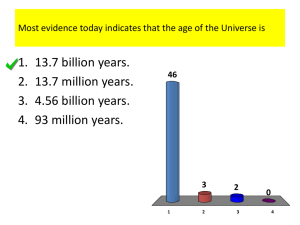
Big Bang Timeline 10-45 sec (1032K) 10-35 sec (1027 K) We have no physics to describe conditions at these large energy densities and high temp. Inflation begins, Quark-Antiquark Freezeout starts (1,000,000,001 quarks to every 1,000,000,000 antiquark) 10-32 sec (1025 K) Inflation ended, present-day observable Universe was ~10 cm across 10-5 sec (1013 K) Protons and neutrons form (no more free quarks) 1-15 min (108 K) First elements (2H and 4He nuclei) form 380,000 yr (3000 K) Atoms form from nuclei and electrons 100 Myr (10 K) Stars, galaxies, and planets begin to form. We think the first stars ionized the Universe and created heavy elements. Then star clusters and dwarf galaxies formed from later generations of stars. These star groups merged together to form larger and larger galaxies. 10 Gyr (3 K) Present Universe, expanding exponentially 1978 Nobel Prize in Physics: discovery of Cosmic Background Radiation(CBR), the “echo” of the Big Bang 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics : The discovery of the accelerating Universe Saul Perlmutter Brian Schmidt Adam Riess Modified from a presentation by: Heidi Newberg Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute With Newtonian physics, it is impossible to predict the future of the Universe Gravitational attraction should pull all the galaxies together Einstein’s Field Equations Stuff describing the curvature of space(time), otherwise thought of as the Force of Gravity. Stuff like mass and energy Einstein’s Field Equations is related to Stuff describing the curvature of space(time), otherwise thought of as the force of gravity. Stuff like mass and energy Is the Universe FLAT? The density of the universe also determines its geometry. If the density of the universe exceeds the critical density, then the geometry of space is closed and positively curved like the surface of a sphere. If the density of the universe is less than the critical density, then the geometry of space is open (infinite), and negatively curved like the surface of a saddle. If the density of the universe exactly equals the critical density, then the geometry of the universe is flat like a sheet of paper, and infinite in extent. http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/media/990006/index.html There is no static solution If mass pulls the Universe together, we cannot have a Universe that stays as it is forever. is related to Einstein’s Field Equations + Λ No static solution is related to Add a part that pushes the Universe apart Λ = the cosmological constant Doppler shift and inverse square law Objects that are moving away have longer wavelengths. Objects that are farther away look dimmer. If you know how bright a source is, you can determine the distance by how bright it seems. Hubble’s Law Around 1930, Hubble showed that the speeds with which galaxies were moving away from us is proportional to their distance from us. (Km/S) v = H0d, where H0 is Hubble’s constant (Measured from Doppler shift of spectral lines) (Mpc) (Measured from brightest stars method) Expanding Universe Expanding Universe Supernova in IC4830 Image of galaxy with supernova Image of galaxy Supernovae get brighter and dimmer again within a few weeks. (Km/S) Hubble Diagram from Type Ia Supernovae (Mpc) Reiss, Press, and Kirschner (1996) z H0 c d The galaxies don’t really have a velocity. is related to Einstein’s Field Equations is related to +Λ No static solution is related to ---- This is the biggest blunder of my life. Don’t need a static solution!!! Low mass Critical density Lots of mass Gnab Gib Cosmological Parameters Quantities that describe the Universe: : H0: The current rate the Universe is expanding Ω0: The current mass density Λ: The funny constant for pushing the Universe apart The State of cosmology in 1988 • Hubble constant controversy – some say it is 50 km/s/Mpc and others insist 100 km/s/Mpc • Age of Universe: 6-12 billion years (depending on Hubble constant). Age of stars in globular clusters: 15-20 billion years • Theorists insist Ω0 = 1.0 • Observers only see Ω0 of 0.2 to 0.4, even including unseen dark matter Graduate Thesis Project is to Weigh the Universe Supernova Cosmology Project The 4.0 meter Anglo-Australian Telescope They built a special wide-field camera This is what we are looking for. Gerson This search failed to find supernovae because: (1)The weather was terrible at the AAT. (2)The seeing was 2”, which meant most supernova positions were less than a seeing disk from the galaxy center. (3)AGN variability produced a large set of false detections. (4)They did not have scheduled follow-up. (5)Supernovae were dimmer than expected. Rich Muller suggested that maybe Gerson had needed to re-orient it. In 1992, the group had overspent all budgets, had no distant supernovae, and was in quite a lot of trouble. The funding and the control was shifted from Carl Pennypacker (who had started the project) and Rich Muller (who was the group leader) to Saul Perlmutter (who was a postdoc and the primary technical driver for the software). The search moved to the CTIO 4m telescope, and began to find supernovae. Success brought competitors The Hi-Z Super Nova (SN) Search team was composed of a dozen well-seasoned astronomers who were experts in SN phenomenology . They were less well funded than the LBL group, not centrally controlled, generally dismissive of the astronomical knowledge of the Supernova Cosmology Project members, and jealous of the constant funding that the physicists were getting to do science. The Hi-Z team had the expertise and the contacts on the telescope time assignment committees. The LBL group were experts in data analysis, had several years head start, consistent funding, and an established organization structure. The race was on. In a flat Universe: ΩM = 0.28 [±0.085 statistical] [±0.05 systematic] Probability of Λ=0; 1% In a flat Universe: ΩM = 0.28 [±0.085 statistical] [±0.05 systematic] Probability of Λ=0: 1% is related to Einstein’s Field Equations is related to is related to +Λ No static solution +Λ Don’t need a static solution!!! But we need an accelerating solution is related to is related to Einstein’s Field Equations is related to is related to 相关于 没有静态解 Don’t need a static solution!!! is related to +Λ No static solution 不需要静态 解 But we need an accelerating solution 但需要 加速解 + Dark Energy The change in the scale factor with time 3 2 1 0 Size of Universe 4 H0 = 71 km/s/Mpc, ΩM = 0.3, ΩΛ = 0.7 -20 -10 0 10 Time (Gyr) 20 30 Dark Energy Since the Λ term contributes positively to the energy density of the Universe, it contributes to the curvature the same way normal matter and dark matter do. Since the pressure has the opposite sign, it is said that “dark energy” has negative pressure, and this causes the Universe to expand exponentially. But there is still much that is unknown: what substance, field, or force is responsible? Can Λ vary with time? Assigning the Credit Saul Perlmutter Recognized leader of Supernova Cosmology Project, first author on prize-winning paper, technical innovator, dedicated years of his life to this cause. Brian Schmidt PI of Hi-Z SN group, wrote software reduction code. Adam Riess First author of prizewinning paper (as a graduate student), later used HST to discover more distant supernovae at z~1.0 Hi-Z SN Search Supernova Cosmology Project The Hi-Z paper was submitted first, but with fewer supernovae. They had the advantage of having seen the SCP results at conferences, and knew that the SCP results agreed with theirs. Robert Kirshner, Harvard Gerson Goldhaber, celebrated professor, and thesis advisor for both Adam Riess and Brian Schmidt. Postdoc advisor of Brian Schmidt. He spent a lifetime studying supernovae. particle physicist who joined Supernova Cosmology Project about 1990. He claims to have been the first to look at the supernova data and believed that it showed an acceleration. Students and postdocs who made the observations, wrote the data reduction software, figured out how to calibrate the light curves, and compiled the results had mixed career results. A Nobel Tradition Arthur Compton Discovered Compton Effect Ernest Lawrence Invented cyclotron Luis Alvarez Richard Muller Invented hydrogn McArthur FellowSaul Perlmutter Discovered Bubble chamber accelerating Universe Dr. Newburg The Nobel Prize in physics is given for making important discoveries. They are not given for: • Intelligence • Hard work • Solid science • Procuring the most grant money • Popularity • The most papers and citations (lifetime achievement) Tips for winning a Nobel Prize None are required, and all together are not sufficient. (1) Dare to work on something really important. (2) Love it so much that it is your top priority. Procure a long-term source of funding that does not depend on short term accomplishments. (3) Choose advisors and mentors who have reached their own professional goals. (4) Have a new idea every day, and a good one every week. (5) Persevere through failure. Where Do We Go From Here? (1) Theorists need to explain the physical meaning of dark matter (cosmological constant, quintessence, …). (2) Experimentalists will measure how closely the expansion of the Universe matches General Relativity with a constant Λ. 。 (3) The stellar models still predict 15 Gyr old globular clusters in a 13.7 Gyr Universe (4) We still need to figure out what the dark matter is.