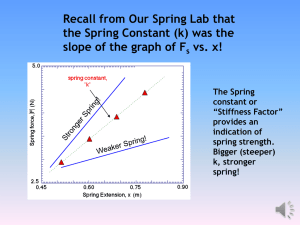
Lesson 3: Hooke`s Law
advertisement

Why study springs? Springs are_____________. This means that if you: elastic a/ apply a ___________to them, and force b/ they become ____________ deformed (bent out of shape), and forced c/ then you remove the ___________, then they bounce back d/ __________________ . Many things have some elasticity, and so they behave like springs: metal •wood _____________ plastic •concrete humans water •air the sun atoms •quartz speakers water musical instruments •______________________________ strings, air, drums… Many elastic objects obey… Hooke's Law: The compression or elongation x of an ___________ equilibrium ideal spring from its ________________ position (x = 0) directly proportional is ____________________________to the applied force Fs. Fs = kx compression: stretching or elongation: x=0 x=0 x x Fs Fs stretch or __________________. compression More F more ____________ Hooke's Law is often written: Fs = -kx This is because it also describes the force that the spring itself exerts on an ___________ object _______________ that is attached to it. The negative sign indicates that the direction of opposite the spring force is always _____________ to the displacement of the object -x compressed spring: undisturbed spring stretched spring: > 0 Fs ___ Fs x=0 equilibrium ______________ 0 position, Fs = __ +x Fs < 0 Fs ___ Ex. A weight of 8.7 N is attached to a spring that has a spring constant of 190 N/m. How much will the spring stretch? w/ weight w/o weight Given: Fs = 8.7 N k = 190 N/m Unknown: x =? Equation: Fs = kx 8.7 N = (190 N/m) x x = 4.6 x 10-2 m x 8.7 N Fs = kx Ex: A force of 5.0 N causes the spring to stretch 0.015 m. How far will it stretch if the force is 10 N? 2 (0.015 m) = 0.030 m Fs direct 10 5 .015 ? x What quantity does the slope represent? slope = Dy/Dx = Fs/x Compare to Fs = kx Solve for Fs/x = k the spring constant, k. The slope represents _______________________________ What are the units of the spring constant, k? Solve… Fs = kx …for k: k = units of k: Fs/x [k] = [ Fs ]/[ x ] = N/m (derived) This can be also seen from the graph: Fs (N) k = the slope = Dy/Dx So k has the same units as Dy/Dx: N/m x (m) Ex. Comparing two springs that stretch different amounts. spring B Fs spring A Applying the same force F to both springs xB xA x Which spring stretches more? A Which is stiffer? B greater larger k stiffer spring _________ slope _________ Elastic ____________ PE - the energy stored in a spring when work is done on it to stretch or compress it PEs = (½)kx2 Ex. A spring with a spring constant of 370 N/m is stretched a distance 6.4 x 10-2 m. How much elastic PE will be stored in the spring? How much work was done to stretch the spring by this amount? Elastic ____________ PE - the energy stored in a spring when work is done on it to stretch or compress it PEs = (½)kx2 Ex. A spring with a spring constant of 370 N/m is stretched a distance 6.4 x 10-2 m. How much elastic PE will be stored in the spring? PEs = (½)kx2 = (0.5)( 370 N/m)(6.4 x 10-2 m)2 = 0.76 (N/m)(m2) = 0.76 Nm = 0.76 J How much work was done to stretch the spring by this amount? W = DPE = 0.76 J PEs = (½)kx2 What happens to PEs when you double x? PES prop. to square The PEs quadruples. When you triple x? x 9x more PEs. Ex: The elastic PE stored in a spring is 0.70 J when it is stretched 0.010 cm. If the same spring is stretched 0.030 cm, how much PE will then be stored in it? x changes from 0.010 to 0.030 it triples 9x more PEs 9x (0.70 J) = 6.3 J Ex: Plot F vs. x for an ideal spring F x What does the grey area represent? area = (½)bh = (½)xF = (½)x(kx) = (½)kx2 = PEs It represents the ____________ work done on the spring, and energy stored the ______________________ in it. W = DPEs Ex: By looking at the area, you can see why the PE is square proportional to the ___________ of the displacement x: F 1x 2x 3x x 4 A 1x 1 triangle ____ A area = ____ A so PE = ____ 1 2 3 2x 3x 4 triangles ____ 4A area = ____ 4A so PE = ____ 9 triangles ____ 9A area = ____ 9A so PE = ____ One last warning: deforms If a spring is stretched too much, it ____________ is no permanently, and Hooke's Law (Fs = kx ) _________ longer valid. ______________ Ex: Which of the graphs below shows a spring that obeys Hooke's Law? F F C/ A/ x x F F D/ B/ x x YES and NO Open your Review Book packet to pages: 82-3 Do problems # 39-56