The+Appendicular+Skeleton
advertisement

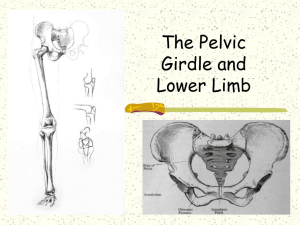
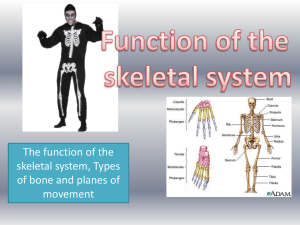
THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON Composed of 126 bones Limbs (appendages) Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON acromion Figure 5.6a THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON Figure 5.6b THE PECTORAL (SHOULDER) GIRDLE Composed of two bones Clavicle—collarbone –slender bone; at risk to fracture Scapula—shoulder blade These bones allow the upper limb to have exceptionally free movement The clavicle serves as a brace to hold the arm away from the top of the thorax…so there is no problem with the arm clearing the widest dimension of the thoracic cage. BONES OF THE SHOULDER GIRDLE Coracoid process greater tubercle Figure 5.21a BONES OF THE SHOULDER GIRDLE CLAVICLE (#2) Figure 5.21b BONES OF THE SHOULDER GIRDLE * SCAPULA (#1) * * * Figure 5.21c–d BONES OF THE UPPER LIMBS Humerus Forms the arm Single bone BONES OF THE UPPER LIMBS Humerus (#3) * * * * * * * * Figure 5.22a–b BONES OF THE UPPER LIMBS The forearm has two bones Ulna Medial bone in anatomical position Radius Lateral bone in anatomical position BONES OF THE UPPER LIMBS Radius (#4) & Ulna (#5) * * * * Figure 5.22c BONES OF THE UPPER LIMBS The hand Carpals—wrist 8 bones Metacarpals—palm Phalanges—fingers 14 bones BONES OF THE UPPER LIMBS Carpal (#6), Metacarpals (#7), Phalanges (#8) Figure 5.23 BONES OF THE PELVIC GIRDLE Formed by two coxal (ossa coxae) bones Composed of three pairs of fused bones Ilium Ischium Pubis Pectoral Girdle is more flexible Pelvic Girdle is more secure and better able to bear weight BONES OF THE PELVIC GIRDLE The total weight of the upper body rests on the pelvis…therefore, must be massive It protects several organs Reproductive organs Urinary bladder Part of the large intestine People instinctively curl over to protect internal organs THE PELVIS More massive than 4 legged creatures because it has to bear more weight. Figure 5.24a Illium = yellow bone #1 Ischium = Purple bone #2 Pubis = Red bone #3 THE PELVIS: RIGHT COXAL BONE * * * * * * * * * * Figure 5.24b GENDER DIFFERENCES OF THE PELVIS The female inlet is larger and more circular The female pelvis as a whole is shallower, and the bones are lighter and thinner The female ilia flare more laterally The female sacrum is shorter and less curved The female ischial spines are shorter and farther apart; thus the outlet is larger The female pubic arch is more rounded because the angle of the pubic arch is greater GENDER DIFFERENCES OF THE PELVIS Figure 5.24c TRUE VS FALSE PELVIS The greater or FALSE pelvis is located above the pelvic brim- SUPERIOR; supports the abdominal viscera the organs contained within the abdominal cavity; they include the stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, pancreas, and parts of the urinary and reproductive tracts The lesser or TRUE pelvis below the brimINFERIOR; limits delivery of baby BONES OF THE LOWER LIMBS The thigh has one bone Femur The heaviest, strongest bone in the body BONES OF THE LOWER LIMBS FEMUR #4 * * * Anterior view of right femur * * Posterior view of right femur * Patella # 5 * * * * Figure 5.25a–b BONES OF THE LOWER LIMBS The lower leg has two bones Tibia Shinbone Larger and medially oriented Fibula Thin and sticklike BONES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Fibula #6 Tibia #7 * * * * * Figure 5.25c BONES OF THE LOWER LIMBS The foot Tarsals Two largest tarsals Calcaneus (heelbone) Talus Metatarsals—sole Phalanges—toes BONES OF THE LOWER LIMB Talus #8 Calcaneus #9 Metatarsals #10 Phalanges #11 Figure 5.26 ARCHES OF THE FOOT Bones of the foot are arranged to form three strong arches Two longitudinal One transverse ARCHES OF THE FOOT Figure 5.27 FALLEN ARCHES The ligament and tendons are weakend, allowing bones to “fall”