Ecology Review
advertisement

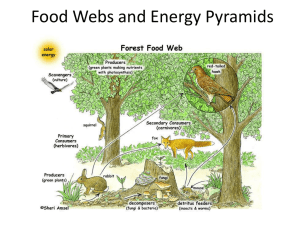
Ecology Review 1. The study of the interaction of living organisms with each other and with their physical environment is called a. health. c. ecology. b. economy. d. geology. 2. A group of organisms of different species living together in a particular place is called a a. community. c. biome. b. population. d. habitat. 3. An ecosystem consists of a. a community of organisms. b. energy. c. the soil, water, and weather. d. All of the above 4. The specific physical location in which a given species lives is called its a. habitat. c. community. b. abiotic factor. d. climate. 5. An organism’s niche includes a. what it eats. c. when it eats. b. where it eats. d. All of the above 6. Which of the following would not be included in a description of an organism’s niche? a. its trophic level b. the humidity and temperature it prefers c. its number of chromosomes d. when it reproduces 7. Organisms that manufacture organic nutrients for an ecosystem are called a. consumers. c. producers. b. predators. d. omnivores. 8. The primary producers in a grassland ecosystem would most likely be a. insects. c. grasses. b. bacteria. d. algae. 9. The organic material in an ecosystem is called a. trophic level. c. energy. b. biomass. d. productivity. 10.cows : herbivores :: a. horses : carnivores c. algae : consumers b. plants : producers d. caterpillars : producers 11.When an organism dies, the nitrogen in its body a. can never be reused by other living things. b. is immediately released into the atmosphere. c. is released by the action of decomposers. d. All of the above 12.Refer to the illustration above. The photosynthetic algae are a. producers. b. consumers. c. parasites. d. decomposers. 13. Refer to the illustration above. The diagram, which shows how energy moves through an ecosystem, is called a a. habitat net. b. food chain. c. trophic level. d. food web. 14.Refer to the illustration above. The leopard seals are a. producers. c. herbivores. b. omnivores. d. carnivores. 15.Refer to the illustration above. Among all of the food chains, the organisms at the highest trophic level are a. the algae. b. the crabeater seals. c. the krill. d. the killer whales. 16.In a food web, which type of organism receives energy from every other type? a. Producer c. decomposer b. carnivore d. All of the above 17. Refer to the illustration above. On the pyramid, animals that feed on plant eaters are no lower than a. level 1. c. level 3. b. level 2. d. level 4. 18.Refer to the illustration above. How much energy is available to the organisms in level 3? a. all of the energy in level 1 plus the energy in level 2 b. all of the energy in level 1 minus the energy in level 2 c. about 10 percent of the energy in level 2 d. about 90 percent of the energy in level 2 19.In an ecological energy pyramid, animals that feed on plants are at least in the a. first trophic level. c. third trophic level. b. second trophic level. d. fourth trophic level. 20.The number of trophic levels in an ecological energy pyramid a. is limitless. b. is limited by the amount of energy that is lost at each trophic level. c. is impossible to count because energy is lost at each trophic level. d. never exceeds three. 21.In going from one trophic level to the next higher level, a. the number of organisms increases. b. the amount of usable energy increases. c. the amount of usable energy decreases. d. None of the above 22. Refer to the illustration above. The diagram represents the decrease in a. the number of organisms between lower and higher trophic levels. b. available energy between lower and higher trophic levels. c. diversity of organisms between lower and higher trophic levels. d. All of the above 23. Refer to the illustration above. At each trophic level, the energy stored in the organisms in that level is a. about 10 percent of the energy in the level below it. b. about 10 percent of the energy in the level above it. c. about 50 percent of the energy in the level below it. d. about 50 percent of the energy in the level above it. 24.Water and minerals needed by all organisms on Earth pass back and forth between the biotic and abiotic portions of the environment in a process called a. a trophic cycle. b. a trophic pathway. c. a biogeochemical cycle. d. a biochemical pathway. 25.Because individuals in a population usually tend to produce more than one offspring, a. populations tend to increase in size. b. populations remain stable in size. c. individuals tend to die quickly. d. the number of individuals declines rapidly. 26.A population of organisms grows a. with no natural restrictions except the availability of food. b. when the birth rate exceeds the death rate. c. only in the absence of predators or natural diseases. d. All of the above 27. Refer to the illustration above. Which time period shows the highest rate of growth of the population? a. period W–X c. period X–Y b. period W–Y d. period Y–Z 28. Refer to the illustration above. Which point on the graph indicates the approximate world population in the year 1950? a. W c. Y b. X d. Z 29. Refer to the illustration above. The American Revolution began in 1776. According to the graph, what was the approximate world population at that time? a. 500 thousand c. 1 billion b. 1 million d. 2 billion 30.exponential model : how all populations can potentially grow without limits :: a. population model : how organisms live in an area b. logistic model : how populations grow when carrying capacity is limited c. demographic model : how people move into and out of countries throughout history d. growth rate model : how populations grow when immigration is limited 31.Birth and death rates are ____ on an exponential growth curve, whereas they are ____ on a logistic growth curve. a. variable; constant c. steady; changing b. high; low d. unrestricted; restricted 32.As a population reaches its carrying capacity, there may be an increase in competition for a. food. c. mates. b. shelter. d. All of the above 33.Which of the following is a densityindependent factor? a. food c. severe weather b. water d. number of nesting sites 34.A tick feeding on a human is an example of a. parasitism. c. competition. b. mutualism. d. commensalism. 35.Refer to the illustration above. The relationship shown in diagram 4 is a. commensalism. b. competition. c. mutualism. d. parasitism. 36.Refer to the illustration above. The relationship shown in diagram 2 is a. commensalism. b. competition. c. mutualism. d. parasitism. 37.Refer to the illustration above. The relationship shown in diagram 1 is a. commensalism. b. competition. c. mutualism. d. parasitism. 38.Refer to the illustration above. The relationship shown in diagram 3 is a. commensalism. b. competition. c. mutualism. d. parasitism. 1 Both organisms benefit from the activity of each other. 2 One organism benefits, and the other organism neither benefits nor suffers harm. 3 One organism obtains its nutrients from another, and the other organism may weaken due to deprivation. 39. Refer to the chart above. The table represents three types of a. competition. c. symbiosis. b. rhythmic patterns. d. secondary succession. 40. Refer to the illustration above. The transformation over time shown in the diagram is known as a. stability. b. succession. c. symbiosis. d. species richness. 41.Succession is a. an organism’s ability to survive in its environment. b. the number of species living in an ecosystem. c. the regular progression of species replacement in an environment. d. the transfer of energy through a food chain. 42.Which of the following types of succession would most likely occur after a forest fire? a. primary succession c. secondary succession b. old field succession d. climax succession 43.When settlers arrived in New England, many forests were turned into agricultural fields. Eventually, some fields were abandoned and then grew back into forests. This is best described as a. primary succession. c. secondary succession. b. coevolution. d. niche realization. 44.Which of the following is not a characteristic of pioneer species? a. They are small. b. They grow quickly. c. They reproduce slowly. d. They disperse many seeds. 45.Area that is in the early stages of primary succession will typically contain a. perennial shrubs. c. annual grasses. b. rock lichens. d. evergreen trees.