B - Classes
advertisement

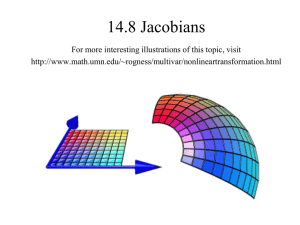
Isoparametric Elements
Element Stiffness Matrices
Structural Mechanics
Displacement-based Formulations
General Approach – Specific Example
• We will look at manipulation of the mechanics quantities
(displacement, strain, stress) using shape functions
• The approach is quite general, and is used to formulate a
number of different elements
• We will use a specific example to make the development
more concrete (Q4)
• We will start from the nodal displacement representation,
work toward strain and stress, and finally element stiffness
• There is a lot going on here, pay attention to both the overall
themes and the detailed steps …
Master Element Mapping
• Note: we will use a for x and b for h because I can’t remember,
pronounce, or legibly write “xi” and “eta”
actual element
master element
Bilinear Quadrilateral (Q4)
• Interpolation involves the summation of nodal values
multiplied by corresponding shapes functions
x
N i x i
N c
y
N i y i
geometry interpolation
u
N i ui
N d
v
N iv i
- where -
field variable interpolation
c x1 y1 x 2 y 2 x 3 y 3 x 4 y 4
nodal coordinates
T
d u1 v1 u2 v 2 u3 v 3 u4 v 4
nodal displacements
T
N1
N
0
0
N1
N2
0
0
N2
N3
0
0
N3
N4
0
0
N 4
shape functions
Q4 - Displacements
• Start with the element displacement field
• We have to give it some functional form in order to work with it
• Let it be defined over the element by our interpolation scheme
u N d
N1
1
1 a1 b
4
N3
1
1 a1 b
4
N2
1
1 a1 b
4
N4
1
1 a1 b
4
{u} = displacements continuously
defined
(all components) over an element
[N] = the element shape functions in master element coordinates
{d} = the nodal (discrete) displacement values
Strain from {u}
• Now calculate element strains from the displacement field
u
x
0
y
0
y
x
x x
y 0
xy
y
0
u
y v
x
• This is just the usual strain-displacement relationship written
in compact form with an operator matrix
Q4 – Strain from {d}
• Let’s now work toward an expression for element strain
N d
- or -
Bd
• We have a bit of
u1
this operation cannot
v1
be done directly
0
u2
x x
N 0 N
0 N 3 0 N 4 0
v 2
1
2
y 0
y
0 N1 0 N 2 0 N 3 0 N 4 u3
xy
v 3
y
x
u
4
v 4
a difficulty here with direct substitution
– The shape functions (N1, N2, N3, N4) are defined in terms of the master
element coordinates (a,b)
to differentiate in terms of the global coordinates (x,y)
– But we need
Coordinate Transformation
• Given any function of the master element coordinates (a,b):
f f a,b
• We can find derivatives with respect to global (x,y) by using the chain rule:
f f
x f y
a x a y a
f f x f y
b x b y b
• We can combine and rearrange these relationships to get our derivatives:
f ,a
f ,x
J
f ,b
f ,y
f ,x
1 f ,a
J
f ,b
f ,y
The Jacobian
• The Jacobian matrix is an important part of element formulation:
x,a
J
x,b
y,a N i,a x i
y,b
N i,b x i
N
N
y i
i,b y i
i,a
• For the Q4 element this becomes:
1 1 b 1 b
J
4
1 a 1 a
1 b
1 a
x1
1 b x 2
1 a x 3
x 4
local coordinate derivatives of
the shape functions
y1
y 2
y 3
y 4
global coordinate
locations of the element
nodes
note the Jacobian
matrix is a function
of location within
the master element
Jacobian Interpretation
• The Jacobian contains information about element size and shape
J11 J12
J
J21 J22
• The Jacobian determinant (j) is a scaling factor that relates the differential
area of the actual element to the differential area of the master element
j det J J11J22 J21J22
• The Jacobian inverse (G) relates global coordinate system (x,y) function
derivatives to master element coordinate system (a,b) function derivatives
G J
1
1 J22 J12 G11 G12
j J21 J11 G21 G22
Jacobian (determinant) Ratio
•
•
•
•
This is one measure of element quality (which affects element accuracy)
Ratio of the highest to lowest quadrature point Jacobian determinant
It is 1.0 for any square or rectangular element (same j throughout element)
It increases as element distortion increases
Strain/Displacement for Q4
• Start with the usual strain-displacement relationship in a slightly different
form:
u,
x 1 0 0 0 x
u,y
y 0 0 0 1
v,x
xy 0 1 1 0
v,y
• Now add the Jacobian approach to master/global coordinate derivative
transformation:
u,x G11 G12
u,y G21 G22
0
v,x 0
0
v,y 0
0
0
G11
G21
0 u,a
0 u,b
G12 v,a
G22
v,b
Strain/Displacement cont.
• Now represent the displacement field master element derivatives in terms
of the shape functions:
u,a N1,a
u,b N1,b
v,a 0
v,b 0
0
N 2,a
0
N 3,a
0
N 4,a
0
N 2,b
0
N 3,b
0
N 4,b
N1,a
0
N 2,a
0
N 3,a
0
N1,b
0
N 2,b
0
N 3,b
0
u1
v1
0 u2
0
v 2
N 4,a u3
N 4,b
v 3
u
4
v 4
All Together Now …
[B]
G G12
x 1 0 0 0 11
G21 G22
y 0 0 0 1
0
0
0
1
1
0
xy
0
0
0
0
G11
G21
0 N1,a
0 N1,b
G12 0
G22
0
organization
- or
Bd
Jacobian inverse
terms, master to
global coordinate
transformation
0
N 2,a
0
N 3,a
0
N 4,a
0
N 2,b
0
N 3,b
0
N 4,b
N1,a
0
N 2,a
0
N 3,a
0
N1,b
0
N 2,b
0
N 3,b
0
shape function
derivatives,
master
coordinates
u1
v1
0 u2
0
v 2
N 4,a u3
N 4,b
v 3
u
4
v 4
nodal
displacements,
global
coordinates
Stress
• If we have strain, we can get to stress by bringing in material properties
E E Bd
• We have to be a little careful here, this simple expression assumes:
– No initial (residual, assembly) stresses present
– Linear elastic behavior
– The
general form above does accommodate anisotropic behavior
• If we further limit ourselves to 2D, isotropic, plane stress, we can write:
1
E
1
E
1 2
0 0
0
0
1
2
1
E
E
1
E E 1 E
0
0
0
E
0 G
21
1
G
Element Stiffness Matrix
• Recall where the element stiffness matrix fits into the finite element
formulation:
k d r
• Take it as a given for the present that the element stiffness matrix [k] is:
k B E B t dA
T
• An integral over the element area in global coordinates (t = thickness)
• Why is integration required?
– Think about what [k] does
– For displacements applied to the element nodes, it determines the required force
– If one element is larger than another, the force required ought to be greater for the
same nodal displacements
– If an element has a rotated orientation, a coordinate axis displacement can produce
forces with multiple coordinate components
Integration in Master Coordinates
• It is not easy to integrate for the terms in [k] using the global coordinate
system (elements are generally distorted and not aligned with global axes)
• But we can do this instead (matrix dimensions for a Q4 element):
1
1
k B E B t j da db
8x 8
symm
1 1 8x 3
T
3x 3 3x8
• Integrate over the master element
• It is undistorted
and aligned with the coordinate system
• Adjust for the change in coordinates by bringing in the Jacobian
determinant j
Quadrature
• Read “quadrature” as “numerical integration”
• Why do we want to numerically integrate to establish [k]?
k
8x 8
symm
1
1
B E B t j da db
1 1 8x 3
T
3x 3 3x8
these contain Jacobian
inverse terms which vary
point-by-point within
the element
this varies point-bypoint too …
• To integrate directly is still computationally expensive, even with the
change to local coordinates
• Quadrature involves sampling at discrete points, multiplying by a
weighting factor, and summing to get an estimate of the integral
Gauss Points
• Gauss quadrature is a method of numerical integration that has optimal
characteristics when the underlying functions have polynomial form
• The figure shows Gauss points for 2nd order and 3rd order quadrature
– For (a), all four points have a weight of 1.0 (total = 4.0)
– For (b): 1,3,7,9 weight = .3086; 2,4,6,8 weight = .4938; 5 weight = .7901 (total = 4.0)
• Note: the quadrature rule is independent of element order (Q4, Q8, Q9)
Computational Procedure
-
-
Clear the array that will contain [k]
Loop over integration points in the a direction (i=1 to ni)
– Set sampling point location ai and the weight factor Wi (i.e. +/- 0.577, 1.0)
– Loop over integration points in the b direction (j=1 to nk)
- Set sampling point location bk and the weight factor Wk (i.e. +/- 0.577, 1.0)
- Call shape function subroutine, return [B] and j=det[J] at the point (ai, bk)
- Calculate [B]T[E][B]tjWiWk, and add into [k]
- End loop k
End loop i
Shape function subroutine
- Input is the local Gauss point coordinates (a,b)
- Access database for element global node coordinates (i.e. x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4)
- Calculate [J], j = det[J], [G [J]-1 and [B]
Efficiency
• One-time element calculations
– The shape function local derivatives are the same for a given element
type and integration scheme
– They are only calculated once and stored each time the shape function
subroutine is called
• File vs. DRAM storage
– If you had to access a hard drive file each time a node location was
required, the shape function subroutine calculations could be slow
– But you need enough DRAM to store the locations, along with all the
other information required during the analysis
Element Distortion
• One of the reasons a distorted element is less than
ideal:
– The integral is estimated by discrete sampling at specific locations
within the element
– If the element is not distorted, the sampled points are highly
representative of the un-sampled near by regions of the element
– If the element is highly distorted, the sampled points are not
representative of the un-sampled regions of the element
Intra-Element Jacobian Variation
•
•
•
Here is a single Q4 element (highly-distorted, not recommended)
For integration purposes, element characteristics are sampled at the discrete
Gauss points shown
How well does the point represent the region around it?
approx area
represented
by the point
Gauss point
Geometric Nonlinearity
•
•
•
•
•
•
The configuration of the element changes as soon as it deforms.
The global locations of the nodes is different at each load increment.
Since global node locations enters into the element stiffness calculation …
The element stiffness evolves during a high-deformation sequence
A single load step is often broken up into a series of increments …
And the element stiffness is updated at each increment.
original element
load increment 1
load increment 2 …