Concept 3 Power Point - Troup 6
advertisement

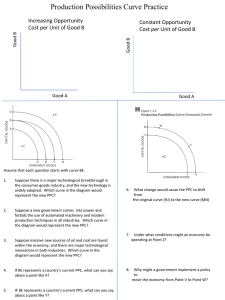
Opportunity Cost • Value of the “next best alternative” Concert Climbing or Mountain • You have $100 to spend at the mall, rank the following in the order (1, 2, 3) you would purchase them. DVD set of a TV Show($60) New outfit ($85) New pair of shoes ($65) • WHAT IS #1? • WHAT IS YOUR OPPORTUNITY COST FOR #1? HOW TO DECIDE? The Decision-Making Model 1. List the alternatives 2. State the criteria The Decision-Making Model 3. Evaluate the alternatives a. Trade-off: the act of making the choice b. Opportunity cost: the next best alternative given up when individuals, businesses, and governments confront scarcity by making choices. The Decision-Making Model 4. Make rational decisions a. Marginal benefit: the extra benefit b. Marginal cost: the extra cost c. When marginal benefit is greater than the cost, he marginal benefit should be obtained. d. When the marginal benefit is less than the marginal cost, the desired good is not worth the cost and should not be obtained. Rational decisions occur when the marginal benefits of an action equal or exceed the marginal costs. Does the benefit exceed the cost? Decision-Making Model Karen’s Decision-making Grid Alternatives Sleep late Wake up early to study Benefits • Enjoy more sleep • Have more energy during the day • Better grade on test • Teacher and parental approval • Personal satisfaction Decision • Sleep late • Wake up early to study for test Opportunity cost • Extra study time • Extra sleep time Benefits forgone • Better grade on test • Teacher and parental approval • Personal satisfaction • Enjoy more sleep • Have more energy during the day Summary Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain the decision making model? What is a trade-off? What is the opportunity cost? When the marginal ___________ is greater than the cost, the marginal benefit should be obtained. 5. When the marginal benefit is less than the marginal___________, the desired good is not worth the cost and should not be obtained. Production Possibilities Frontier When a company plots their opportunity costs and decides what is most profitable to produce PPC A graph that shows the trade-off between two production options – A visual representation of OPPORTUNITY COSTS PPC – an example • Suppose a country makes Pencils and Pens. • If they devoted ALL of their resources to pencils, they could make 500 a day • …..to pens, they could make 300 a day 500 300 PPC – an example 500 Pencils The country/business can produce anywhere on the line when they use ALL of their resources Pens 300 PPC – an example If the country is producing ONLY pencils, and they want pens, they have to give up pencils. 500 450 Pencils The more pens they want….. 200 125 200 Pens 300 PPC – an example 500 At point X, the country or business is producing below its possibilities and is INEFFICIENT Y Pencils 200 At point Y, the country or business is producing beyond its possibilities and is NON-SUSTAINABLE. X 75 Pens 300 Graph this country’s PPC After graphing, answer these questions: Food Computers 200 0 180 25 150 50 100 75 25 100 0 110 1. Assume the country is currently producing 180 of food and 25 of computers. If the country wants to make 75 of computers, how many of food must they give up? 2. If the country was producing 150 of food and 30 of computers, what could you conclude about the country’s economy? Production Possibilities Frontier If more computers are produced, less food is produced. If more Food is produced, fewer computers are produced The Production Possibilities Curve 1. The production process takes inputs and uses them to produce outputs. Inputs include land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurs. 2. The PPF curve measures the maximum combination of two outputs that can be achieved from a given number of inputs. It demonstrates the trade-off among choices, given existing institutions, resources, and technologies. 3. The curve slopes downward from left to right. This represents the opportunity cost because you always have to give up some product A to get more product B. 4. The curve bowed out to represent the principle of increasing marginal opportunity cost: in order to get more of something, one must give up increasing quantities of something else. 5. Point A, B, and C represents efficiency: achieving as much output as possible from a given number of inputs. 6. Point Y represents an unattainable point at the moment because of limited resources or technology. 7. Point X represents an attainable point but undesirable. Reasons for a shift 1. Technology 2. Resources Draw these PPFs on your own paper Choice Steel Food Choice Steel A B C D 0 25 50 75 Food 100 90 70 40 A 0 120 B 25 115 C 50 105 D 75 90 E 100 60 F 125 0 Draw these PPFs on your own paper Choice Guns Flowers Choice A 0 100 1 Econ Grade 80 Math Grade 0 B 25 90 2 65 50 C 50 70 3 30 75 D 100 0 4 0 80 Summary Questions 1. What does A, B, and C represent on the PPF curve? 2. What does X represent on the PPF curve? 3. What does Y represent of the PPF curve? 4. What are the reasons for a shift in the PP curve?