Malaysia Valuation Standard: Financial Reporting (MVS 3,4,5)
advertisement

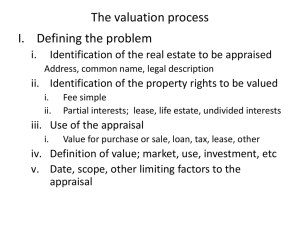
MALAYSIA VALUATION STANDARD RED BOOK ( MVS 3,4,5) By: SAIFUL NIZAM ALI Department of Urban Studies(D.O.U.S.T),IITechnology MVS 3 – Valuation for Financial Reporting INTRODUCTION: Adoption to the “mark to market value” or Fair Value for Accountants. Companies require valuation of their assets at more regular intervals need to show these assests (held for use in their business or as investments or surplus) Why we need to prepare VFR Requirement by MASB for financial reporting standards which has the force of law and is mandatory for public listed company under SC, CB and CCM. i.e. Financial statement for year ended 2012 for Sentoria Group Berhad. Our report no to reflect the overall performance of the company but state the value of an assets owned by company (tangible and intangible) Statements of Standard Valuers must have basic understanding of accounting concepts and principles. In particular valuers must have a working knowledge of how property, plant and equipment are recognized in the accounts acquisition price and depreciated replacement cost basis (DRC) Knowledge and understanding of MASB terms: - FRS 116 – Property, Plant and Equipment. - FRS 117 – leases -FRS 140 – Investment property -FRS 102 – Inventories - FRS 136 – Impairment of assets - FRS 3 – Business combinations - FRS 5 - Assets for sale and discontinuation Knowledge in IVS also need to be updated. Basis of valuation Valuation Reporting “ Fair Value” Definition to FV “ as the amount for which an asset could be exchange or a liability settled between knowledgeable, willing parties in arm’s length transaction” –Malaysian Accounting Standard Board. Similar to MV definition as guided by MVS. Inspecting Ascertaining and confirm with the companies the appropriate asset class – Interest to be valued. Reporting valuation reports methodology used in arriving at the MV bearing in mind the requirements with MASB such as “market-based evidence”. If non “market-based evidence of fair value” Depreciated replacement cost (DRC) need to be adopted in arriving the FV. i.e special charac. Assets silo, ships and oil rigs. Explanation Land and building normally used “market based evidence” adopt 5 methods of valuation. DRC to calculate value of assets at the end of economic life. Thus, depreciation approach need to be considered. D = P ( 1 - i )n, where n is years. Revision 1) Every year depreciation of certain plant is taken as 8% of its value at the beginning of the year. If the acquisition initial value is RM 300,000, calculate the value of after 7 years. 2) Toyota Hiace is RM 70,000 when new. It is estimated that it depreciates in value by 10% each year. In how many years will it be reduced to salvage value for company’s assets disposal purposes. Advice your client.