PowerPoint ****
advertisement

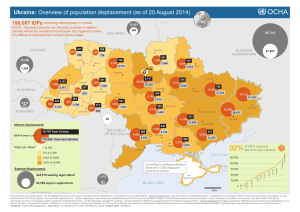
بسم ا ...الرحمن الرحيم ابزار دقیق دکتر سید مجید اسما عیل زاده زمستان1389 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 2 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 3 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 4 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 5 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 6 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 7 Motion Detection(Linear Displacement) A linear encoder is a sensor, transducer or readhead paired with a scale that encodes position. The sensor reads the scale in order to convert the encoded position into an analog or digital signal, which can then be decoded into position by a digital readout (DRO) or motion controller. The encoder can be either incremental or absolute. Motion can be determined by change in position over time. Linear encoder technologies include optical, magnetic, inductive, capacitive and eddy current. Optical technologies include shadow, self imaging and interferometric. Linear encoders are used in metrology instruments and high precision machining tools ranging from digital calipers to coordinate measuring machines. 8 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 9 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) RVDT transducers with AC output have the basic construction with only the primary and secondary winding inside. • RVDT transducers with DC signal output have embedded electronics responsible for powering and process the sensor internal signals, converting the detected displacement into a stable DC voltage signal. 10 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) • Flight control actuators • Valves • Nose wheel steering systems • Cockpit controls • Fuel controls • Fly-by-wire systems • Brake-by-wire systems • Power plant 11 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) Schematic of Synchro Transducer The complete circle represents the rotor. The solid bars represent the cores of the windings next to them. Power to the rotor is connected by slip rings and brushes, represented by the circles at the ends of the rotor winding. As shown, the rotor induces equal voltages in the 120° and 240° windings, and no voltage in the 0° winding. [Vex] does not necessarily need to be connected to the common lead of the stator star windings. 12 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 13 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 14 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 15 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 16 17 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 18 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) A device with a two-phase stator is known as a resolver. A resolver produces sine and cosine outputs which indicate shaft position. 19 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) A resolver is a type of rotary electrical transformer used for measuring degrees of rotation. It is considered an analog device, and has a digital counterpart, the rotary (or pulse) encoder. 20 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 21 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 22 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 23 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 24 Motion Detection(Rotational Displacement) 25 Motion Detection(Rotational and Linear Displacement) 26 Motion Detection 27 Motion Detection 28 Motion Detection A tachometer (also called a revolution-counter, "Tach", rev-counter, or RPM gauge) is an instrument that measures the rotation speed of a shaft or disk, as in a motor or other machine. The device usually displays the revolutions per minute (RPM) on a calibrated analogue dial, but digital displays are increasingly common. The term comes from Greek Ταχος, tachos, "speed", and metron, "to measure".[1] 29 Motion Detection 30 Motion Detection 31 Motion Detection 32 Motion Detection 33 Motion Detection 34 Motion Detection 35 Motion Detection 36 Motion Detection 37 Motion Detection 38 Motion Detection 39 Motion Detection 40 Motion Detection 41 42 Motion Detection 43 Motion Detection 44 Motion Detection 45 Motion Detection 46 Motion Detection 47 Motion Detection 48 Motion Detection 49